Role of Immigrations in International Trade of the US
Immigration as a process is the movement from one country to another for a permanent stay. Immigration is a significant dimension of current globalisation as per Karayil, (2021), and immigration has a certain positive and negative impact on the trade and economy of both the host country and the region an individual has migrated from. As per various cross-sectional studies, it is identified that an estimated 10% increase in immigration can boost 1.5% of international trade. However, there are concerns relating to immigration as governments may open borders for migrants, yet, immigration as a process may face resistance from the community or other socio-economic challenges. Thus, studies have revealed that immigration may have a positive impact on international trade; however, it depends upon the nature of the sending countries, the type of products and commodities and nature of immigrants and the size of the existing migrants within a country.
It is to be noted immigration and its trade impact is a single factor among the various dimensions of globalisation. Illustration of immigration and its impact shall require various ethical and political considerations, which means that the stakeholders of a country may have diverse views regarding immigration despite the positive impact on trade or may condemn immigration as it may have a negative impact on the domestic labour market of the country. Thus, the focus of the current study is to simply identify a) the positive and negative impact of immigration on international trade of the host country and b) the relation of international migration and international trade. Hence, based on the give two critical points the study considers evaluating the impact of immigration on international trade and economics. Therefore, in order to gain a critical overview on the topic of discussion, the study considers the analysis of the United States of America as it is a developed country and has been associated with a large scale immigration process since the last decades.
The relation of immigration and international trade
In order to understand the impact of international migrants on the trade and economics of the host and the country of origin, it is important to understand the relationship between the given two factors. Most of the studies have highlighted that immigration can help in increasing bilateral trade (Mihi-Ramirez, Sobieraj & Garcia-Rodriguez, 2020). This trade correlation is in between the host country and the country of origin, which is also termed as ‘nostalgia trade’. According to Hinojosa Ojeda & Telles, (2021) the major aspect of international migration is wage difference as it creates an economic incentive for labour migrations. In other words the difference in currency value of a developing country and a country with strong industrial infrastructure, in addition to this, the international trade theories and economic concept of international trade as per Shingal & Cottier, (2021) collectively refer to various assumptions that link trade and migration in economic theory. The assumptions mainly indicate that trade between nations reduces wage differentials, nations can gain comparative cost advantages, increase in export and benefit in specific production units, thus, the models attribute to the changes in the production cost, wage and creating opportunity for trading partners, however, allowing a platform for intense competition.
Impact of immigration on the economy of United States
It is reported that the foreign-born population since the last decades have increased from 5% to 13% and in the current years, it is noted that by 2021 15% of the resident in the United States are foreign-born.
Figure 1: Foreign-born population in the US
Source: (Jeanne Batalova, 2021)
Based on the given data, it is further noted that immigration from less developed countries creates competition in the labour market. It is often argued that the domestic or native workforce is deprived off of certain odds jobs, wherein, college or educations do not play a significant role. It is also stated by Borjas, (2015) that labour supply is increased due to wage difference and it, however, do not affect the capital-labour ratio as over time firms increases investment to restore the amount of capital employed per worker. In this context, Burstein, Hanson, Tian & Vogel, (2017) highlights a significant aspect, which is contrary to the negative notion of job deprivation of the native workers and that is increase supply of labour helps in increasing the domestic economic demand for goods and services. This implies that immigrant labours will spend in the host country for basic livelihood, which eventually helps in increasing jobs to build homes, sell food or sell basic amenities and services (Genç & Wesselbaum, 2021).
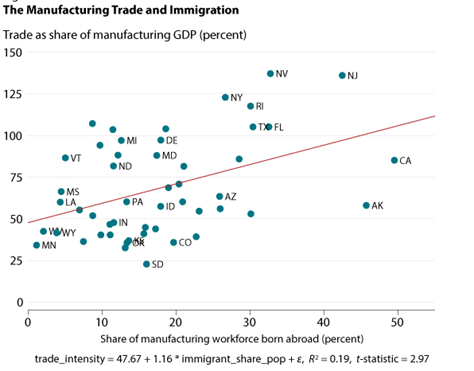
In accordance with the above discussion, another article proposed by Uprety, (2017) on the impact of immigration on the manufactured goods of the United States of America provides an examination that includes the relation between immigration and manufacturing trade across different states in the US along with geographical dispersion and the amount of workforce employed in the manufacturing units both foreign-born and native to identify the correlation of immigrants and international trade. In the following illustration, the article focuses on the aspect that immigrants can boost the productivity of domestic firms, which can eventually increase international competitiveness.
In doing so the article illustrates the concept by further focusing on two critical aspects, which are first, the measurement of immigrant workforce in the manufacturing units across the US and ways it correlates with the cross-state differences in the international manufacturing trade. Given the two broad aspects, it has been identified with the help of statistical representation shown in the figure below that correlation within the two measures is positive.
Figure 2: Manufacturing trade and immigration
Source: (Famiglietti & Leibovici, 2020)
As per the findings provided in the article, it has been stated that the red linear line shows the regression, which indicates that statistically significant level of 1% denoting that the correlation is economically large and viable. This finding also states the increase in 1.16% of international trade due to the 1% increase in the portion of foreign-born manufacturing workers. Thus, the findings as per the examination further highlight that states in the US with more shares of immigrant workers are likely to trade more in manufacturing goods. Hence, it is assumed that familiarity of the immigrants with foreign goods and processes may help in improving domestic production.
Conceptual framework of international trade and immigration
Analysis of international trade and immigration in a developed nation such as the United States has led to the identification of the international trade concept of the ‘Gravity Model’ highlighted in various studies discussing the relationship between international trade and immigration. (Connections between Trade Policy and Migration, 2021) explains the concept of gravity in simple words, which is international trade is conducted by determining two significant aspects of a country or region and which are mainly the size of a particular economy and the proximity to the region. This signifies the importance of countries often trading with neighbour countries and forming international trading unions such as NAFTA or EU.
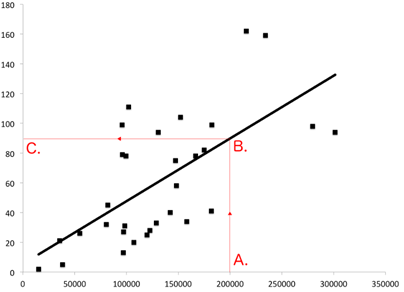
Therefore, similar to the gravity model of international trade, the gravity model of immigration depicts that the cause of attraction of the immigrants to a host country is caused by the distance and cost of moving from one country to another country. It is noted earlier that the wages and income difference are a potential cause of immigration, moreover, it is further attributed with a population size that provides a positive potential of a larger labour maker in the host country for the immigrants. Hence, it is said that immigration is related to the cost and distance of moving and is correlated. Thus, as per Noland, (2018), it can be added that with more the population there is more possibility of immigrants as shown in the figure below.
Figure 3: Linear regression showing population (x-axis) and number of immigrants observed (y-axis)
Source: (Crymble, 2019)
Therefore, it has been further identified from similar studies that using the gravity model researchers were able to state that there is a link of bilateral trade, which is mainly influenced by immigrants. The given information can be further illustrated by stating that immigrants help in creating a flow for bilateral international trade, which as per Burstein, Hanson, Tian & Vogel, (2017) is instances of immigrants bringing their preferences for products from their country of origin. This indicates that there is a possibility of the immigrants consuming products from their home country, thus, creating an opportunity for the host country to import such goods. It has been further stated that immigrants can help in reducing the transaction cost in terms of assessing foreign market information. The reduction of cost will eventually help in creating a positive flow for both import and export in the host country. Furthermore, with relation to the reduction of transaction cost, it is assumed that cost of transaction is reduced due to the elimination of communication barriers as certain immigrants may be fluent in both the languages of the host and native country.
Accordingly, an exact preference for native products can be gained without the need for investment in large amounts for obtaining foreign market information. In the same context, Das, Marjit & Kar, (2020) also highlights that immigrants can help in building networks for business due to the expansion of contacts that can further help trade negotiation and contracts. Hence, as per the concept, it is assumed that skilled immigrants with a longer stay in their homeland and an adequate volume can help developing international trade by increasing the level of cross border trade. However, in this regard, Ottaviano, Peri & Wright, (2018) argues that immigrants from refugee countries may not have the same potential as the economic and socio-political situations of the country of origin may not favour positive growth in international trade for both the countries.
Role of immigrants in international trade
A study on the identification of the role of income generated by immigrants and its relation with international trade conducted Hatzigeorgiou & Lodefalk, (2015) raises the concern of whether trade and immigration are substitutes or complements. This signifies that if bilateral trade agreements or immigration policies will help min lowering immigration from Mexico to the US by increasing the Mexican wages making labour flow and trade substitutes. Rather, it was identified that trade agreements are more like complements as a shift in demand pattern of immigrants influences the trade between the host country and the country sending the immigrants. However, based on the previous findings of immigrants’ information and demand for home-country effect influences bilateral trade, thus, it is further identified that it helps in creating networks as stated earlier. This creation of the network is significantly effective for the host country as it helps to boost import and do not influence the export sector. Indian immigrants demanding spice from India creates an opportunity for Indian and non-Indian people to involve in the transaction process. Moreover, a significant aspect is highlighted by Noland, (2018) is that in case the immigrants’ income rises demand for the costly product from home country will increase instead of any cheaper local substitute.
On the other hand, Bak-Klimek, Karatzias, Elliott & Maclean, (2015) argues regarding the social impact on the immigrants as studies have also suggested that immigrants residing in the US have developed a fondness of the culture of the host country, which eventually leads to the decline in imports for native products as those are not in demand as such. Moreover, a higher concentration of immigrants of a particular region, for instance, a rise in Indian immigrants leads to the production of certain products in the host country that was previously imported, thus declining the import of the host country. Despite the given scenario, Desilus, (2020) also states that the rise in income of the immigrants in the host country will create opportunity for export in terms of specialised goods and products to their home country, this implies that over time immigrants in the US will climb up the economic scale and engage more in entrepreneurial activities with more developed social networks and providing potential for new trade channels. Thus based on further analysis, it is eventually identified that an increase in immigrant stock, which is a number of immigrants with an increase in immigrant income will impact the import and export of the host country and it is similar in the case of the United States. Therefore, there is a need for a framework that can assume an adequate number of immigrants that can channel a positive flow of trade in terms of both import and export with continuous ties with the home country.
The overall analysis of immigration policies and its impact on international trade relations
Based on the given illustration in the section above, it can be said that immigration in terms of international trade has several positive correlations. As per an analysis conducted by Mayda, Peri & Steingress, (2018) it is observed that immigration provides developed nations to access new market opportunities. Multinational companies in the United States have improved their strategy for market innovation and economic competitiveness. The MNCs in the United States will have the experience to cater for the needs of a diverse population in the home country, which eventually will help the organisation to expand overseas. According to the survey report, it is estimated that more than 60% of the MNCs from the United States showed positive performance in overseas countries.
Further, in terms of international trade relations and immigration, it can be added that immigration creates opportunities for foreign direct investment, which is boosted by the inclusion of skilled immigrants in the workforce under the US immigration policy. Hence, such an approach as per Karayil, (2021) helps the US to receive investment from partner countries that eventually develops the economic and innovative aspect of the nation. However, recent changes in the immigration policies in the US have led to various concerns among the stakeholders. The stakeholder argues regarding the association of Free Trade Agreements with immigration policies and seeks a reasonable explanation of whether FTAs should govern immigration policies. In doing so, the major area of dispute is allowing or directing limitations on the flow of immigrants by the sending countries under the FTAs. However, various other stakeholders argue that limitations on the number of immigrants should be considered by the federal departments. Based on the given issues, it is clear that discrepancies in immigration policies and trade policies will have a negative impact on the international trade relations of the host country. Hence, it is recommended that policymaking and formulation on the given aspects should be based on the consideration of the needs and interests of the close stakeholders of the developed country.
It is also noted from the previous discussions that trade agreements and immigration policies are more likely to be complements rather than supplements. Therefore, the recent changes in the immigration policies as per Koczan, Peri, Pinat & Rozhkov, (2021) made by Trump may have negative consequences for the US’s internal economy and international trade relations. It is assumed that nations that were highlighted by the ministry to remain exempted from the new immigration policy may consider other options for academic contributions as most of the workforce that drives innovation in the US are foreign-born studying in the US and later receiving employment in the US, hence, it is a negative influence for the academic and scientific community. Moreover, orders for the deportation of the undocumented emigrants may pose threat to the economic viability of the nation as it will affect the regular life of several million people, which eventually will impact the production and service sector of the United States as the majority of the work force in this sector are immigrants that drive productivity. As a result, the US may experience a price rise in the service sector or the different job sectors as there will be a reduction in low paid workers.
As per Kahn, (2021) further implications can be in the long run for the US as the country benefits from its innovative and skilled workforce. This implies that changes in the immigration policies and lack of openness towards immigrants will lead to a decline in the inflow of skilled and highly educated immigrants, which will eventually affect the professional or engineering and health sector of the country and would rather move to countries like Canada or Australia. Since the US was an economic leader as it benefited from this sector heavily lack immigrants skilled and educated will impact the positive nature of international trade for the country.
Thus, Burstein, Hanson, Tian & Vogel, (2020) recommends that skilled immigration is necessary, whereas, most of the developed country or the host country’s population may oppose the same. Yet, it is essential to state the for a country such as the US skilled immigrants are highly essential as most of the immigrants as per an estimate of 70% are self-employed and contributes to domestic taxes, in addition, most immigrants are also contributing towards employment generation ensuring a sustainable labour market in the US.
Conclusion
According to the critical evaluation of the impact of immigration and international trade by analysing the scenario in the US and comprehending the basic concept, it is identified that immigration for a developed nation is viable for its economic growth. Thus, it can be said that immigration has more positive impacts in comparison to the negative ones as the major positive attribute of the process is an increase in trade between the host and the country of origin. Moreover, the prospect for the host country to expand business overseas is increased due to the market information gained from the immigrants and this allows the host country’s firms to perform well in the international market. Access to foreign direct investment helps the host country to gain more investments and expand its area of operation with skilled labour at low wages. Overall it is noted that immigration can provide opportunities for import and export, development of the labour market and innovation in the business sector. Yet, it needs to be added that there is a requirement for more research on the policy-making for immigration and its correlation with international trade to gain a further detailed insight on the subject matter.