Introduction
Countries are merging to form trading blocks that will ensure that they ease trade restrictions that hinder sufficient economic growth. The integration is crucial in ensuring that there is regional and international cooperation, which reduces conflicts between nations that sometimes result in affecting the economic growth of nations negatively. Smaller countries have more reasons to join the trading blocks, as they enjoy economies of scale, trade creation, and increasing their bargaining power in negotiating international trade deals. Large nations also enjoy an increased market for their products and even cheaper access to raw materials plus labour. Common market objectives are mostly economic convergence, with the end goal being to create a single integrated market. Some of the measures that countries are adopting to improve regional and economic integration include forming custom and single market unions, which are crucial in ensuring that trade barriers are eliminated between member states.
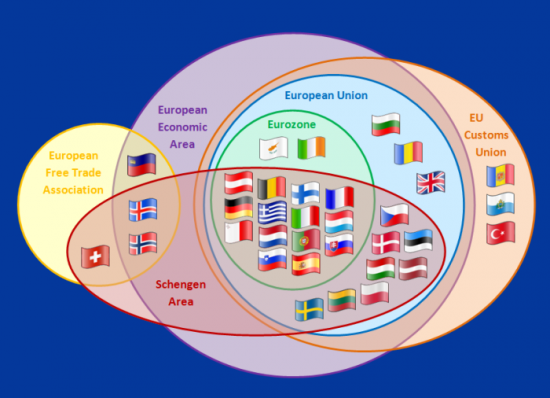
Customs union
Customs union result in allowing member states to freely trade, which results in reducing the financial and administrative trade barriers burden. Member countries in custom unions do not have the freedom that would allow them to negotiate their trade deals. Member nations in the customs union have to restructure their economic policies and their domestic policies to ensure that they fully gain from the union. Custom union main aim is to allow countries to facilitate trade between nations, which results in increasing the trade volumes between nations. Baldwin (2016) noted that Countries work hard to ensure that trade tariffs are eliminated, which makes it easier for businesses to export and import products from other nations. Foreign direct investment also increases between the member countries, as investors have less legal restrictions that may hinder the movement of real and intellectual capital.
Consumers also gain from the single market as they enjoy better product choices. The product choices are a result of the competitive environment that ensures that several businesses from various countries compete for the same customer. Santana-Gallego et al. (2016) Consumers enjoy cheaper and better quality products due to the availability of efficient product suppliers and more choices to select. Innovation is also encouraged in the single market, which also gains the customer as the business ensures that they produce innovative products to gain a competitive advantage.
Customs unions are also essential in ensuring that there is an increase in the trade creation and more diversion of products from member states. Trade creation in custom unions happens when countries with efficient production processes are restricted from selling their products to other nations due to external tariffs that restrict trade actions. .Santana-Gallego et al. (2016) noted that it is beneficial as it gives opportunities to the less efficient countries to capitalize and sell more products to other nations within the union. Trade creation gains should exceed the losses from trade diversion, leading to improved economic activities and welfare among the member nations. Custom unions’ success results in creating trade efficiency among the member states. It is because the countries that have companies with more efficient production processes sell to member states with businesses that have less effective production processes. Consumers usually felt the benefit as they can enjoy products at lower costs and higher quality. It also eliminates monopolistic tendencies in countries, as businesses are aware that competitors have easier entry to their borders.
Disadvantages
Customs unions result in countries losing their economic sovereignty, which limits the country’s liberty to negotiate their bilateral or multilateral deals. It is because the countries in the customs union have to bargain collectively with trade organizations or non-member states. The loss of economic sovereignty also results in ensuring that countries cannot protect their infant industries, as they do not have the power to enact and impose protective barriers. The lack of negotiating power ensures the country cannot guarantee its financial survival and sustainability. Xiao et al. (2017) Membership in the customs union limits a country negotiating power with states as they are not free to make the trade-in that considers their national interest. The customs market is not fully effective as there exist large barriers that hinder effective trade since some trade non-tariff barriers exist (Marti et al., 2014). The differences could result from packaging requirements, marketing frameworks, product safety rules, minimum labour wages regulations, and the national administrative procedures.
Custom unions’ members sometimes result in some nations not receiving their fair share of tariffs. The problem is widespread in nations like the UK, which usually trade more with nations that are non-members of the union. Cnossen (2018) noted that some tariff revenues are typically retained by the member states that collect the tax. Customs union membership also has challenges in the setting of the tariff rate to be applied as the process is time-consuming and costly due to the complexities involved. The complexities are due to member states finding it hard to relinquish the trade of some of their sensitive trade products as other member states are producing them more efficiently. The challenge is most common in the least developed nations in the union, who fear that their industries will be cannibalized by the products from other developed nations (Dür et al., 2014). The entrance of the products could result in loss of employment and taxes, which may limit economic growth in those nations. Member states sometimes may not agree on how to set the standard tariffs, which sometimes limits the setting of a practical framework to control the customs union.
Single market
The single market union is the formal agreement and arrangement between nations that allows them to access every other’s markets freely. The free access is the unrestricted movement of real and intellectual capital, labour, plus their products as it leads to the elimination of all trade tariffs and quotas from goods within the area of jurisdiction. The single market is essential in facilitating better trade between nations as they allow for services and goods to move much easier within the union. Ito (2016) emphasizes that Businesses in single markets tend to enjoy more products produced in all the member states, with some examples of single-market unions being the EU and the CARICOM. The single market facilitates the easier movement of people and capital than a customs market, as there is less hindrance to trade due to national regulations. Citizens of countries in the single market have more opportunities to study, work, retire, or even shop in another country in the union. It is because the countries have integrated various economic and political areas that facilitate easier access to their citizens.
Benefits of single market
The single market allows for the movement of all the factors of production between all the countries in the union, resulting in them becoming more efficiently allocated. The efficient allocation results in industries to become more competitive, which results in increased productivity. Efficient firms in the union benefit a lot from the union as they can trade their products within any member state in any country as they have fewer legal hindrances to limit their business activities (De Grauwe, 2020). Firms that have efficient operations also benefit from increased competitiveness, easier accessibility of raw materials, and better economies of scale. The movement of goods and capital from one state to another ensures that monopolies are hard to find in single markets. It is because companies can trade their products and even set up their operations in any part of the union. Companies’ ability to set up their operations in any part of the world ensures that businesses with inefficient operations lose their market share and ultimately close their operations as their ability to compete is limited.
Single or common markets help businesses to gain from an increased market share due to the availability of more customers. The single market, such as the EU ensures that nations have fewer restrictions that may hinder trade between their member states, thereby facilitating the effective movement of capital and products. De Grauwe (2020) notes that Businesses can plan their production schedules better due to the enhanced predictability in logistics of products. Businesses can also enjoy the free movement of capital, which results in ensuring that they are not entitled to customs duties when transporting their products within the member states’ borders. It saves time and resources for the businesses as they are sure that they will not be a lot of delays in the border points.
Businesses also enjoy from consolidating their production processes in all the member states they have operations, thereby ensuring that they enjoy from maximizing from the economies of scale. The economics of scale enjoyed by the businesses ensure that the cost of production is low, making customers enjoy lower commodity prices. Czermińska (2016) observes that Single markets are also better than customs unions as they also deal with non-tariff barriers. Single market unions ensure that nations have uniformity in their products and business regulations, such as environmental standards and product safety. The uniform regulations provide a level economic playing field for all businesses in the union, which the customs union cannot achieve.
Single markets result in increasing the FDI within the member states, which results in improving the production efficiency, which is due to better and enhanced possibilities that provide opportunities for large scale production. The single market ensures that nations can enjoy more influence when negotiating with more economically powerful nations. The single market ensures that member states reduce transport and administrative costs, as there are fewer documentary requirements needed. Czermińska (2016) states that fewer costs ensure that the prices of goods are low, meaning cheaper products for customers. The single union has promoted the free movement of labour to countries that face severe labour shortages, which is crucial in ensuring that those nations do not suffer from economic stagnation. Yudina et al. (2015) Countries such as Germany and the UK have benefitted from the single market as they were able to get the labour for their industries from the less developed Eastern nations that had higher unemployment rates. The movement of capital is also crucial in ensuring that businesses can set up their operations in countries that offer cheaper production costs. The policy is beneficial as it ensures that companies can save on costs through cheaper labour and taxes.
Challenges to single market
The main challenge to the single market union is that they erode a country’s decision making capability compared to a customs union. It is due to them allowing for the free movement of labour and capital, which a state cannot limit. It has seen labour from less developed nations in unions such as the EU move to the more developed nations of western Europe to seek better employment opportunities, offering the denial of local populations employment opportunities. Czermińska (2016) noted that the Protection of infant industries in a single market is non-existent, as a country cannot decline cheaper products from another state. The free movement of labour within the union may result in people seeking employment opportunities where there are higher wages and better employment opportunities, which may result in the local populations not getting work.
Table showing differences
| economic integration between countries | No Internal Trade Barriers | Common External Tariffs | Asset and factor Mobility |
| Customs Union | yes | yes | no |
| Single Market | yes | yes | yes |
Conclusion
Economic integration of nations is essential in promoting international cooperation and economic growth. Integration ensures that citizens can access the goods that they do not produce in their countries at an affordable price, while also selling surplus products to other nations at a lower price. Single market and custom market unions are a form of economic integration that countries use to ease and facilitate trade between member nations. Custom unions and single market treaties are crucial in eliminating trade barriers such as tariffs and border restrictions. Both of them also allow countries to negotiate better trade deals with non-member states and international organizations, resulting in them saving time and costs. The trade deals also reduce trade deflection among the countries in the union. It is because countries have a common external tariff that eliminates the issues of tariff differentials.
Single market unions are better than custom unions as they a deeper form of economic integration with more benefits. Custom unions only allow nations free movement of goods and services, compared with single markets that enable even the free movement of capital and labour. The free movement of labour has ensured that the countries with high unemployment rates can offer their citizens to countries that need the workforce, with the example being Germany benefiting from the Eastern nation’s citizens who work in their industries. The free movement of capital is also essential in ensuring that businesses can move their operations to any member state that is offering cheaper production costs, which leads to better profit margins and enhances their competitive advantage. Single market unions also eliminate the non-trade barriers that hinder a business from effective marketing in all the member nations of the custom market, which may be due to some countries desiring to protect their industries and jobs. Unlike custom unions, single-market unions also ensure that businesses do have uniform standards for products and services that are sold in the union, which is crucial in eliminating unfair trade practices.
For more academic help please check a wide range of services our Economics Writing Help team offers:
– Economics Assignment Writing Services
– Economics Essay Writing Services
– Economics Dissertation Writing Services
– Buy An Economics Research Paper






