When writing dissertations, keep in mind that the first chapter is the most important since it is the first thing that readers view. The beginning of a dissertation should be simple, succinct, logical, and informative. It should provide a high-level summary of the whole project, establish the tone, clarify the goal, and leave a good overall impression.
The most flawless piece of literature may be ruined by a poor start. You will have to modify your introduction if the material does not match the substance of the paper. As a result, delegating all of the work to academic professionals who will compose your essay makes sense.
Continue reading to learn about the components of a strong dissertation beginning, what to put in them, and examples of excellent dissertation introductions for a better understanding.
What Is the Purpose of a Dissertation Introduction?
A dissertation or thesis’s introduction is the first chapter or point of departure. It should describe the study subject, give a brief overview of your work, and pique the reader’s interest in your article.
The primary aim of creating a dissertation beginning is to accomplish the following objectives:
- Introduce your study’s subject and goal.
- Provide historical context and scientific context.
- Persuade readers of the book’s practical and scientific value.
- Give the reader a sense of the breadth of your research.
Key Elements of a Great Dissertation Introduction
An introduction is crucial since it sets the tone for the whole work. Its aim is to provide an overview of the dissertation. It should also be done in a manner that catches the interest of the readers. The queries, “who?” & “what?” should be answered briefly in an introduction section. When, where, why, and how did it happen? Each of these issues is addressed in detail in the dissertation introduction.
The following are the essential components of a dissertation beginning.
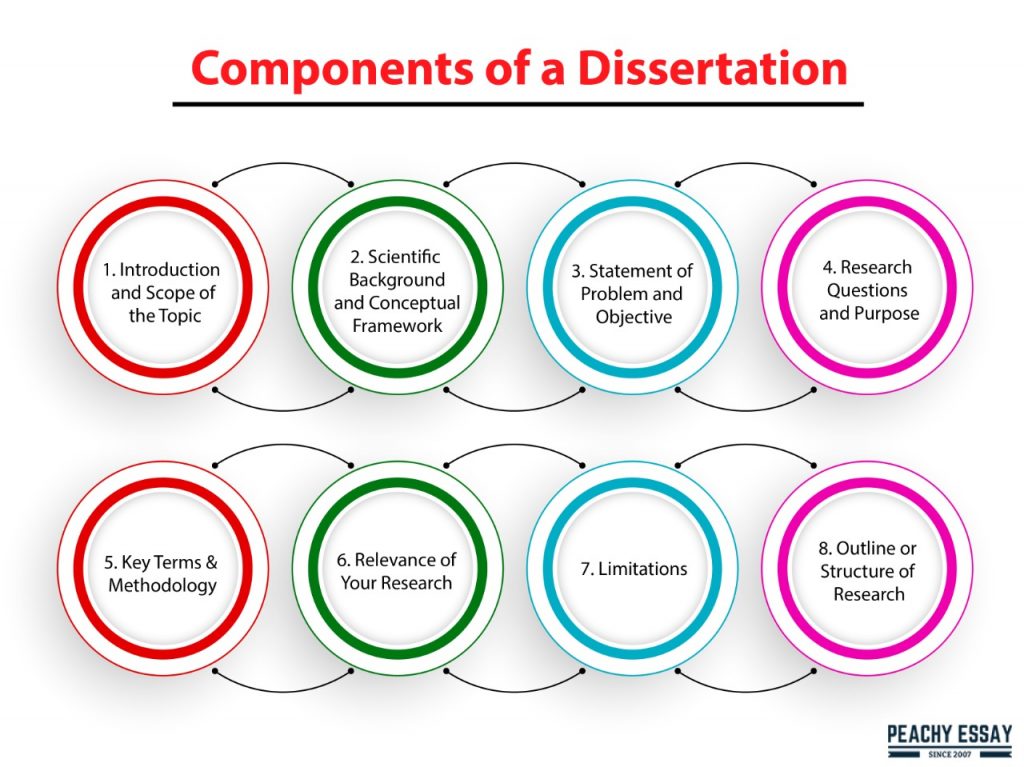
Introduction and Scope of the Topic
To educate the reader on the substance of your dissertation, the first paragraph of the introduction should provide a scope of your dissertation. As you would in a research article, define the subject of your dissertation, introduce it, and give background information. Indicate who may be interested in reading this article.
Also, if feasible, specify the specific element of the subject you will study as well as the time period.
Scientific Background and Conceptual Framework
Present the theoretical foundation of the research in this section of your dissertation introduction (also known as a literature review). Give an overview of your work. Also, include any related papers or other scientific materials that already exist. Determine the theories and concepts that serve as the foundation for your work.
You may also provide information on the topic’s development or research. In general, you should educate the reader about current knowledge on your subject and place your work in perspective.
Statement of Problem and Objective
In this section, clearly explain the problem you’re looking into. Identify the knowledge gap and present the issue to do this. Determine the problem you’ll solve and your primary goal, or the outcome you aim to accomplish.
Use research questions or hypotheses to respond to your issue statement. Conduct your literature research before creating a conceptual framework if you are unable to generate any compelling assumptions for various reasons.
Research Questions and Purpose
Define the goal of your study and the specifics of what you’ll be looking at. Mention the research questions you’ll be answering. These are the questions that need to be answered in order for you to achieve your goals. Descriptive, comparative, and causal research questions are the three kinds of research questions.
Their nature is determined by the aim of your study. These inquiries should be extremely precise and unambiguous. There are usually at least three questions included, although there is no standard number. It’s also a good idea to explain how and why you came up with these queries. In this section, you may also add your theory.
Key Terms and Methodology
Outline your dissertation’s methodology in a few sentences. It implies you should describe the techniques you’ll employ to achieve your study goals. You may also add a list of important words that you’ll utilize in your dissertation.
Relevance of Your Research on a Practical and Theoretical Level
To demonstrate the scientific significance of your study, use strong arguments and your expertise. To do so, first determine the knowledge gap in relation to the item under consideration. Make a list of the questions that haven’t been looked at previously.
Explain how your research will help you bridge that gap, solve the problem, or contribute to what you already know. You may also provide a new perspective on an existing problem. Don’t forget to mention the practical advantages that your dissertation will provide.
Limitations
Every research project has its own set of constraints. They are outside the researcher’s control. Every research project must include this step. On the one hand, pointing out the limits will aid in future research. On the other hand, you’ll show that you’ve done your homework and are aware of the factors that restrict your research.
If the limits section of your paper is missing, it may indicate that you either don’t comprehend the subject nor did just cursory research. Limitations may occur in any section of your article. It may be due to the uniqueness of the researched subject, research techniques, or a lack of time and evidence, for example.
Outline or Structure of Research
You briefly explain the framework of your dissertation in this section of the introduction. Give a broad overview of your work to help the reader understand how it is organized. Don’t go into too much detail. For each chapter, a handful of phrases will enough. You might use a bulleted list to convey it.
Tips on How to Write a Good Introduction
Here are some pointers on how to write a good introduction.

Pique the reader’s curiosity
You need to grab the reader’s interest right away with a discussion of a larger topic related to your study. Use research, statistics, and quotes from worldwide or national professional groups, governmental organizations, or important writers on the study’s subject to enhance impact.
Give a brief summary of your study subject
Your talk should then begin by delving further into the subject’s wider elements before focusing on your research’s particular topic. When doing this, it’s a good idea to pretend the reader has no prior knowledge of the subject. As a result, terminology must be defined and explained, based on important studies. Alternatively, if you are dissatisfied with current definitions after reading essential material for the literature review chapter, draw on them to create your own (but make it clear you have done this).
Describe how your research will contribute to the field
You must next sell your study subject suggestion by showing the key reasons why the research will contribute significantly to the existing body of knowledge. This may be done by identifying a gap or restriction in current research and then explaining how your study will fill that gap or constraint.
Explain why you’re interested in the topic
The next step is to explain why you chose this particular subject. These may be related to prior study, work, or experiences.
Make a list of your research objectives
Your three or four overarching research goals must be included. If it’s a qualitative study, add related research questions; if it’s a quantitative study, offer hypotheses. The former are often derived from the study goals. However, keep in mind that these goals, questions, and hypotheses are all flexible and may be changed as you do your study.
Give a forthcoming chapter overview
The introduction concludes with a summary of the remaining chapters of the thesis. The remaining parts may be placed in any order as long as they are in a logical order.
Learn from your other students
The bulk of journal papers in your topic’s content will also offer you with valuable information.
Consult with your supervisor
Always communicate with your boss and schedule frequent catch-ups. They’ll be able to provide you with advice and support, as well as point you on the correct path.
Dissertation Introduction Examples
Strategies of Advertising for Indian Market
Chapter 1: Introduction
One of the main responsibilities of every business, whether local or foreign, is to raise public knowledge of the product and attract consumers. Creating a brand or a great product image is difficult without product understanding and consumer wants. The greatest way for a business to accomplish this is to create an effective advertising campaign that positively affects consumers’ emotions.
Advertising is the easiest method to inform, attract, or inform a target audience about a product or service. Advertising may take many forms, and it is up to the company’s advertising department to perform market research and determine what should be focused on when starting an advertising campaign.
How can we as marketers combine different communication channels to create an efficient advertising campaign and a profitable product? This chapter’s primary goal is to provide background information. This chapter will also discuss the research goals. The primary focus is on how advertising tactics differ when entering India. The researcher performed thorough research to comprehend India’s surroundings.
1.1 Background of the Study
India has a population of 1.14 billion people and is constantly expanding, therefore whatever market share a global business targets in India may never be adequate. However, it contains 28 states and 18 languages. Though English is the official language of education, Hindi is the second most frequently used language. Any business entering India must determine which region of the nation to enter, which market niche to target, and which language to employ.
North and south India may be separated. Companies need to create advertisements that not only combine cultural influences but also respond to the local requirements of each area.
Since China joined the WTO, India has become a prospective rising country. Geographic advantage is just one of the elements accelerating Indian economic development. However, other variables such as FDI attractiveness, low labor costs, and low education rates also attract international investment. When foreign businesses join the Indian market, extensive advertising is important to make a sale.
As a result of this, advertising may influence customers to think about their own self-image. However, when entering a market like India, cultural differences matter since consumers have distinct preferences. Marketers must thus consider standardization and adaptability since local consumers will respond differently to advertising. The company’s image also influences the consumer. Because the brand is derived from the company’s image, the advertising campaign may either follow a conventional plan or be tailored to the product’s brand appeal. However, since India is a vast nation with many languages, cultures, and beliefs, businesses entering India will have to work hard.
1.2 Research Aim
To develop successful advertising tactics for international companies entering the Indian market.
1.3 Research Objectives
- To learn what makes Indian consumers remember ads
- To understand Indian consumers’ buying habits
- To understand how advertising affects consumer behavior
- To determine the importance of advertising
1.4 Indian media channels
My study shows that 80 percent of Indians over 16 are exposed to some kind of media. Students, children, parents, or professionals. The issue is how the business will distribute in different media and determine which media will provide the greatest results.
In India, there is television, print, radio, cinema, posters/advertising, and the internet. In terms of television, the business must determine whether to target homemakers, children, working professionals, or students. News and sports networks are two channels that the business cannot afford to lose.
There are many news stations, but there are also media networks that broadcast in each regional state’s language. Then there are sports channels, and in India, most people watch TV to watch cricket events. The numerous serial shows may be the target place for addressing homemakers in India. Kids’ channels are the greatest destination for kids.
We’ll go into the different television categories later. They may be classified in newspapers and radio. However, the businesses choose who and how to promote their product.
1.5 Culture in India
India is one of the oldest and most distinct cultures in the world. The country is so big and has so many cultures that it is tough to grasp fast. As a consequence, culture in India differs greatly throughout the nation.
The cultures of the country’s north, south, and north east all have their own unique characteristics. With 28 states, it is impossible to respond to the cultural needs of the whole country. India is the birthplace of four main global religions: Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. India has many cultures, languages, cuisines, and music.
For example, food differs from culture to culture within a nation, and each cuisine is unique. Similarly, music and dance vary greatly between the north and south. Northerners call it bhangara. In the south, it’s bharatanatayam, folk. Festivals are celebrated in India with lights, fireworks, prayers and rituals.
So any multinational coming must first grasp the culture and then attempt to influence the advertising. They must determine whether their product is appropriate for that culture.
1.8 Significance & Scope of the Study
The research performed meets the dissertation goals. An extensive research was conducted using questionnaires and secondary data in order to analyze what advertising strategies a multinational company should use when entering India, and what cultural influences must be focused on in order to succeed.
1.9 Study Limitations
As a result, most of our respondents are students, and we only got responses from a small group since we couldn’t analyze the whole market due to time constraints. Most of the surveys were completed by people aged 18-25, and their answers cannot be fully examined since it is impossible to anticipate their meaning. The results were cross-checked. But the answers can’t be 100% accurate.
1.10 Dissertation Format
The dissertation is split into five chapters to examine how international corporations may promote in India. It provides an overview of advertising in India and a short explanation of the media. The second chapter reviews the literature by defining advertising, ethics, and how culture and advertisement must be combined. What are the different advertising styles?
The third chapter covers research techniques and advertising tactics. Understand customer behavior and needs to know this. This chapter presents descriptive study results. The results are compared qualitatively with other research of a comparable kind. This study’s last chapter attempts to offer suggestions, clarify limits, and propose further research.


