Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
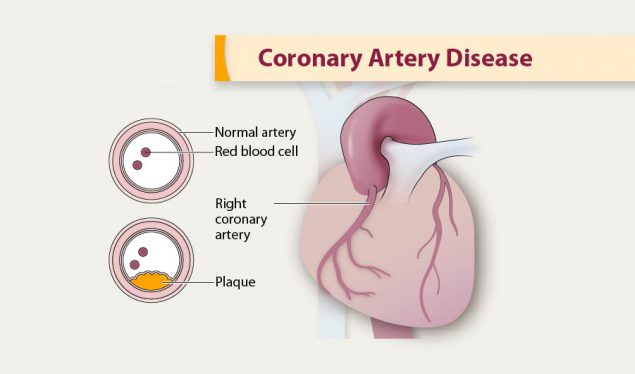
Ischemia describes a heart disease caused by the stoppage of blood vessels, resulting in an inadequate supply of blood and oxygen. Ischemic Heart Disease or Coronary Artery Disease is a problem of the heart that results from narrowed arteries that provide blood to heart muscles. Ischemic Heart Disease is primarily caused by the buildup of atherosclerosis along the blood vessels of the heart. When the flow of blood is blocked to the muscles of the heart results in the death of cells or a heart attack. The discomfort faced when the muscle of the heart is deprived of enough oxygen is referred to as angina pectoris and it is highly common during emotional stress and exercise. An analysis of patients with Ischemic Heart Disease explains the disease’s risk factors, preoperative assessment, diagnosis of myocardial infarction, management strategies, and post-operative Ischemia.
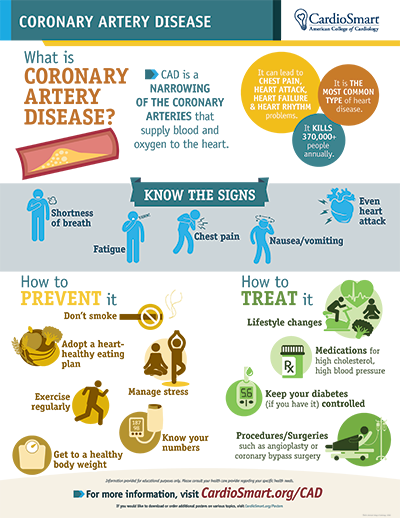
Coronary Artery Disease is caused by plaque buildup, limiting the flow of blood to the heart. Risk factors associated with CAD include smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, genetics, sedentary life, and obesity. Ischemia is manifested through various symptoms, such as extreme fatigue, breath shortness, chest pain, edema, and heart palpitations. Preoperative assessment for Coronary Ischemia involves patients for vascular surgeons even when they have no signs because of physical activity limitation. According to Gandelman, “Preoperative tests give your nurse or doctor more information about: whether you have any medical problems that might need to be treated before surgery” (Gandelman 137). For this reason, preoperative assessment about CHD helps patients understand if they need any special care and risks associated.
Myocardial Infarction is diagnosed through a stress test, examining how the heart is responding to different situations, like exercise. An angiogram is employed to search for blockage areas in heart arteries. An echocardiogram helps in identifying heart areas that are not working properly. Anesthesia risks associated with the disease are temporary, including nausea, chills, and confusion. According to Gandelman, “Patients who have undergone coronary revascularisation procedure within 5 years and are asymptomatic have low perioperative risk surgery and can undergo surgery without any further evaluation” (Gandelman 145). As a result, preoperative questionnaires, especially, the computer-based versions that are filled by other anesthesiologists could be highly helpful.
Ischemic Heart Disease can be managed by promoting a healthy weight, limiting dietary sodium intake, limiting alcohol consumption, increasing fresh fruits intake, and increasing physical activities. During treatment, angiotensin, angiotensin receptor blockers, and anti-ischemic are commonly used in drug therapy. According to Gandelman, “The postoperative period is characterized by adrenergic stress, which can induce myocardial ischemia in patients with CAD; cause coronary vasoconstriction, and facilitate platelet aggregation” (Gandelman 211). For this reason, Ischemic Heart Disease is a serious condition of repeated chest pains occurring when an area of the heart fails to receive sufficient blood.
In conclusion, this paper has examined patients with Ischemic Heart Disease and illustrated the disease’s risk factors, preoperative assessment, diagnosis of myocardial infarction, management strategies, and post-operative Ischemia. Ischemic Heart Disease or Coronary Heart Disease is primarily caused by plaque buildup, leading to the obstruction of the blood flow to the heart. The disease can be maintained by promoting a healthy weight, limiting drinking of alcohol, increasing eating of fresh fruits, and increasing exercise. Therefore, Ischemic Heart Disease is a serious condition characterized by continuous chest pains happening when an area of the heart does not receive sufficient blood.