Abstract
Students are suffering from stress and procrastination, and this negatively affects their performance in school. The participants were Baruch College Psychology students studying an Experimental Psychology class. The primary techniques used to gather data included questionnaires and surveys. In this research, we will discuss the implications of stress in students and the strategies that we can use to avoid suffering from anxiety. We will provide participants with questions that they will be required to answer. The survey questions asked will be provided in this study paper. The answers that participants will provide will determine the results that we will obtain. In this research, we predict that there will be a significant correlation between stress and procrastination in academic performance. The best method to avoid procrastination as a result of stress is avoiding stress by all means possible.
Introduction.
In earlier days, students’ academic achievement was related to intelligence; however, recent studies have shown the importance of other significant aspects that lead to high academic achievement. Stress is an example of a factor that may affect the achievement of students in their academics. There is a tendency for increased stress levels due to academic procrastination; this can decrease academic performance. This research will aid us in getting an overview of the impacts of tension on academic procrastination and find solutions to overcome this problem. We are also going to find out the gender that mainly suffers from procrastination and stress.
Academic procrastination is said to be the aspect where students postpone academic assignments, for example, studying for an examination. This problem can cause and can also be caused by stress which will, in turn, affect student performance in academics (Khalid et al., 2019). Academic procrastination the main problem facing most students. Studies have proved that more than 70% of university pupils suffer from postponing tasks that affect their learning performance. About 58% of undergraduate comrades procrastinate for three hours or more within a day.
This research will help students plan themselves to help them avoid postponing their studies, thus increasing school activities’ performance. This research will also enlighten teachers on tackling students suffering from academic procrastination and stress, giving them tips on how to guide them, and help them understand the compelling interaction between anxiety and procrastination. Increased levels of academic stress and procrastination may lead to academic failure.
Procrastination is termed as a willing habit in which the skeptical consequences surpass the positive effects of delays. Students who procrastinate often have lower coursework scores and minimal results in their end exams. Pupils who procrastinate understand their assignments and their importance but still cannot do them due to excuses they make and their delays.
In the previous years, academic researchers have given close procrastination attention and have done many studies based on getting foreign research backgrounds. They however did not find any connection between procrastination and academic achievement, others stated that procrastination positively impacted academic achievement. Despite the different opinions given on procrastination, the truth of the matter remains. Good research on procrastination and stress helps us understand procrastination in a better view.
According to studies carried out, procrastination is divided into two; passive and active procrastination. The two types of procrastination are used as the connecting variables. Academic procrastination was first voiced in the American Psychological Association in 1984. According to Chu, active procrastination is an adaptive studying method where the learner temporarily avoids academic jobs to obtain more resources to complete an assignment or reduce stress.
Chu also defines passive procrastination as the non-intentional procrastination of academic tasks. The time taken to complete the academic assignment is often delayed. We may cause passive procrastination due to the difficulty of producing stress and other emotions, thus causing delay, which is involuntarily.
Boysan & Kiral, (2017) showed that distress and lousy performance in academics is caused by insufficient time and last-minute reading for examinations. Peer influence is also a factor causing procrastination among young adults. According to stress Felix Smoltz on Academic Procrastination and its effects on Perceived Stress and Mental Well-Being, the 12-item procrastination scale known as PASS created by Solomon in 1984 used in that research analyzed the academics procrastination frequency six academic domains established on a five-point Likert scale.
The passing score for this research was 4. Samples were to be taken, and they recorded their averages; anything higher than four was considered above average procrastination while anything below four was considered below average procrastination. The total high score was calculated by adding up the academic domains’ items, thus showing more self-reported procrastinations.
One of the leading causes of procrastination by students is due to stress. Stress by students may be associated with family problems, environmental issues, and personal problems (Ashraf, Malik, & Musharraf, 2019). How parents raise their children contributes a lot to the procrastination of their children towards school. High parent expectations from their children is also a significant cause of stress among the students. Positive parenting makes a child have a good personality, character, whereas negative parenting behaviors weakens the child, leading to lower academic progress (Khalid et al., 2019).
The high tuition fees and long duration of study by medical students is a factor causing stress among those students. Academic progress is affected by academic procrastination, which later causes stress and anxiety.
The current research aimed to find how procrastination and stress experienced by students relate. We hypothesized that there would be a significant correlation between stress and procrastination in academic performance.
Methodology
To determine the research hypothesis, the study applied the qualitative analysis method. According to Mack (2005) qualitative research comprises of collecting and analyzing non-numeric data such as texts, audios, podcasts, and videos to develop an in-depth understanding of opinions, concepts, or experiences. The data is often collected through focus groups, observation, and interviews. Whenever qualitative research methods, the study seeks to explore a phenomenon besides explain relationships.
Target Population.
The research identified a representative sample from the Baruch College of Psychology students studying an Experimental Psychology class. The students were selected randomly to avoid issues of biasness. Age and sex were not put into consideration since the research aimed to test the students’ experiences.
As earlier noted, the qualitative analysis approach collects primary data through in-depth interviews. This research used open-ended questionnaires and the observation method to understand how stress and procrastination influenced each other. The open-ended questionnaires aimed to focus on factors that promote students to delay or postpone their academic assignments while the observation method was conducted to validate the questionnaire findings. This was anticipated to increase data validity and reliability.
Prior to conducting the research, the research team adhered to the ethical research guidelines. That is, the participants selected for the research volunteered to partake in the study with informed consent. The American Psychological Association recommends that participants should willingly participate in any scientific research with full knowledge of the research benefits and risks (Smith, 2003). The research team sought permission to conduct a study in Baruch College students. This process included explaining to the school administration the objectives of the research, its benefits and potential risks. For the students who agreed to partake in the research, a confidentiality agreement was signed and respect of autonomy assured.
During data collection, the study issued a total of 19 questionnaires, which they were to fill at their own time and submit anonymously to a shared Google sheet after completion. The observation was further applied where the students’ assignment submission was monitored anonymously for two weeks and their routine when the assignments or assessment tests had long deadlines. Assessment of participants’ scores on procrastination and stress was done with the help of a scoring guide. Participants were instructed to have a pen and paper or use their phones to keep a record of their scores. The scores for every participant were then compiled using Google Sheets, while JASP retrieved statistical data.
Results.
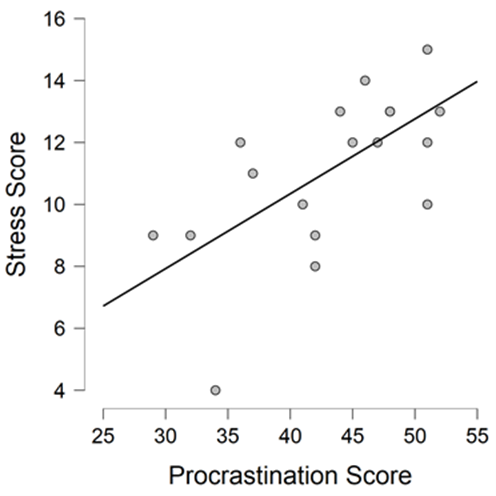
The collected data was put through a Pearson correlation test to investigate the relationship between academic procrastination and stress among college students. The results are as shown;
The results revealed that there is a significant positive correlation between stress and postponing academic work (r = .647, n = 19, p = .003).
Discussion.
Procrastination and stress have a significant positive correlation.
Academic procrastination promotes academic stress among students and negatively impact their academic performance. Based on the study results, high procrastination scores were directly proportional to high stress scores. That is, the longer a student delayed to submit their assignments, the more they experienced increased stressed while doing the assignment close to deadline and some past deadlines. According to Nayak (2019) academic procrastination is an adverse impact in students’ academic progress that leads to stress and anxiety. A study relates that academic postponing by doctoral students increased their levels of anxiety and guilt in future thus overall academic stress. Therefore, we can conclude that academic procrastination induces stress alternatively stress can cause academic procrastination. Past research from social sciences confirm that stress negatively affects a person’s emotional well-being and cognitive function. Although research has not explored much on this concept, scholars agree that stress is an outcome of various completing factors. With regards to our research, one of the factors that promoted academic procrastination was mobile phone addiction especially among students who used their phones to record their scores. These findings relate to Yang, Wang, & Hu, (2020) research, which explain that long use of mobile phones distract students from their academic agendas thus instigate procrastination behavior that later induce stress and poor academic progression.
Despite this, the findings of this research present limitations with data generalizability. A prime example, our research focuses on a small group of 19 participants which limits its scope. This makes it hard to explores multiple factors that can contribute to accuracy of data. Such a small representative sample of participants can disregard the generalizability of our data since the data findings relate to a small population. On the other hand, the research findings rely on one test, the Pearson Correlation analysis thus questions its aspect of data integrity. Regardless, the research uses two methods, where one validates the findings of the other. This assures data reliability.
Conclusion
We put into consideration the correlation between stress and procrastination. Our sources show that the leading cause of procrastination was anxiety among the students. We also found that academic procrastination affects academic focus. Procrastination itself increases stress among the students, which is caused by the worry of not completing the task. Our findings suggest that parents should enhance their parent-to-child relationship to note the behavior of their children when they are stressed out. Improving the parent-child relationship during childhood would aid overcome the procrastination of students.