Feeling sad or low at some point in life is common for everybody. However, if these feelings become prolonged and coping strategies prove to be ineffective, then something must be wrong somewhere. When a person reaches a point where he or she is overwhelmed by feelings of sadness for an unusually long period, say weeks, then it is highly likely depression has set in. Depression can be defined as a mood disorder that is characterized by lack of happiness, boredom, prolonged sadness, and loss of interest in routine activities. According to the Center for Diseases Control (CDC), millions of people suffer from depression every year though most of them fail to recognize the condition to begin treatment. It is estimated that depression affects more than 10 percent of the adult population in America. According to the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-V), depression can be categorized into three main types namely; major depression, dysthymia, and bipolar disorder.
Major depression normally takes places in relatively short episodes that are separated with different periods of time such as days or weeks. In these episodes, a person feels sad most of the time and losses interest in nearly all activities that he or she had previously enjoyed or engaged in. During this time, a person may experience several physical and psychological discomforts such as lack of sleep, loss of appetite, and feelings of worthlessness. In some extreme cases, some people tend to have thoughts of suicide (Yapko, 2013). Dysthymia is a mild type of depression that sometimes can go undetected but lasts for longer periods than major depression like two to four years. This type of depression impedes the feelings of happiness thereby negatively affect work and social life. Bipolar disorder is characterized by manic episodes where a person experiences severe mood swings. Between episodes of bipolar, a person may not exhibit any sign of depression even for years.
Causes of depression
Unlike other psychological problems, depression has many causes depending on one’s life history and environment. However, researchers have identified a unique combination of factors that may exacerbate the likelihood of one getting depression. For instance, when an individual undergoes stressful moments or passes through traumatic events such as the death of a loved one, loss of property, or financial issues, chances are very high that he or she may end up being depressed. Hormones changes caused by biological processes such as pregnancy and menstruation can also cause depression (Olfson, Blanco, & Marcus, 2016). In addition, depression can be genetic in that younger generations from a family with depression history are also likely to suffer the same condition.
Signs and symptoms of depression
Depression has many signs and symptoms depending on the type and the person. The signs tend to differ from one person to another in terms of how long they last and severity. However, some of the common indications are sadness, feelings of worthlessness or helplessness, pessimism, and irritable mood. Some people also experience lack of energy or motivation to do important tasks because the activities appear to be too hard to manage.
Major Depression
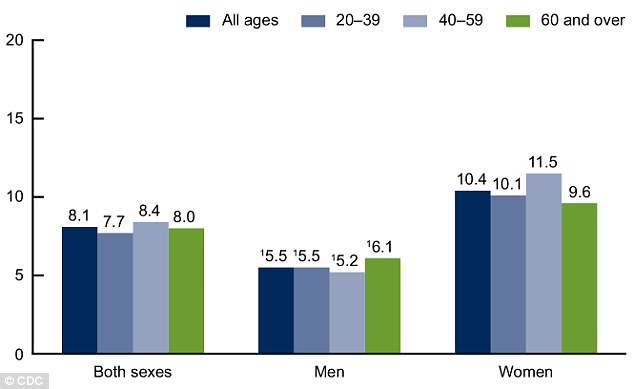
Major depression is the most prevalent type of depression in the United States. Nearly 15 million Americans are affected by major depression annually. It is also important to note that women are usually disproportionately affected by major depression compared to men as shown in the figure below. The main reason why women suffer more than men is that of the biological changes. Women tend to be prone to hormonal changes and genetic predisposition during important life stages such as puberty, menstruation, and childbirth.
Like any other psychological disorder, major depression can be fatal if left untreated. Fortunately, the condition is treatable and more than 80 percent of the patients who seek treatment full recover in less than two months (Yapko, 2013). Several treatment methods are used including medication and talk therapy. Major depression is caused by an array of factors depending on which circumstance one is in. For instance, scientists have discovered that genetics is the main cause of major depression. In other words, the major depressive disorder is often found in the family tree of the patient. Some of the notable symptoms include agitation, inability to thinking clearly, weight loss, restlessness, among others.
Major depression can be treated through various methods including antidepressant medication, psychotherapy, and electroconvulsive treatment (ECT). However, ECT is usually avoided and only to be used dire situations because of its adverse side effects. Psychiatrists provide psychotherapy services that may also vary from one patient to another depending on the cause of major depression and the environment. Major depression can also be divided into small types depending on the cause because the symptoms tend to be the same. They include seasonal affective disorder or SAD, psychotic depression, postpartum depression, and melancholic depression. SAD is a form of depression that is caused by lack of adequate exposure to sunlight, especially during winter months. Psychotic depression is caused by the belief in delusions that are not in touch with the reality that may have been brought about by a traumatic event in the past. Postpartum depression is a common experience for mothers after the birth of a child because of the variation in the hormonal balance. Melancholic depression is associated with intense grief due to a sad event like the death of a loved one.
Dysthymia
Dysthymia is a low-level depression that often tends to be less severe but more chronic. The condition shares many symptoms as the major depression that one many confuse the two at initial stages. However, the main difference between the conditions is that dysthymia is normally experienced for long periods ranging from two to five years. Dysthymia, which is also referred to as persistent depressive disorder (PDD) is twice as common in women as in men. People suffering from dysthymia are not only depressed, but also have no interest in routine activities either at work, school, or home. Feelings of hopelessness and low self-esteem are the characteristics of the condition. Given the fact that these feelings can last for many years, it is undoubtedly true that the condition can negatively affect relationships over time. People with dysthymia are difficult to impress or make happy because they are always gloomy and appear to lack interest in almost everything happening around them. Statistics estimate that nearly 3.3 million Americans are suffering from dysthymia making it the least prevalent depressive condition (Olfson, Blanco, & Marcus, 2016). However, these numbers may not reflect the real picture because the majority of those suffering from dysthymia often fail to seek medical assistance. Children and adolescents are also prone to dysthymia.
As mentioned, many people do not seek treatment because they think sadness and lack of interest is usually part of life that they would eventually overcome sooner than later. However, the chronicity of the symptoms may prove otherwise that the condition can go on for many years. For example, social isolation and decreased activity may be perceived as normal occurrences while in reality, they are symptoms of a much bigger problem (Pratt and Brody, 2008). For those who seek help, dysthymia can be treated with medication and psychotherapy. Medications can be in the form of antidepressants although some have been linked to adverse side effects such as having suicidal thoughts. Psychotherapy can be administered through various options such as group therapy, family therapy, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is sometimes referred to manic depression or bipolar affective disorder. This type of depression is characterized by cycles of extreme mood swings. For instance, one may have an elevated mood making one feel pretty good and happy maybe after passing examinations. However, this may change abruptly to periods of depression due to certain occurrences like a relationship breakup. During the depressive state, one feels extremely bad and may cry from time to time. He or she also feels life is distasteful and hopeless. These extreme changes in the mood can have a defined pattern, say, every first week of a month, or every Monday of a new week. Bipolar is a common condition that affects nearly 3 percent of the U.S adult population (Olfson, Blanco, & Marcus, 2016). Bipolar has no gender preference. Both men and women have equal chances of being victims. The signs and symptoms of bipolar disorder vary from one person to another even though most of them do feel extremely irritable, restless, and agitated. The manic behaviors can have a serious impact on one’s functioning at work, school, or social situations. Depressive behaviors, on the other hand, can significantly affect family and personal relationships.






