The Ethics of Conjoined Twins Separation
Introduction
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights explicitly guarantees the right to life. This guarantee by the universal declaration raises serious ethical questions in the case where doctors and parents are faced with the dilemma of killing one child to guarantee the life of the other.
The case
On 8th August 2000 conjoined twins known as Mary and Jodie were born at the St. Mirren’s Hospital in Manchester. An initial ultrasound during the third month of pregnancy indicated that the unborn children were conjoined, at the time the parents were domiciled on the Island of Gozo, off Malta, in a strongly Roman Catholic community that did not entertain the idea of abortion. The parents sought specialist care in Britain, and it was not until the birth of the conjoined twins that the health status of the twins was revealed. Their bodies were fused at the base of the spine; there was a fusion of circulatory systems which translated to the twins sharing a single bladder. The heart of the Weaker twin (Mary) was not effective, her lungs were not functional and had only a primitive brain. The effect of this dependence meant that Mary depended on Jodie for life support.
On the other hand, Jodie had normal brain function and was not dependent on the twin for any function. Doctors advised that surgery was inevitable because the strain on Jodies Heart would kill both twins at between 3 and 6 months. However, the separation surgery would lead to the death of Mary.
Conjoined twins
The scientific understanding of conjoined twins holds them to be monozygotic twins that failed to complete normal division after conception. Medical practitioners often suggest surgical separation. However, this suggestion raises serious ethical questions and dilemmas to parents, health professionals, lawyers, and judges(Smith et al 2017). These ethical and moral questions include; parental autonomy, informed consent, beneficence, justice, personhood and sanctity of life.
Ethical Theories
Consequentialism
As the name suggests, consequentialism is an ethical theory that judges the rightness or wrongness of an action by the consequence that the action attracts. Consequentialism belongs to a broader class of normative ethical theories that hold the consequences of one’s conduct being the ultimate basis for any judgment. As such, from a consequentialist view; a morally right act or omission is one that attracts a good outcome.
Application of Consequentialism on Separation of Conjoined Twins
Act consequentialism asserts that action is right if there is a balance of good over bad. Rule consequentialism contradicts act consequentialism to the extent of holding that the rule that maximizes the benefits is the preferred rule. On the other hand utilitarianism insists on the aggregate good of all parties, it is concerned with and promotes the welfare, happiness, and absence of pain.
In this case, utilitarianism supports the separation of the twins. The expected good from surgical separation is the safety of the life of Jodie while improving the quality of life for both the parents and Jodie who risks losing her life, with regards to parents their quality of life will be improved by the fact that they will not have to bury both children. When faced with the same dilemma, normal intuition appeals to the utilitarian reasoning; when one is limited to two choices of losing two lives or one life, the only reasonable and justifiable course of action would be saving one life.
Ethical Issues and Questions Raised
Parental Autonomy, Informed Consent
Autonomy refers to self-rule to the extent of retaining absolute control over one’s affairs. In the case of medicine. Consent to treatment refers to medical and ethical principle that demands for consent to be sought before any medical treatment, test or examination is conducted on a person. For consent to be valid, it must be voluntary, informed and most importantly the person giving the consent must have the capacity to issue it or deny it(Hansen 2018).
In the case of Mary and Jodie who are infants hence cannot give consent. As such, the responsibility of giving consent is transferred to their parents by virtue of the fact that parents are best suited to make decisions for kids because they have their best interests at heart. However, in the case where the decision made by parents seems unfair or detrimental to the life of a child; the courts may be petitioned to advise on the best course of action.
In the case of Mary and Jodie, by mid-September and as a result of delayed consent, Mary was getting bigger at the expense of Jodie who had stopped growing normally because of the overload on her body organs. In this case, medical practitioners are under an obligation to petition the court on the most reasonable and justifiable cause of action.
In this case, consequentialism does not offer a reasonable explanation of the ethics of the delayed consent. Indeed, the act of delaying consent proves that the parents did not appreciate the maximization of the good consequences. As such, in determining the case courts are more likely to depend on the utilitarianism theory that guarantees the welfare of all concerned parties, rather than the interests and feelings of parents.
Sanctity of life
It is easy to insist that every person enjoys the right to life because every human action is informed by the desire to live. However, this opinion goes beyond the realm of calculation of the consequences that this insistence attracts(Clero 2018). As such, the right to live does not conform to the characteristics of legal rights that can be conferred or withdrawn through appropriate legal mechanisms. Indeed, the right to life is a moral right because it is absolute and cannot be infringed upon.
The absolute nature of the right to life raises serious ethical questions, the most dominant being there can never be any justification or morally acceptable reason for killing. This view is reinforced by the Declaration of Euthanasia that affirms, “nothing and no one can in any way permit the killing of an innocent human being, whether fetus or an embryo, an infant or an adult, or one suffering from an incurable disease or a person who is dying.” However, the limitations placed on the declaration of Euthanasia do not impose an absolute duty to prevent the death of innocent human beings.
In the case of Mary and Jodie; both enjoy the right to life. Under utilitarianism, while it would be morally unacceptable to kill Mary intentionally by undertaking an operation whose primary goal is to kill her, the effect of which would guarantee the life of Jodie serves as the tiebreaker. Indeed, Mary’s death would not be the purpose of the operation. Instead, it would be an inevitable consequence.
The Double effect Doctrine
The double effect doctrine that holds that it is always wrong to intentionally engage in the commision or omission of a bad act for the sake of good consequences that will ensue, but that it may be permissible to do a good act(Hanson 2018).
The utilitarian approach in determining the ethics of conjoined twins separation regards outcomes or events rather than actions, as of primary moral significance. The distinctions extending to intended and foresight or between commision and omission have no value on moral significance.
Conclusion
Consequential ethics
The picture embodies consequential ethics. Consequential ethics determine the morality of an action on the scales that the action attracts. In this, case the kid is returning home after being suspended for cheating in an examination. The action of cheating has resulted to the child being suspended from school and being reprimanded by the parents.
Utilitarian ethics
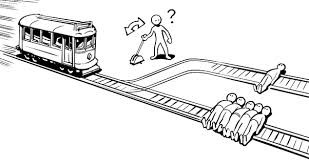
The principle of utility recognizes the role of pain and pleasure in human life and approves and disapproves an action based on the amount of pain or pleasure it will bring. In the picture above the train, steward is about to sacrifice the life of one person for the sake of five people because the pain caused by one death does not equate to the pain caused by the death of five people.
Our solid and well-experienced philosophy writing team provides a wide range of academic help including:
– Philosophy Paper Writing Services
– Philosophy Assignment Help Service
– Buy Philosophy Essay
– Philosophy Dissertation Writing Services
– Philosophy Essay Writing Services