Macroeconomics of Russia
In this report I gauge the macroeconomic trend in Russia to see how macroeconomic variables are behaving in last ten years in Russia and by looking at the available data I tried to find the major economic problems that Russia faced in these ten years along with some suggestions about policies that should be implemented to overcome these economic issues.
I have collected the data for my country Russia on three major macroeconomics variables including unemployment rate, Inflation rate and economic growth measured in terms of GDP. The data has been collected for last 10 years from 2009 to 2018.
| Year | Unemployment Rate (%) | Annual Change In Unemployment Rate | GDP | Per Capita GDP | Growth Rate In GDP | Inflation Rate (%) | Annual Change In Inflation rate |
| 2018 | 4.74% | -0.47% | $1,657.55B | $11,289 | 2.25% | 2.88% | -0.81% |
| 2017 | 5.21% | -0.35% | $1,578.62B | $10,751 | 1.63% | 3.68% | -3.36% |
| 2016 | 5.56% | -0.01% | $1,282.72B | $8,745 | 0.33% | 7.04% | -8.49% |
| 2015 | 5.57% | 0.41% | $1,363.59B | $9,314 | -2.31% | 15.53% | 7.71% |
| 2014 | 5.16% | -0.30% | $2,059.98B | $14,101 | 0.70% | 7.82% | 1.07% |
| 2013 | 5.46% | 0.02% | $2,297.13B | $16,007 | 1.80% | 6.75% | 1.68% |
| 2012 | 5.44% | -1.10% | $2,210.26B | $15,435 | 3.70% | 5.07% | -3.37% |
| 2011 | 6.54% | -0.83% | $2,051.66B | $14,351 | 4.30% | 8.44% | 1.59% |
| 2010 | 7.37% | -0.93% | $1,524.92B | $10,675 | 4.50% | 6.85% | -4.80% |
| 2009 | 8.30% | 2.10% | $1,222.64B | $8,563 | -7.80% | 11.65% | -2.46% |
RUSSIA: HISTORICAL DATA
In the above table economic growth is measured by growth rate in GDP or the GDP per capita can also be seen as a measurement of economic growth. The table above shows that economy tends to fluctuate during these ten years, there is not a single trend of increasing or decreasing in any of these three variables.
Another more easy way to look at the trends of inflation, unemployment and economic growth is the graphical presentation of this data. Below, separate graphs of all these three variables have been shown.
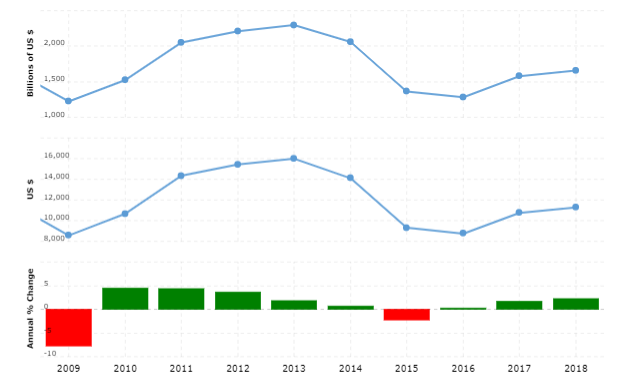
Economic Growth Rate/ GDP Growth Rate
The graph above represents the growth rate of GDP from 2009 to 2018 for Russia. This graph shows that there was an increasing trend from 2009 to 2014 in GDP but then there is sharp decrease in GDP growth in 2014 to 2015 and far slight decrease between 2015 and 2016 but again it increases slightly in 2017 and 2018. In 2013 GDP growth is at its top. Two year period from 2014 and 2016 can be considered as a recession for Russian economy because of decreasing GDP and economic growth at increasing rate.
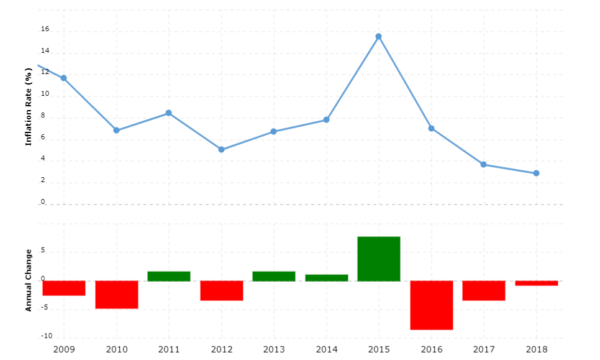
Inflation Rate
Above graph shows the rate of inflation in Russia in the period of the years from 2009 to 2018. In 2009 inflation rate is far high at almost 12% but then we observe a fine decline in inflation rate to almost 7% in 2010, this drop and rise in inflation rate continue till 20014. Along with the some fluctuations and a high inflation rate (more than 4 %) throughout the period there is a huge increase in inflation rate after 2014 till 2015. And again after 2015 inflation rate starts to decrease till the year 2018 to a relatively lower level.
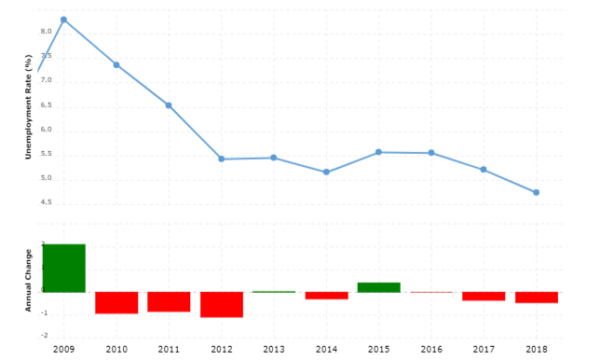
Unemployment Rate
The graphical presentation of unemployment rate of Russia from 2009 to 2018 is shown in above figure. The above graph shows that in 2009 the unemployment rate was as high as 8.3% almost but rest of the graph shows a continuous decrease in unemployment rate with the passing years excluding an increase in year from 2014 to 2015 and then this increase in unemployment persists till 2016.
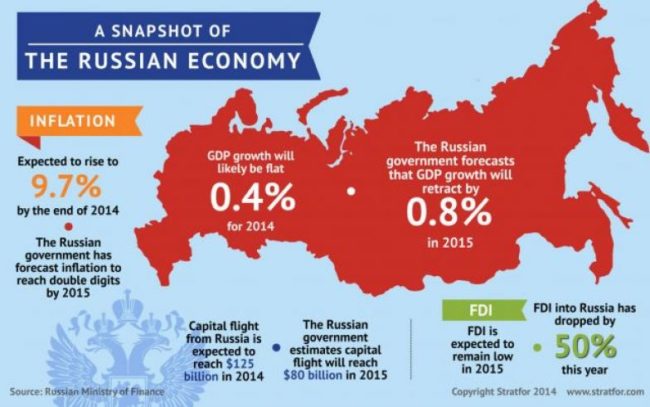
All these above graphs and table indicates that 2014 and 2015 were bad economical years for Russia. The reason for this was named Russian Financial crisis 2014-1015. This financial crisis in Russia was stemmed from sharp devaluation of the Russian ruble in the beginning of second half of 2014. There were several reasons for this devaluation of Russian ruble. Including almost 50% fall in crude oil prices and decline in major exports of Russia in mid-2014 and also due to the international economic sanctions imposed on Russia following Crimean Peninsula’s annexation by Russian federation in the start of 2014 and the Russian military intervention in Ukraine (“The financial crisis,” n.d).
Thus the decreased oil prices, devaluation of Russian ruble, inflation rate more than 4%, imbalance terms of trade and exchange rate shock due to banned imports were the main problems that Russian economy faced in this period.
According to the Bank of Russia the exchange rate plays a significant role in inflation dynamic forces in Russia due to an enormous share of imported consumer goods in retail trade. Then the significant exchange rate depreciation in late 2014 was the major factor behind the inflationary upswing in 2015. And then this increased exchange rate volatility magnified the second-round effects of currency depreciation in Russia.
When inflation remains same at a high level for a long period of time then people also make high inflation expectations for the future which is another hurdle for the Bank of Russia to bring the rate of inflation down to 4%.
To overcome this crises Russian economy has to implement some effective policies to let the economy grow with low prices and low levels of unemployment.
The main target for The Bank of Russia was to reduce the inflation rate and then sustain it to a lower level. For this The Bank of Russia firstly has to maintain the price stability in order to attain low inflation rate and a stable ruble exchange rate.
The stable prices allows maintaining a purchasing power of the domestic currency which is one of the requirements of a stable growth of Russia. When economy succeeded in ensuring a sustainable and low inflation it will result in creating a more predictable environment for the economic activities of households and producers. It facilitates the individuals and manufacturers in making rational and positive expectations in decision-making regarding consumption and investment matters. Thus, price stability helps lowering economic uncertainty and generates financial resources for the investment in long run, which provides the economy a ground for well-balanced and stable growth.
A contractionary monetary policy that restricts the spending and incentivize savings can act as a breakdown on inflation. Lowering the money supply or increasing the interest rates tends to appreciate the local currency. But it has its shortcomings with it as monetary policy effects are usually short term and does not impact the real economy.
On the other hand there is a policy suggested by Keynesian economists and targets the aggregate demand known as fiscal policy. A contractionary fiscal policy by government can stimulate the economic growth by lowering the tax rates or offering tax rebates to increase aggregate demand and spending to give a boost to the economy.
Unfortunately, there is no silver bullet or a standard strategy that can be implemented alone to correct all thing at the same time with no loss, as both policy tools, the fiscal policy and the monetary policy carry with them their own costs and benefits. However, an effective use of these policies will result in some positive benefit to society, especially in stimulating demand after some crisis. Thus a mixed policy is effective to come out of this crises.
According to The Central Bank of Russian Federation, The Russian economy follows a mixed policy strategy. They implement monetary policy using interest rate to maintain price levels and to much extent they follows a classical point of view of laissez faire economy by preventing the government intervention in most of the macroeconomic variables excluding prices. They followed a strategy of floating exchange rate where government do not set any exchange rate by itself. And the data on macro trends of Russia shows that this strategy of Russian government worked. As the economic growth rate of Russia has increased from almost 1,200 to 1,700 billion US$ from year 2016 t0 2018. Likewise, unemployment rate has fall from 5.56% to 4.74% and inflation rate reached from 7.04% to 2.88% in two year period of 2016 and 2018.
So concluding, in my point of view to sustain this rate of growth Russian government has to make sure the stable prices. Furthermore, The Russian Bank has to incentivize savings by increasing interest rates on savings and restricts the spending to reduce overall spending in order to reduce inflation. Also an expansionary fiscal policy can help the economy to boost by increasing the tax rates to lower the spending and thus reducing inflation. However, if the economy is near full capacity, expansionary fiscal policy risks sparking inflation. This inflation reduce the margins of certain corporations in competitive industries that may not be able to easily pass on costs to customers. So Russian government should be very precise in selecting specific industries for imposing taxes on them.
For more academic help please check a wide range of services our Economics Writing Help team offers:
– Economics Assignment Writing Services
– Economics Essay Writing Services
– Economics Dissertation Writing Services
– Buy An Economics Research Paper