Introduction
Portugal’s economy has experienced the effects of the different crises over the years. The various crises affected the GDP, economic growth, inflation, and unemployment rates. Portugal experienced a recession in 2008 and 2011 and is currently dealing with the effects of the Covid 19. During these crises, the government intervened to help its citizens weather the conditions.
GDP and Economic Growth
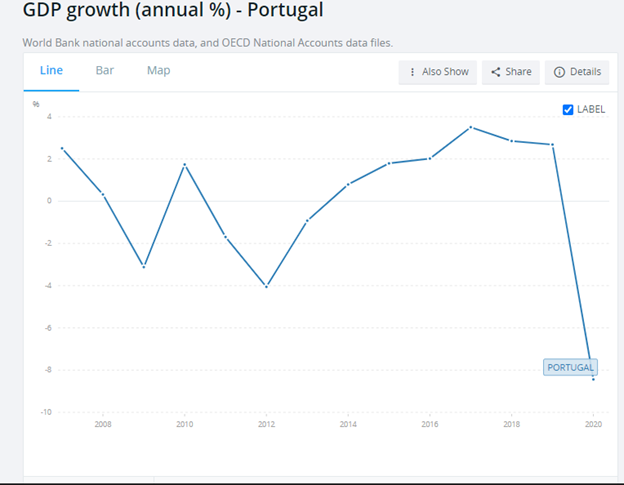
Portugal saw a decline in GDP growth between 2008 and 2009. The growth declined from 0.32% to -3.12% because of the financial crisis, then increased to 1.74% in 2010. There was a sharp decrease in 2011 to -1.7% and further in 2012 to -4.06%. The decline was due to the recession in the European region during this period. Portugal later saw steady growth from 2012 to 2017(World Bank, 2022).
In 2018, the GDP growth declined, but a sharp decline between 2019 and 2020. The decline is due to the global covid 19 pandemic. Portugal recorded a GDP growth of -7.56%, the lowest the country has ever seen since the financial crisis. Portugal’s GDP is projected to increase as the country recovers from the Covid 19 pandemic (OECD, 2022). The GDP was projected to grow by 4.8% in 2021, 5.8% in 2022, and 2.8% in 2023.
Source: The World Bank
Unemployment in Portugal
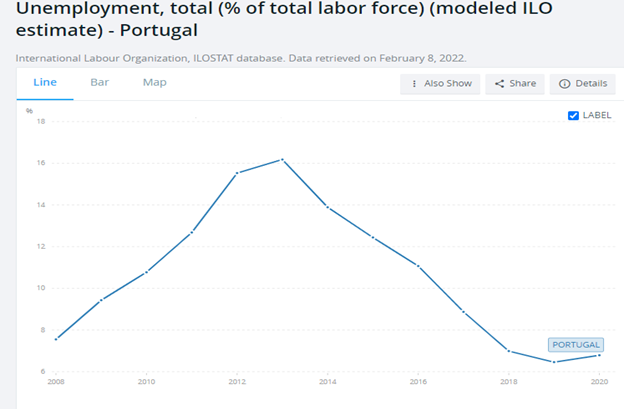
The unemployment rate in Portugal has increased over time. Portugal experienced a recession in 2010. By 2014 the country’s public debt levels rose so much (Brown, 2021), leading to people losing their jobs and increasing unemployment rates. The high unemployment rate was aggravated by the Covid 19 pandemic, which has seen the unemployment rate increase even further.
The Portugal government instituted measures to deal with the unemployment increase due to the global Covid 19 pandemic. The government reduced the tax rates to increase disposable income for its citizens. The government also adjusted the credit policies to enable businesses to access more funds to spark growth and offer employment to the citizens. Portugal also introduced education programs. It involved apprenticeship where the youth between 25-and 35 years get to learn from the labor markets to gain skills. Portugal also instituted a policy to limit the inflow of labor to increase the availability of jobs for the citizens. The limit would reduce competition for job opportunities.
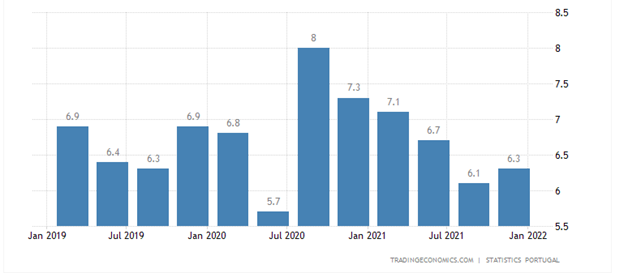
The unemployment rate in 2021 reduced from 7% in 2020 to 6.6% in 2021 and has still not reduced to acceptable levels as Portugal is recovering from the covid 19 pandemic. The unemployment rate will likely be at 6.2 % in 2023 (Trading Economics, 2022).
Source: The World Bank
Inflation and Balance of Payment
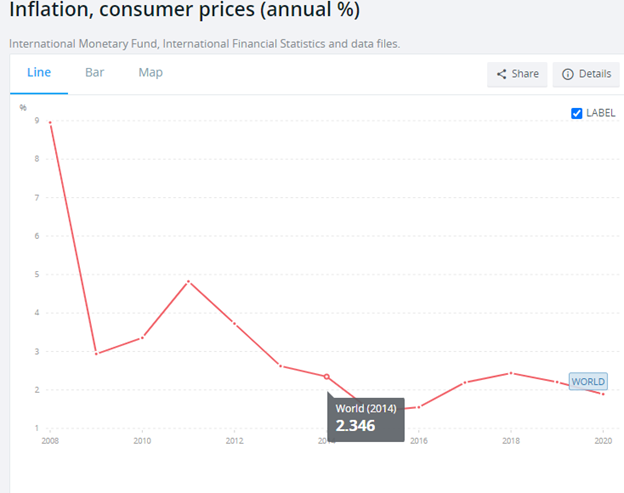
Portugal’s inflation is measured using the consumer price index. The inflation rate in Portugal has reduced over the years. Portugal, however, saw a sharp increase in 2011 due to the recession in the European region. After the covid pandemic, Portugal saw a decline in the inflation rate, but inflation increased in 2021. Portugal is recovering from the effects of Covid. Portugal has recorded an inflation rate of 3.4%, the second-lowest in the Eurostat as the Eurozone recorded an inflation rate of 5.1%. It is projected that Portugal’s inflation rate will be 1.20% in 2023 (Trading Economics, 2022)
Source: The World Bank
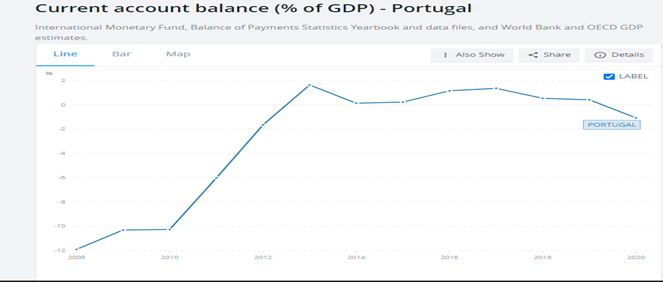
Portugal’s balance of payment movement was the inverse of inflation. The balance of payment declined between the years 2016 and 2020. The most significant decline was in 2020 when Portugal recorded a deficit of 4.55 billion. The trade percentage of trade to GDP constantly increased from 2017 to 2019. Portugal recorded 84.44% in 2017 and 86.71% in 2019. A decline of 11.34% in 2020 was attributed to Covid 19. The balance of payment as of January 2022 was 137 million euros (Trading Economics, 2022).
Economic Policy to deal with covid 19 and financial crisis
Demand side
To assist Portugal’s citizens in dealing with the covid 19 and the financial crises, the government and the central bank intervened. Fiscal and monetary policies had to be instituted.
Fiscal policies
The government of Portugal increased its spending. When there is an increase in government spending, the people have more disposable income to spend. They can also afford basic needs, which sparks the economy’s growth. Additionally, the businesses would have more funds at their disposal. They would be able to invest more, igniting economic growth and increasing employment opportunities, thus reducing the employment rate in Portugal and increasing economic growth (Gomes, 2021).
The government also reduced the tax rates. The reduction in taxes affected both the households and the businesses (Gomes, 2021). The households were left with more disposable income to spend and cater to their basic needs. On the other hand, the businesses were left with more funds to invest. Therefore, the economic growth was increased, which reduced the unemployment rate in Portugal.
Monetary policy
The central bank reduced the interest rate to deal with the financial and the covid 19 pandemics (Moessner and de Haan, 2022). A reduction in the interest rates increases funds to the businesses which increases investment leading to increased economic growth. The increased economic growth led to a reduction in the unemployment rate as the businesses increased employment opportunities.
Supply side
The government of Portugal dealt with the pandemic by instituting some measures. First, the government put restrictions on the inflow of the labor force to ensure that the country’s citizens got the few job opportunities available—the restricted competition from other people coming into the country. The citizens were then able to get employment, and they could cater to their needs amidst the crises (Brown, 2021). Additionally, Portugal introduced education programs through apprenticeship; thus, they would have the right skills by the time they joined the job market.
Conclusion
Portugal’s economy has seen growth and decline over the years. Portugal was affected by the global financial crisis and the European region recession in 2011 and is currently dealing with the effects of the covid 19 pandemic. The government and the central bank instituted measures to help the country deal with the crises. The country is now recovering from the effects of covid 19.