Executive Summary
Vodafone is one of the world’s successful mobile communications corporations in regards to revenues, functioning across the globe, offering an extensive scope of communications services. Vodafone’s vision is to be the leader in the provision of communication services within an increasingly connected world. The company has an aggregate returns of £44.5 billion, active 8.4% accompanied by advancing developments in most markets over the years — the accustomed operational turnover of £11.5 billion, along with a 2.5% reduction in a declining setting. Its data profit surpassed £4 billion, which is currently 10% of the entire service turnover.
The company higher bonuses reinforced by £7.2 billion of unrestricted cash flow, which is a growth of 26.5%. Additionally, the firm has enhanced performance in developing markets along with growing profits and market shares in South Africa, Turkey, and India; thus the company is planning on to expand its operations in Kenya, which happens to be the leading economy in East and Central Africa.
Introduction
Strategic planning is the procedure of creating and preserving a viable fit between the organisational skills, resources, and objectives, in addition to its changing promotion prospects (Baker, 2016). In actual fact, “strategy” is a continuing plan of a given company to attain its organisational goals and objectives.
The market is changing and very vigorous. Different services and products are created by various companies to offer the best services to consumers. Strategic marketing will attempt to assist businesses or organisations in generating services or products based on the changes, which are taking place within the market. Consumers’ needs and preferences change more frequently. According to Chernev, (2018) as a result of numerous external and internal facets, there occur necessary changes in the business environment. In such cases, strategic marketing is interested in performing well within the changing market conditions instead of increasing its revenue or sales statistics to have consistent impacts on consumers. High-quality services and products offered to consumers in hard times is the facet, which assists in managing the future of a given company.
Accordingly, strategic marketing is concentrated on creating a continuing and productive correlation along with its consumer base instead of marketing the services or products just once (Baker, 2016). Consumer retention and establishing reliability along with the brand will eventually aid in increasing the revenues and profits of the company, which makes the stakeholders and shareholders happy (O’Keeffe, Ozuem, and Lancaster, 2016). Stakeholders ought to be kept contented and motivated to introduce creative and innovative business plans for consistent growth.
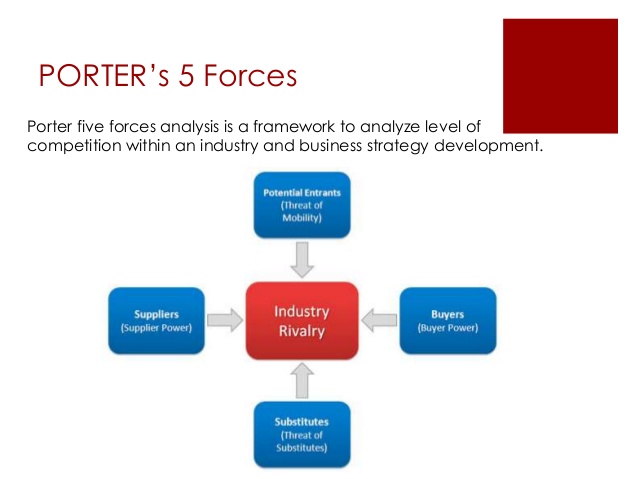
As a result, the report will analyse the macro-environmental of Kenya to evaluate the prospects and extortions that Vodafone can experience, as well as analysis of market entry strategies to determine a suitable plan for the company to access the Kenyan communication market. Additionally, market segmentation will be examined to determine a highlighted market segment for Vodafone. Porter’s generic policies will also be scrutinised on the preferred company, where there are essential recommendations and justifications in regards to the attainment of competitive advantages.
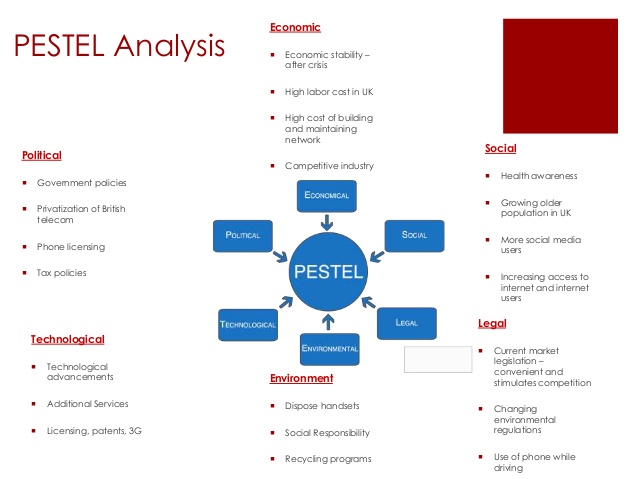
PESTEL Analysis
As pointed out by Marmol, and Feys, (2015) PESTEL scrutiny is a tool or framework employed by salespersons to observe and examine the external marketing environment (macro-environmental aspects), which have an essential impact on a company or business. The outcome of which is employed to realise opportunities, strengths, weaknesses, and threats that are utilised within SWOT scrutiny. PESTEL is the abridgement for political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal facets.
Political Features
These are factors regarding how, and to what magnitude a governing power act as a mediator within the economy, this can consist of political instability or stability in foreign marketplaces, administration procedures, tax policies, ecological laws, international commercial policies, trade restrictions, labour laws, etc. (Marmol and Feys, 2015). It is clear that political features frequently have an essential consequence on businesses or organisations and how they conduct their business activities. Business or organisations require the capacity to respond to the existing and projected future regulation and modify their marketing strategy accordingly.
Kenya is a democratic country where the president is the government and head of the state. The investment environment is inspired by the resilient nationalist predispositions followed by the governing authority as from 2002, were relaxed and as an outcome, the administration has been attempting to upsurge the inflow of foreign direct ventures and to advance the business and legal framework within the state. Regardless of government’s assurances to mitigate fraud and bribery, minimal advancement has been attained of this concern, and as pointed out by Transparency International’s 2009 East African Bribery Index, the East African state is ranked among the most corruption-prone countries within Africa, together with dishonesty predominantly widespread within the civic segment. Unwieldy labour unrest and bureaucracy might also enforce exorbitant interruptions on business activities; additionally, the employment of regulations have a tendency to be unpredictable.
Economic Features
Economic aspects have a substantial influence on how a company or business conducts its commercial activities and how cost-effective they are, these financial aspects consist of interest rates, economic growth, inflation, exchange rates, etc. These critical facets might be simplified into external and internal elements. External factors focus on the management of demand in a particular market system. Governing authorities make use of taxation policies, interest rates, besides administration spending as their main apparatuses they utilise this framework. Internal aspects are how individuals spend their earnings, which has a substantial effect on B2B businesses and organisations.
Kenya is an economic hub that is based on numerous state-managed enterprises and a relaxed commercial structure. Kenya’s market system is exceptionally reliant on industrial and agricultural sectors that remain undeveloped. Large amounts of foreign aid attained by the state are utilised to finance infrastructural projects and to import large quantities of consumer merchandises.
The primary economic challenges experienced by Kenya comprise proliferating corruption, increasing population growth, and inflation. As a result, Kenya’s GDP has been unreliable since independence. It realised an adequate growth rate of six percent that fell below four percent. During the 1990s Kenya’s GDP growth rate reduced to less than two percent. Since the early 2000s, the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) provided the Kenyan government with loans to prevent severe financial catastrophe along with a reduction of GDP growth range.
Social Features
Social features are also commonly referred to as socio-ethnic facets, which are subdivisions that consist of the shared attitudes and beliefs of the masses (McFarlin and Sweeney, 2015). These aspects comprise age distribution, career attitudes, health consciousness, population growth, etc. They are of precise interest since they have a direct influence on how marketing experts comprehend consumers and what motivates them.
Kenya has the most significant and most diversified market structure in East Africa, along with an average yearly development proportion of over 5% closely to a span of ten years. In regards to the Human Development Index, the state positions highest within the East African region. Its human and entrepreneurship capital provide the state with an enormous potential for future growth and development, creation of job opportunities, in addition to the reduction of poverty. The topical discovery of oil and other essential mineral resources produces substantial prospective for Kenyan economic system. Nevertheless, in spite of a deterioration of the state’s entire paucity proportion, wealth has not been dispersed correspondingly.
The country remains a significantly uneven society by gender, geographical location, and income. Poverty is ranked highest within the arid and semi-arid regions, which comprise nearly 80% of the land cover, which is inhibited by roughly 20% of the entire Kenyan population. High levels of poverty also impact the coastal region that has been receiving fewer resources in decades before the inauguration the 2010 Constitution. More than sixty percent of the Kenyan population are youths below the age of thirty, and the populace under the age of fourteen alone quantifies to 43%.
Technological Features
The world has experienced fast and dynamic technological advancements and its impacts the manner in which businesses and organisations promote their services and products. Technical aspects influence marketing, as well as overall management in the following approaches, innovative ways of creating services and products, modernised means of supplying products and services, in addition to the new procedures of communicating with the targeted market segments.
In contrast to the 1990s, the state has made some substantial advancements in the arena of technology, mainly the information and communications segment. With the essential aid of innovative communication companies such as Safaricom, the leading telecommunications company in East Africa, the government has been able to implement e-government services, mobile money transfer, and promotion of technological innovation in the country, which is the primary way the company might invest in the country.
The influence of technology on people has impacted legislation, which concentrates on protecting an individual’s confidentiality to ensure that companies have attained an individual’s approval before messaging or contacting them. Telecommunication companies such as Vodafone ought to provide consumers with thoughtful reflections to the type and nature of conceivable legislation, which governing authorities might inaugurate to confine what is commonly regarded as the treacherous advancement of the fast development of modern technology.
Environmental Features
Environmental aspects have become an essential concern as a result of the increasing scarcity of pollution targets, raw materials, conducting business activities as a sustainable and ethical company, as well as targets implemented by governments associated with the carbon footprint. These are just some of the critical subjects that sales managers and experts are experiencing within this facet. Moreover, customers are demanding the authenticity of the services or products and that they are sourced ethically, and if probably from a maintainable foundation.
Kenya’s typical weather differs from semi-arid within the Northern part of the state to the high rainfall regions of western, coastal and central areas. Thus, this diversity in weather patterns, attached with the increasing rates of urbanisation and rural-urban migration, has facilitated the rise of varied ethnic backgrounds within the state, each with its distinctive way of life and developmental needs and challenges. The equatorial climate in the country has given rise to beautiful flora and fauna that is a key tourist desirability for individuals from different parts of the world. Thus, this overseas populace is a vital foundation of general income for the state. Similarly, it has occasioned in a prosperous traveller destination and expeditions in the state. At this point, Vodafone can market products and services that appreciate the environmental diversity of Kenya.
Legal Features
Legal aspects consist of equivalent prospects, customer s’ civil liberties and regulations, product well-being, marketing principles, product classification, health and safety considerations. Businesses and organisations ought to comprehend and appreciate what is and what is not lawful to ease trade. If a firm conducts its business activities in the international market, this becomes a complicated subject to access foreign markets since each state has its unique set of rules and regulations.
Kenya has a universal law that is identical to the British mandate, but Kenya has a written constitution. There are also structures of Tribal and Sharia laws, which are often employed to settle disputes between people in a given ethnic community or between Muslims (Ombija, 2019).
The laws governing intellectual property is the remedy for any telecommunication organisation that markets technological services. Such companies ought to be supplied and protected to ensure that the foreign direct investment does not collapse or make losses. Vodafone conducts its business activities in a competitive market system where it is challenging to generate unique products or services. Consequently, Vodafone ought to guarantee that they remain vigorous by producing and marketing innovative services or products that hard to imitate and affordable.
Market-Entry Options
A market entry or location examination goes further than a prospective scrutiny and scrutinises the market, business rivalry, and the external factors. As a result, there different and unique techniques that a company can employ to access a foreign market (Grünig, and Morschett, 2017). The significant component of productively entering a new region is selecting the exceptional market entry strategy. There are numerous unique prospects for implementing this, from indirect approaches such as making use of supplier or licensing to foreign direct investment. The principal inaccuracy of market entry strategies is assuming that what was successful in other markets will work effectively in a new one. The following are market entry strategies, which might be utilised by Vodafone.
Direct exports
Direct exports are instances when a company promotes, sells, and delivers its services and goods directly to consumers. In the condition of services, a company negotiates, contracts, and works directly with customers. By circumventing the interference of intermediaries, the company can get higher returns on its foreign investment, formulate affordable rates, and become more competitive. Additionally, the firm can have a productive direct correlation with its consumer base.
Indirect exports
Vodafone can decide to export incidentally via an intermediate like an agent, a trading house, a foreign supplier, or a representative such as an export management company (EMC). Based on the prearrangement, they might complete a few legworks on behalf of the company, but a substantial cost. Essential merit that the company can benefit from indirect exporting is that the commercial exporter undertakes all the credit and sales risks. Furthermore, the intermediary manages all formalities associated with recording, distribution preparations, commercial, credit, and political uncertainties, in addition to getting licences from the governing authorities, etc. As a result, the company is relieved from the botheration of observing the monotonous formalities contained in the export undertakings.
Alliances and partnerships
Selecting to create a partnership or alliance with a local or foreign organisation is another essential approach to access an overseas market structure. Affiliating with an international firm might offer the necessary proficiency, technological advancements, market accesses, and capital, which a company might be capable of affording on its independent capacity — allying company’s operations and activities with a Kenyan company whose services or products that match with Vodafone’s provisions to reduce operational costs via joint marketing procedures or the involvement in similar distribution mediums.
The most suitable market entry mode for the company is alliances and partnerships since Vodafone can benefit from the employment partnerships and alliances by creating economies of scale, which refers to cost advantages that the firm attains from intensifying and managing more substantial volumes of supplies to the targeted market share. When orders increase in capacity, dealers and distributors tend to offer the company considerable discounts, that allows the firm to reduce production and operational costs, thus enabling the company to save money. As a result, in commercial alliances, this might also consist of access to extensive marketing mediums, that the firm might not be able to meet its foreign expenses without the partnership. Cost reductions might be an outcome of joint ventures like research and development.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is a commercial practice, which is based on the reach that facilitates the direction of how a company such as Vodafone splits its consumer base into minor, more convenient units according to the shared common ground. However, customers in each consumer base share the same traits, which companies can leverage to enhance their marketing, sales, and promotional efforts (Cross, Belich, and Rudelius, 2015). Rezaei, (2015) argues that the primary motive of market segmentation is that companies can innovate and introduce a more personalised message, which will be received effectively. Thus, this is valuable for businesses who may have a service or service in the market structure, which reinforces numerous benefits or employs for varying forms of consumers.
Price segmentation ought to be the main priority within the market segmentation of Vodafone in order to fulfil the needs and preferences of the potential target customer segment, which is the Kenyan telecommunications industry. Dissimilarities in regards to earnings in the Kenyan economy is an essential determinant for dividing the market with price quantities. If personal income ranges from low to high, the validation endures; thus, Vodafone ought to create and distribute innovative products and services along with affordable rates. As a result, this form of price segmentation is sound and epitomised by the mixture mobile products and services marketed by the company from the most expensive to the most affordable, which ensure a valuable range to stimulate profitability from social units.
Porter’s Generic Strategy
It is also referred to as Porter marketing techniques, which are planned tactics utilised by businesses and organisations to access a given market and after entry, then maintain resilient merit over business competitors (Ouma and Oloko, 2017). It might also be intricate as “the primary purpose of an organisation is to draw consumer interest within the industry where it conducts its business activities, and its secondary aim of the business is to position itself within that market structure. A company locates itself, its services, or products by the assistance of its strong points. The strengths can be product attributes and features or might be a competent sales representative, or a well-organised marketing strategy. Moreover, the substantial aspects of a business lie within its positioning and cost advantage. Porter’s generic strategy consists of three main approaches, which include cost leadership plan, differentiation plan, and focus project.
Cost management strategy
Cost management promotion approach employed to access an emerging market by making use of the cost of a business’s services or products. Thus, this could be probable when a firm advances effectiveness and reducing production and operational costs, an organisation will be able to provide its unique services or products at affordable rates to its consumer base, which makes the business more attractive compared to its commercial rivals. The strategy might be sufficient for companies that plan to access a market that is highly dominated by a few high-cost firms. To uphold the competitive advantage, Vodafone needs to frequently advance its amenities and products, while sustaining cost management.
Differentiation Strategy
Businesses in the modern era to survive within a saturated market structure in addition to resilient market competition. Therefore, this form of Porter’s generic strategy translates to the development of such amenities and products, which offer distinctive traits that are valuable to the targeted market segment. Prosperous companies such as Vodafone ought to be design and generate services and products that are unique and stand in a competitive market.
Focus Approach
It employs the ancient “divide-and-conquer” concept, and it consists of the segmentation the targeted consumer base into specific market segments. Then a firm ought to create detailed commercial marketing plans for every market segment. Simple words that focus approach targets a given consumer base should apply both differentiation and cost management strategies.
Accordingly, since businesses and organisations have their predesigned and predefined aims and purposes, the company ought to accomplish them by the application of the Porters generic strategies that offer a significant platform for business prosperity.
Conclusion
Marketing and promotional strategies assist companies in making use of the essential skills of their personnel and stakeholders, which aids businesses to come up with innovative ways of increasing sales and reinforcing consumer services. The primary purpose of this account was to realise and analyse the essential factors that are involved in the management of marketing strategies of commercial entities when they concentrate on investing in foreign markets. The company we nominated to generate the tactical marketing structure was Vodafone. The market examination was conducted of the selected market, which is Kenya to study the prospects and vulnerabilities manageable for our telecommunication products and services in the overseas market. Subsequently, bearing in mind the external factors of the targeted market structure, beneficial strategies for marketing blends were articulated, and a market entry strategy was designated to enter the rationalised global market structure.
Students working on case studies or might need academic help, might find our custom Case Studies Writing Services helpful.
Please make sure you check our marketing writing help:
– Marketing dissertation writing services
– Marketing essay writing services
– Marketing assignment help
Also look at some of our business services
– Business Essay Writing Service
– Business Dissertation Writing Services
– Business Report Writing
– Business Assignment Help
– Business Planning Writing Service
– Business Assignment Writing Service
Here you can check some of our dissertation services:
– Dissertation Writing Services
– Write My Dissertation
– Buy Dissertation Online
– Dissertation Editing Services
– Custom Dissertation Writing Help Service
– Dissertation Proposal Services
– Dissertation Literature Review Writing
– Dissertation Consultation Services
– Dissertation Survey Help






