Preventive Measures on Falls among Elderly Patients
Introduction
Falls among mentally ill geriatric and dementia patients occur and result in injuries and sometimes death. Hospitals have reported that many falls happen to dementia and geriatric psychiatric patients. National Council on Aging (NCOA) states that one out of four Americans of 65 or older falls every year. People leaving with dementia and Geriatric psychiatric patients are at high risk of loss due to drug treatments, psychological factors, impaired vision, and physical fitness decline. Many medications used in a geriatric mental health setting can affect a patient’s balance, motor skills, coordination, depth perception, and some are hypersensitive to lights and sounds. Many of our patients have had changes in their vision and hearing due to age, which makes them feel less safe and vulnerable. External factors include non-moderated lighting, faulty equipment, and failure to used assistive equipment correctly. There is a need to forge strategies to keep public health safe for geriatric psychiatric patients. This research will provide guidelines for specialized assistance to geriatric psychiatric and dementia patients. Which will improve and implement various nursing interventions to avert falls.
Goal statement.
The need to orchestrate and implement a sustainable and patient-friendly intervention to prevent falls in health facilities is overwhelming. Saccomano and Ferrara (2015) insist that specialized nursing care is needed. Collaborative with implementable strategies on all departments involved in the care of the elderly, especially psychiatric and dementia patients. The project aims to maximize interventions to develop the value and safety of health care services and stop falls among people living with dementia and elderly patients.
Objectives of the project
The project’s objective is to determine the hospital’s current interventions to prevent falling among dementia and geriatric psychiatric patients. Further, to check the available policies and guidelines used by nurses in fall prevention. It is harmonizing the interventions and approaches to construct improved policies for dementia and geriatric patients’ prevention and care. Usage of additional educational materials to be used by nurses in the handling of the patients.
The project aims at learning the roles and responsibilities of occupational therapists in taking care of geriatric psychiatric patients. The therapists are conscious of the frequency of falls amongst the aged patients; hence, the therapists teach each patient procedures that can make them avoid falls. The therapists possess diverse understanding and skill collections to deliver effective intermediations inside the geriatric mental health situation. However, many factors should be considered concerning fall risk prevention, especially when working with patients with dementia and mental illness.
The project uses data from the hospital about the number of falls that occur, causes of the falls, and the number of times a specific type of fall occurs. It considers the patient’s age, medication in use, condition, and assistive devices in use. The data is used to gauge it against current care policies by the hospitals. Nurses will be interviewed to get information on the causes of the falls and better ways to prevent falls among dementia and elderly psychiatric patients.
The collected information is analyzed and compared against current guidelines. Additional information sorted out from implemented policies from journals and books is synthesized in the report. Interviews from professionals associations on better ways of intervention and prevention of falls by patients are done. The data collected is then harmonized to create a final report and recommendation. Improvement and creation of better guidelines for the prevention of falls among elderly psychiatric patients.
Purpose Statement
The purpose of this research is to determine the hospital’s current interventions on prevent falling among geriatric psychiatric patients and offer sustainable and adoptable recommendations and guidelines to the nurses and the hospital staff to help prevent falls.
Literature review
Falls among geriatric dementia and psychiatric patients can be avoided by effective and timely rounds done by nurses, according to Daniels (2016). Geriatric psychiatric patients require timed and specialized care by nurses to ensure their safety in the hospital. Practical and safety-oriented guidelines give the patients a safety assurance when in need of help that might prevent falls, Brosey (2015) ascertains.
Kruschke and Butcher (2017) emphasize the need for periodic review of safety guidelines in hospitals that prevent elderly patients from falling. Brosey (2015) further explain the need for effective interventions that promote satisfaction among patients. The evaluation of the interventions will provide outcomes that ensure quality nursing services are provided alongside adequate measures. They promote evidence-based interventions. The need for creation and improvement of safety measures to curb falls in hospitals. The rise of falls in hospitals among elderly patients has made the health sector invest in continuous evaluation and safety measures to prevent falls.
According to Saccomano and Ferrara (2015), fall prevention among elderly patients is a significant concern in the health sector. The interventions need periodic reviews and improvements. Elderly patients require specialized professional care, especially psychiatric patients.
Patients leaving with Dementia should be given close surveillance and care. Information and common reminders should be kept at a common area for easy reach when needed (Kosse et al. 2015). It is useful to label objects and stairways with different contrasting colors to enable them differentiate top and bottom of the stars. The authors explain the need for safety companions for dementia patients.
Falls among adults with dementia is a concern and strategies should be formulated to prevent the falls (Fernando et al 2017). A strategy such as keeping the patients busy with activities so they are immobile can be used. However, the authors insist on the need to expand and provide knowledge and skills needed for effective interventions to support and prevent these unique type of patients. The caregivers should be equipped with techniques that are supportive of specific and special services they provide to elderly ill dementia patients.
Methodology,
The research will engage the nurses that work in the dementia and geriatric psychiatric patients’ department. Since they are a smaller number, oral and written interviews will be used. Questionnaires will be used along with verbal engagements. Focus groups will also be used to give room for discussions and offer feedback about the research (Snyder 2019). Where necessary, the nurses will help them ask few essential questions to the patients—aimed at involving them on ways to prevent the falls. The support staff will be interviewed and engaged in providing more information. They hold different perspectives from the nurses.
The questionnaires will be direct and simple questions to allow the interviewee to give a more evident answer (Palinkas et al. 2015). The nurses and support staff will be provided with informative books that will broaden their knowledge of modern fall prevention methods. The books will prepare them with ideas to bring up during discussions and final meetings.
Additionally, the hospital representatives will hold an open discussion meeting to allow all parties to express their views. The interviews will be done in the conference room, while the questionnaires will be given and collected the following day. The data collection process will take two weeks.
Resource.
The research will need three personnel to help with interviews and two data analysis personnel. They will consist of people well conversant with health care, especially senior care. The project will require the hospital management’s approval to conduct the interviews since the interviews will be shown in the hospital’s conference room. Necessary support from the administration will be required in the provision of documents needed for evaluation and review. The approvals will allow our personnel access to current hospital policies and guidelines to prevent falling among geriatric psychiatric patients.
A laptop for data recording, analysis, and storage is required. The computer will enable mobility around the school while making it easy to record notable observations. Books and journals are needed for referencing and analysis. The scholarly items are crucial in providing and extracting information on ways to improve the prevention of falling in hospitals. Books and journals offer guidance in the health sector, making it easy to make references from credible and well-known sources. The project requires books and papers for record-keeping, printing, and photocopying services. These items will be used to prepare the questionnaires, the plans, and the reports’ writing. The whole documentation process requires the constant taking of notes and recording of observations.
Evaluation
The evaluation process is progressive. The purpose of the evaluation process is to gather and analyze the program’s information (Palinkas et al. 2015). This information is used to determine the various advanced levels of the implementation of the program. The evaluation helps improve the efficiency of the program and ways to maximize the performance of the program. The evaluation process has formative and summative stages.
Formative evaluation of the project will be done after sixty days upon adopting the program’s recommendations. The purpose of the assessment is to allow appropriate identification and revision of the implementation process. The information helps in the improvement of the implementation of the interventions. The evaluation will be done through systematic observation: random checks will be done to observe the program’s implementations.
Evaluation, analysis, and comparison of records to examine if there is a difference. The statistics of falls occurring among the patients from previous times before implementing the program and after the implementation. The difference in recorded figures is stored. Discussion with the nurses and staff to understand if the program is progressive and offers improvement. The engagements will help determine whether the set goals are met: prevention and decrease in the number of falls among geriatric psychiatric patients.
The acquired results from the formative evaluation will be used to determine the program’s success (Palinkas et al. 2015). The results will allow the hospital to decide whether to maintain or harden the grip on the program’s implementation. The data will help examine, address and capitalize on the program’s implementation. Additionally, the data will help the hospital identify areas of improvement while still implementing the program.
Summative evaluation will be carried out when the program is fully functional and has achieved its objectives. The summative assessment will be conducted through interviews, assessments, documents review, and focused discussions. Interviews will be conducted with nursing personnel to give a first-hand appraisal and feedback of the program. Focus groups will be carried out to provide detailed insight into the program, its effectiveness, and the achieved goals. Focus groups will be used in a time-efficient manner to get a more collective view of the program. Assessments will provide a more explorative outcome from participants since they will give clear perception, understanding, and knowledge about the interventions (Snyder 2019). Documents and data stored by the hospital will be used to track and reveal the project’s outcome. The data provide numerical representation that is easy to interpret and make conclusions.
The data from the summative evaluation will be used to determine the effectiveness of the program. The evaluation data will be used to set trends and construct ways to improve the interventions further, preventing falls among geriatric psychiatric patients.
The evaluation process, both formative and summative, provides essential information and feedback from hospital staff. The feedback information is used to determine the effectiveness of the program. The determination gives room for improvement and effective adjustments to be made, and the adjustments ensure the programs’ interventions are implemented effectively. The evaluation process allows seamless implementation progress (Palinkas et al. 2015). The nursing personnel and hospital staff offer feedback on possible issues they face during the progress. The feedback helps in making the process patient and staff friendly.
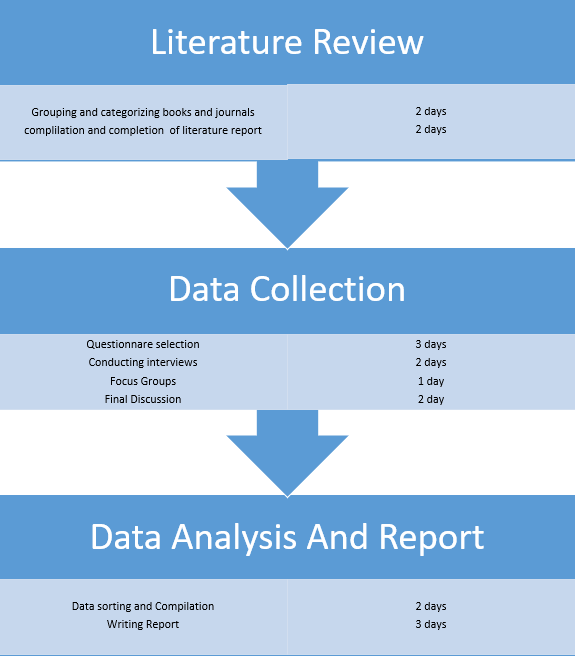
Graphic Timeline
The first stage involves categorizing and researching available books and journals. The setting in includes identifying relevant books that the program will need in the acquisition of information. Later, they are categorized into relevant groups to allow quick revision when required. The journals and books are reviewed in support of the project.
Data collection involves selecting and preparing identified questionnaires, conduction of interviews, and formation of focus groups (Palinkas et al. 2015). The questionnaire is distributed to nurses and hospital staff. Concurrently, the interviews are conducted, and the focus groups are formed. The final discussion with various representatives is the last part of data collection. The final stage involves data sorting and compilation, and later the writing of the final report.
Conclusion
Falls among elderly ill patients are the leading causes of injury; in most hospitals, falls happen to people leaving with dementia and/or geriatric psychiatric patients. The prevention of falls among these patients is a health concern. There is a need for improvement of measures to prevent falls. Current guidelines and policies need reinforcement, while other improved measures need to be put into place. This project will provide professional patient-friendly care to geriatric psychiatric and dementia patients. It aims at implementing improved and quality nursing interventions that can prevent falls in the hospital. It aims at harmonizing the current guidelines and policies to bring better measures to aid the prevention of patient falls in the hospital. The project’s objective is to construct an educational manual that will give nurses better guidelines to professionally take care of the patients to prevent geriatric psychiatric and dementia patients from falling. Through data collection, compilation, and analysis, the research creates a program to improve the hospital in preventing falls. It offers a roadmap of data collection to the final stage of follow-up evaluation.
There is a concern to educate, improve, and implement better professional nursing care to dementia and geriatric psychiatric patients, who are always at risk of falling in hospitals.