Authors: Yusuf Iftekhar, Khuram Khan
P5: Select a variety of techniques to undertake a situational analysis of a given organization
(Sudhakaran, 2022)
SWOT
Strengths
Since Dave Lewis took over as CEO, Tesco has gone from losing £6.4 billion in 2015 to making a profit of £1.9 billion in 2020. According to Kantar (2021), Tesco has a 26 percent share of the British grocery market. Sainsbury’s, one of Tesco’s key competitors, controls 14.9% of the market. Therefore, there is no competition for Tesco’s market supremacy. During the three months ending in September, Tesco gained 10.5% despite the global pandemic. Tesco increased its online sales, contributing to the gain (Sudhakaran, 2022). An indication of the scope of the growth is Tesco’s decision to hire an additional 16,000. Couchbase has awarded Tesco the prize for best Advanced NoSQL Architecture in the EMEA region. Tesco has been honoured for strengthening its distribution strategy in the face of COVID-19-related shortages. Couchbase states that Tesco evaluated about 2 billion unique variations of an app.
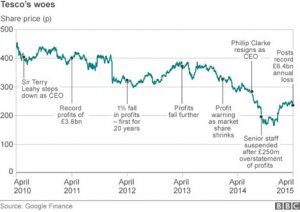
Figure 1: Graph showing £6.4 billion loss in 2015
Weaknesses
Tesco asserts stringent quality control measures, yet an upset customer complaint reveals room for improvement. Although it should never have occurred, Tesco has apologised for selling birds that had been inappropriately fed. In an effort to prevent shortages caused by panic buying, Tesco has begun to limit the sale of certain items. Tesco has reassured its consumers that it has enough stock to meet typical demand. Tesco was fined £175,000 because they sold food 15 days over its expiration date (Sudhakaran, 2022). Tesco took immediate action upon becoming aware of the incident, removing the offending goods and instituting measures to prevent a recurrence. Any infractions of food safety laws by Tesco would have far-reaching implications due to the breadth of its distribution network. After uncovering safety flaws and faults that risk consumers, for instance, Tesco initiated urgent food recalls.
Opportunities
People are not venturing outside as much as before because of precautions taken to halt the spread of COVID-19. These rules are largely responsible for the proliferation of supermarket delivery services online. Ocado saw a 76% increase in its online sales as a result. It makes sense for Tesco to take advantage of the trend. The Guardian reports that the employment rate for young adults (defined as those 16–24) has dropped dramatically (Sudhakaran, 2022). Tesco might benefit from the current high unemployment rates since supermarkets are one of the few industries where people can still find work. Plant-based protein sources are expected to generate a global market of £4.1 billion by 2020. Changing to a plant-based diet instead of animal products is good for business. Tesco plans to take advantage of this gap in the market by tripling the number of meatless products it offers by the year 2025. Unsold items having a reasonable amount of time left on their expiration date are kept at communal supermarkets until they may be sold. To cut down on food waste and hunger, the supermarket then sells the extra food at affordable costs. Tesco cares deeply about both issues; hence the company should take an active role in the project.
Threats
The free trade agreement with the EU might be placed on hold if the United Kingdom quits the union. Should the UK’s commerce with the EU be suspended, it would have to do so following the World Trade Organization’s guidelines. Taxes, customs checks, and quotas might rise when new rules are implemented. About 80% of supermarkets’ imported food supply will be affected by Brexit. The disruption Brexit would cause to the flow of goods imported from the EU to the UK at the ports of entry will significantly impact Tesco’s supply chain (Sudhakaran, 2022). Tesco’s newly appointed CEO, Ken Murphy, expects challenging conditions throughout the winter holidays. The major causes for alarm are the ongoing economic downturn and the subsequent erosion of consumer confidence and spending. Customers of Tesco face more financial instability as a result of growing unemployment. Tesco’s swift move to online service allowed it to thrive at a time when many huge firms collapsed. Meanwhile, the costs of the coronavirus reached £533 million. The valuation of Ocado, a UK supermarket chain, has surpassed that of Tesco. This may indicate a major change in the market.
Table 1: SWOT Analysis
| Strengths
· Tesco has gone from losing £6.4 billion in 2015 to making a profit of £1.9 billion in 2020. · Tesco has a 26 percent share of the British grocery market. · Tesco gained 10.5% despite the global pandemic. · Couchbase has awarded Tesco the prize for best Advanced NoSQL Architecture in the EMEA region. · Tesco has been honoured for strengthening its distribution strategy in the face of COVID-19-related shortages. |
Weaknesses
· Tesco asserts stringent quality control measures, yet an upset customer complaint reveals room for improvement. · In an effort to prevent shortages caused by panic buying, Tesco has begun to limit the sale of certain items. Tesco has reassured its consumers that it has enough stock to meet typical demand. · Tesco was fined £175,000 because they sold food 15 days over its expiration date
|
| Opportunities
· Ocado saw a 76% increase in its online sales as a result. It makes sense for Tesco to take advantage of the trend. · Tesco might benefit from the current high unemployment rates since supermarkets are one of the few industries where people can still find work. · Changing to a plant-based diet instead of animal products is good for business. Tesco plans to take advantage of this gap in the market by tripling the number of meatless products it offers by the year 2025. |
Threats
· The free trade agreement with the EU might be placed on hold if the United Kingdom quits the union. · The disruption Brexit would cause to the flow of goods imported from the EU to the UK at the ports of entry will significantly impact Tesco’s supply chain. · Customers of Tesco face more financial instability as a result of growing unemployment. · The valuation of Ocado, a UK supermarket chain, has surpassed that of Tesco. |
Five C’s
Company
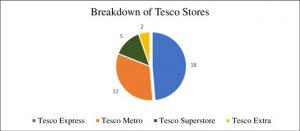
Tesco is an international supermarket chain headquartered in the United Kingdom. Over a century in business is a significant advantage. It operates in several nations and weekly provides services to millions of people. The company operates many supermarkets, including the Tesco superstore, Tesco Metro, Tesco extra, and Tesco Express formats. Tesco controls 27 percent of the United Kingdom’s supermarket market (Kantar, 2021). With online sales doubling by 2020, the company saw a boost in profitability. It has a variety of committees, including the Executive Committee and the Board Committee, to operate its activities smoothly. Nonetheless, it has been impacted by controversy on several occasions. For example, in 2014, it settled an accounting scandal case by agreeing to pay a £120 million fine.
Figure 2: Tesco Stores
Customers
Tesco bases its business decisions on what it believes its consumers want. Client service is one of the company’s three main focuses (Tesco, 2021). The goods and distribution methods make up the other two pillars. When providing the finest service possible, Tesco places a premium on hearing from its consumers. Tesco has open and regular dialogue with its clientele. It averages over 15 million weekly email deliveries to them. The company shows its thanks by frequently sending them Clubcard coupons (Tesco, 2021). Consumers in the UK are less satisfied with it than with some of its rivals.
Competitors
Competition for Tesco in the United Kingdom comes from supermarkets, including Aldi, Lidl, Co-op, Morrison’s, Sainsbury’s, and ASDA. As a result, it employs various techniques, such as price matching with Aldi, to ensure its success. Lidl, Aldi, and other international supermarket behemoths, including SPAR, Walmart, Carrefour, CBA, and Penny Market, all pose new threats to its international expansion.
Collaborators
Tesco has tens of thousands of key partners and suppliers. Suppliers are broken down by region: “UK own label suppliers,” “ROI (Republic of Ireland) own label suppliers,” “Branded suppliers,” “CE (Central Europe) own label suppliers,” and “Global growers.” Unilever, Princes, PepsiCo, Nestle, Kellogg, General Mills, and Coca-Cola are among its most prominent brand-name suppliers. Tesco’s connection with its suppliers and key partners is crucial to its success. Tesco has been detected postponing payments to suppliers to raise its profits, despite the dependability of the alliance. To stay competitive with discounters like Lidl and Aldi, it had also asked for price cuts from its suppliers, which alarmed many of those providers (BBC, 2020).
Climate
The business’s operations are affected by a variety of macro variables. For selling expired food in Birmingham, UK, shops, for instance, the company was fined £7.56 million (Sky, 2021). The ethnic market is rapidly expanding in the United Kingdom and other industrialised nations; thus, the store caters to it by stocking a broad range of items. It caters to shoppers of many income levels by stocking its well-known brand names.
Figure 3: Tesco Fined
Table 2: Five C’s
| Company
|
· Tesco is an international supermarket chain headquartered in the United Kingdom.
· It operates in several nations and weekly provides services to millions of people. · The company operates many supermarkets, including the Tesco superstore, Metro, Tesco, and Tesco Express formats. · It has a variety of committees, including the Executive Committee and the Board Committee, to operate its activities smoothly. |
| Customers | · Tesco bases its business decisions on what it believes its consumers want.
· When providing the finest service possible, Tesco places a premium on hearing from its consumers. · Tesco has open and regular dialogue with its clientele. It averages over 15 million weekly email deliveries to them. · The company shows its thanks by frequently sending them Clubcard coupons |
| Competitors | · Competition for Tesco in the United Kingdom comes from supermarkets, including Aldi, Lidl, Co-op, Morrison’s, Sainsbury’s, and ASDA.
· Lidl, Aldi, and other international supermarket behemoths, including SPAR, Walmart, Carrefour, CBA, and Penny Market, all pose new threats to its international expansion. |
| Collaborators | · Tesco has tens of thousands of key partners and suppliers.
· Unilever, Princes, PepsiCo, Nestle, Kellogg, General Mills, and Coca-Cola are among its most prominent brand-name suppliers. |
| Climate | · The business’s operations are affected by a variety of macro variables.
· The ethnic market is rapidly expanding in the United Kingdom and other industrialised nations; thus, the store caters to it by stocking a broad range of items. |
Porters 5 Forces
Supplier power
Tesco works with thousands of vendors worldwide and 2,500 in the UK alone. There are many vendors like these, so they cannot threaten Tesco. In order to boost its profit margins, Tesco negotiates aggressively with its suppliers. The fact that Tesco has been charged with forcing its suppliers into decreasing their pricing is nevertheless important to note. Their methods of supplier consolidation have prompted comparisons to the mafia, and thus, some have adopted that word to describe their behaviour (Poulter, 2016).
Buyer power
Tesco’s in-store and online offerings attract tens of millions of consumers every week (Tesco, 2020). Buyers in the UK have little leverage since they are disorganised, and they would not be better off at supermarkets like Asda and Sainsbury’s. Tesco is drawn to the retail industry as a result. However, some analysts claim that because there are so many discount retailers vying for the same customers as Tesco, including Aldi, Lidl, and Poundland, UK grocery shoppers have a significant advantage. This necessitates cheap pricing, which cuts into Tesco’s profit margins.
Competitive rivalry
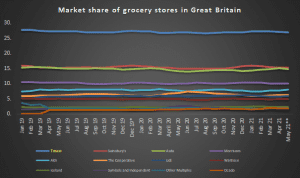
Among the biggest UK supermarkets, Tesco has a lot of competition. These competitors put a lot of money and effort into advertising. Tesco may be the market leader, but it is still up against formidable rivals. It’s no secret that the price wars between Aldi and Lidl are hurting Tesco’s bottom line. In order to deal with the issue of increasing competition, Tesco has been looking at suitable solutions. For instance, in 2018, the budget grocery store Jack’s was launched to take on market leaders Aldi and Lidl. Nonetheless, it has failed to meet expectations, as seen by dismal sales, employment losses, and fewer new locations than anticipated (Wood, 2019).
Figure 4: market share of grocery stores in the Great Britain
Threat of substitution
Tesco provides its consumers with a diverse selection of goods. Alternatives to most things are also available for purchase there. It offers both margarine and butter for purchase. It also offers milk concentrate, fresh milk, and dry milk powder. Therefore, it is simple to conclude that competition from other suppliers is largely unimportant to Tesco.
Threat of new entry
Due in large part to the high initial investment needed, new competitors in the UK grocery sector are a minor concern. Because of its unique skills, profitability, and size, Tesco is well-protected from potential new competitors. Potential rivals in the UK supermarket business could lack the capital, distribution channels, and knowledge to enter the market.
Table 3: Porters 5 Forces
| Supplier power
|
· Tesco works with thousands of vendors worldwide and 2,500 in the UK alone.
· There are many vendors like these, so they cannot threaten Tesco. · In order to boost its profit margins, Tesco negotiates aggressively with its suppliers. |
| Buyer power
|
· Tesco’s in-store and online offerings attract tens of millions of consumers every week (Tesco, 2020).
· Buyers in the UK have little leverage since they are disorganised, and they would not be better off at supermarkets like Asda and Sainsbury’s. |
| Competitive rivalry
|
· Among the biggest UK supermarkets, Tesco has a lot of competition.
· These competitors put a lot of money and effort into advertising. · The budget grocery store Jack’s was launched to take on market leaders Aldi and Lidl. |
| Threat of substitution
|
· Tesco provides its consumers with a diverse selection of goods.
· It also offers milk concentrate, fresh milk, and dry milk powder. Therefore, it is simple to conclude that competition from other suppliers is largely unimportant to Tesco. |
| Threat of new entry
|
· Due in large part to the high initial investment needed, new competitors in the UK grocery sector are a minor concern.
· Because of its unique skills, profitability, and size, Tesco is well-protected from potential new competitors. |
D2: Evaluate the extent to which the business environment affects a given organization, using a variety of situational analysis techniques
Based on the given information above, it seems that Tesco is a company that can adapt to changes in the business environment relatively well. In the past, Tesco has responded to changes in the business environment by expanding its online presence, increasing its workforce, and improving its distribution strategy. Tesco will likely continue to respond to future changes in the business environment in a similar manner. In response to the global pandemic, Tesco increased its online sales and added 16,000 workers. They also won an award for their dedication to improving their distribution strategy. In response to Brexit, Tesco has pledged to triple their sales of meat substitutes by 2025. They have also started a project to store unsold goods in social supermarkets (Sudhakaran, 2022). Also, TESCO could respond to future changes by adapting its business model. For example, if trade barriers are erected between the UK and EU, TESCO could source more goods from UK suppliers. This would help to avoid the higher tariffs on goods imported from the EU. TESCO could also focus on providing more value for money to attract customers looking for cheaper alternatives.
It is reasonable to expect that TESCO will continue to be a major player in the UK food market, regardless of what changes occur. One potential impact of leaving the European Union is that TESCO could become less competitive, as tariffs and other trade barriers make importing food from other countries more difficult. This could lead to higher consumer prices, as TESCO may need to raise prices to offset the increased cost of doing business. Additionally, TESCO could lose access to certain EU-based suppliers, decreasing the variety of products available in stores. Alternatively, leaving the EU could positively impact TESCO, as the UK would have more control over its food standards and regulations. This could allow TESCO to source cheaper ingredients from within the UK and give it more flexibility to tailor its products to the needs of UK consumers. In addition, leaving the EU could open up new markets for TESCO, as the UK would no longer be bound by the trade agreements that currently restrict its exports. Overall, the impact of leaving the EU on TESCO is difficult to predict, as several potential outcomes exist. However, it is reasonable to expect that TESCO will continue to be a major force in the UK food market, regardless of the specific changes that occur.
This could impact TESCO’s market share, as customers may turn to other retailers who can easily source their food. TESCO would need to adapt its business model to remain competitive, which could involve investing in more local suppliers. This would likely have a positive impact on TESCO’s customers, as they would be able to access fresher, more local produce. In the long term, leaving the European Union could be a positive move for TESCO if it can successfully navigate the challenges that come with it.
P4 and M3: Internal, External and Competitive Environment on Tesco
Introduction
The retail industry in the United Kingdom has recently expanded and grown enormously. Tesco U.K. has been able to sustain its dominance in the U.K. retail business by concentrating on digitalization and ecological manufacturing while also catering to the demands of various demographics. Tesco must enhance its performance to maintain its position as the premier retailer in the U.K., notwithstanding its development. In this coursework component, I will investigate how the PESTLE analysis impacts my selected company, Tesco, by analyzing the internal, external, and competitive environments.
PESTLE Analysis
Political Factors
Many political factors have affected TESCO within the U.K. from 2018 to 2021. Minimum wage laws were changed within the country, which meant that TESCO had to start paying their employees more per hour based on their age. This knocked on their costs, which meant they had to increase the selling price for many of their products. Another political factor that impacted TESCO was that in 2018 Boris Johnson became prime minister and decided to make many changes to employment laws. Another even bigger political decision was made and came into effect: BREXIT, which was the decision and process of Britain leaving the European Union. This would impact TESCO and many different aspects of its business.
Economic Factors
The cost of labour is a major economic aspect that may impact U.K. supermarkets. Its yearly salary expense, for instance, is a staggering GBP 4.5 billion. For those above 25 in the United Kingdom, the minimum wage rate will rise by 4.4% in 2018. Tesco has lost millions of pounds due to this increase in price in the U.K. Tesco is affected not just by pricing but also by other variables such as costs and profitability. The organisation has to pay attention to the rising cost of borrowing money in the U.K. (Farooq, 2020). Costs will rise, prices will rise, and profits will fall. It has the potential to undermine the cost-leading positioning of the brand. The firm has done well in recent years thanks to two main strategies: diversification and expansion into overseas markets. It’s important to note that with its 27.7% share of the U.K. food industry, Tesco is still heavily reliant on the British market.
Figure 1: National Minimum Wage rates 2018
Social Factors
Supermarkets place a premium on equal rights inside their employee contracts. Tesco values its male and female employees equally since it carries items for both sexes. Consumers’ tastes and preferences in terms of what they buy are ever-evolving. People have tight schedules and want products delivered the same day, if not the next. The convenience of a store that sells everything they need is important to them. Tesco’s success depends on its ability to address the needs of its consumers in the United Kingdom; thus, the company must be aware of and adapt its services to these concerns (Farooq, 2020). Also in the spotlight is the connection between customer perceptions and attitudes and the demand for products and services. Customers are more worried about the health effects of obesity. Tesco has to consider the growing interest in and need for organic foods. Sixty-five percent of British consumers are repeat buyers, says a PWC study. In order to capitalise on this situation, Tesco has to get to know its consumers on a more personal level. During times of economic hardship, Tesco’s price selections are impacted by supply and demand and the average disposable income. For instance, Tesco’s pricing strategy may need to change if the pandemic causes widespread unemployment in the region since this would prevent many people from being able to buy the store’s higher-priced, higher-quality items.
Technological Factors
ICT, R&D, software, and e-commerce are all examples of cutting-edge practices and technologies that may impact businesses. Since then, technological advances have expanded the range of options available to businesses for managing their operations. Because of advancements in information and communications technology, businesses can provide more personalized services and make buying more convenient for their customers. A few years ago, Tesco had problems with customer service and the horsemeat incident. Tesco was given new chances through technological development to win back the confidence of its customers. Tesco sees technological progress as an opportunity and is quick to adopt new, improved business methods. In an effort to better serve their clientele, they have used RFID technology. It keeps track of inventory and removes it mechanically after sales (Farooq, 2020). This data is also useful for the store’s suppliers, who may use it to restock shelves as needed. Tesco has created PayQwid, its online mobile payment system, so consumers can pay as they choose. The app is used at 524 Tesco locations throughout the U.K., from London to Edinburgh. In order to use Clubcard and NFC technology, customers may download an app. Paid purchases also earn customers loyalty points. The “scan as you shop” system was created for shoppers who value efficiency above everything else. Individuals browse and use price tags to organise their purchases. Time and money are both saved as a result of this.
Figure 2: Workflow of RFID Workfolw
Legal Factors
The Competition Act 1998 is a key statute that affects Tesco since it outlaws any commercial activity or behavior that has or might have an adverse effect on competition in the United Kingdom. Tesco might feel the effects of competition regulations both directly and indirectly. They may take their case to Europe for approval, which would immediately affect their ability to combine with or acquire other firms without regulatory intervention. This government action would also have a knock-on effect of encouraging and boosting innovation because of the increased rivalry in these areas, which would drive down the prices of the products and services offered by Tesco. This rule has far-reaching consequences for Tesco since it prevents Tesco from growing via acquisitions while simultaneously opening the door for new firms to flourish without being stifled by established corporations like Tesco. This is problematic for Tesco since they want to expand its market share and become the dominant grocery chain (Farooq, 2020). The rising annual cost of doing business means that businesses must constantly explore new methods to boost their revenue to survive. Tesco has previously sought to prohibit property owners from renting out premises near its shops to competitors, although this was illegal and resulted in a warning for the company.
Environmental Factors
The term “environmental” may also refer to all external elements that affect a business. Nonrenewable resources cannot be replenished as quickly as they are used. It’s not going to last forever and is thus a limited commodity. Nonrenewable resources include fossil fuels like oil, gas, and coal. Because of the time and effort required to produce them, plus the fact that they would not run out for thousands of years, the price of these items will only rise as the years pass and they are used up. It negatively affects Tesco’s bottom line since oil prices are rising, and it’s expensive for suppliers to import oil from other nations (Farooq, 2020). Oil is one of Tesco’s most important items, and its price is expected to rise significantly due to inflation. For the time being, the effects of oil availability are negligible, and the minimum wage will rise in tandem with oil prices so that people can afford to buy it. As a huge retail chain, Tesco often has considerable negotiation leverage with its suppliers, allowing them to purchase their items at a discount.
Table 1: PESTLE Analysis
| Political Factors
· Minimum wage laws were changed within the country, which meant that TESCO had to start paying their employees more per hour based on their age. · Another political factor that impacted TESCO was that in 2018 Boris Johnson became prime minister and decided to make many changes to employment laws.
|
Economic Factors
· The cost of labour is a major economic aspect that may impact U.K. supermarkets. · Tesco has lost millions of pounds due to this increase in price in the U.K. · Tesco is affected not just by pricing but also by other variables such as costs and profitability. |
| Social Factors
· Tesco values its male and female employees equally since it carries items for both sexes. · Tesco has to consider the growing interest in and need for organic foods. · Tesco’s price selections are impacted by supply and demand and the average disposable income.
|
Technological Factors
· A few years ago, Tesco had problems with customer service and the horsemeat incident. · Tesco sees technological progress as an opportunity and is quick to adopt new, improved business methods. · In an effort to better serve their clientele, they have used RFID technology. · It keeps track of inventory and removes it mechanically after sales |
| Legal Factors
· The Competition Act 1998 is a key statute that affects Tesco · Tesco might feel the effects of competition regulations both directly and indirectly. · This rule has far-reaching consequences for Tesco since it prevents Tesco from growing via acquisitions while simultaneously opening the door for new firms to flourish without being stifled by established corporations like Tesco.
|
Environmental Factors
· Nonrenewable resources cannot be replenished as quickly as they are used. It’s not going to last forever and is thus a limited commodity. · Because of the time and effort required to produce them, plus the fact that they would not run out for thousands of years, the price of these items will only rise as the years pass and they are used up. · It negatively affects Tesco’s bottom line since oil prices are rising, and it’s expensive for suppliers to import oil from other nations |
Corporate culture
Corporate culture refers to how a company is set up and how people interact. When they are at work, they act and think differently and communicate differently. For instance, Tesco staff dress professionally and appropriately for the workplace, while Fridays are okay for casual clothes. They value every bit of assistance and want their staff to demonstrate this attitude toward their clients. They also have frequent meetings because they think workers must communicate well with one another.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
The value of CSR is not lost on individuals or businesses. CSR has historically been a deciding factor in whether businesses succeed (Botten, 2009). By investing in its employees, local community, and the country as a whole, a company may increase its marketability via CSR and increase its profits. A company engages in CSR when its leaders commit resources to improve society or help causes outside their own. As a result, Tesco’s name recognition might improve, and the retailer could become renowned not only for its competitive prices and wide selection but also as a kind community partner. Buying from an organization is a simple way for supporters to show their appreciation for the wonderful work it is doing in the world. The Irish branch of Tesco has made an effort to lessen the environmental impact of its operations by determining the extent to which its business generates greenhouse gas emissions and then taking the necessary steps to mitigate those emissions. Tesco benefits from this because it increases the likelihood that its stakeholders, such as customers, would stick with the company while it finds or develops a solution to lessen the impact on society.
Competitive Environment
Competition
In recent years, the fair-trade sector in Europe has seen a surge in popularity. The demand for fair-trade items is predicted to increase over the next several years because they help “disadvantaged producers in developing nations earn decent pricing for their goods” (Booth and Whetstone, 2007). In addition, green items are more popular among U.K. customers. The future of the fair-trade cotton industry seems promising because of this. There is not a great demand for Fair-trade items in the United Kingdom. Tesco may become a market leader in this sector by expanding its product offering to include fair-trade certified cotton goods. Currently, Tesco offers roughly a thousand items produced using fair-trade practices (Booth and Whetstone, 2007). However, in recent years, numerous companies have engaged in this industry, including Monsoon, Asda, and M&S (Edwards, 2010). Each rival uses a unique strategy to seize control of this new market. With this in mind, Tesco has to think outside the box to develop a strategy to give them an edge in this market.
Figure 3: The UK’s favorite supermarkets
Competitive advantage
Tesco as one of the global leaders in the grocery sector, Tesco has used various business strategies to ensure its continued success. Tesco has grown from its 1950s roots via organic expansion and strategic acquisitions to its current position as owner of more than 800 supermarkets (Tesco, 2022). Market observers disagree on how Tesco’s leadership has been able to compete successfully with other major grocery chains. This section seeks to analyse the major company structure, strategy, and operations that have made Tesco one of the kingpins in the grocery sector using numerous analytical models, including Porter’s Five Forces model and PESTLES.
Factors that influence competitive advantage
A variety of key success factors (CSF) that Tesco has established have contributed to the company’s longevity and prosperity in the retail industry. These elements are intrinsically linked to the organization’s beliefs, principles, and policies. Employee output, strategic management, and leadership are all crucial, as are efforts to improve the business’s operations and the level of service it provides to customers. Employees’ dedication to their customers, honesty, ambition, teamwork, and personal growth are all elements of their professional success. When fostering consumer loyalty, faith in the company’s employees is just as vital as the products or services. Teamwork ensures that staff pools their resources to provide superior service to customers. Decision-making, problem-solving, information sharing, and creative thinking are all boosted as a result. Leadership and management qualities that contribute to success include effectively analyzing data and making decisions.
M3: Assess the effects of the business environment on a given organisation
Looking at the PESTLE Analysis above, the first and most important or relevant factor for TESCO is social hence the company must avoid racial and regional discrimination, and their product selection is affected by the average size of their customers’ families. Economic factor is the second because Tesco’s consumers and workers are affected by employment and unemployment rates, and the company must consider inflation when making business decisions. The last factor is political since minimum wage laws were changed within the country, which meant that TESCO had to start paying their employees more per hour based on their age, and BREXIT is a big political decision that will have several impacts on TESCO’s business.
The two most important factors in the internal environment of Tesco are corporate culture and corporate social responsibility. Corporate culture refers to how the company is set up and how people interact with it. Corporate social responsibility refers to the company’s commitment to improving society. These two factors are important because they show how Tesco is dedicated to its employees and improving the world.
From the above, it is evident that Tesco has to maintain a competitive advantage to stay ahead of the competition. Factors influencing competitive advantage include employee output, strategic management, leadership, and efforts to improve business operations and service levels.