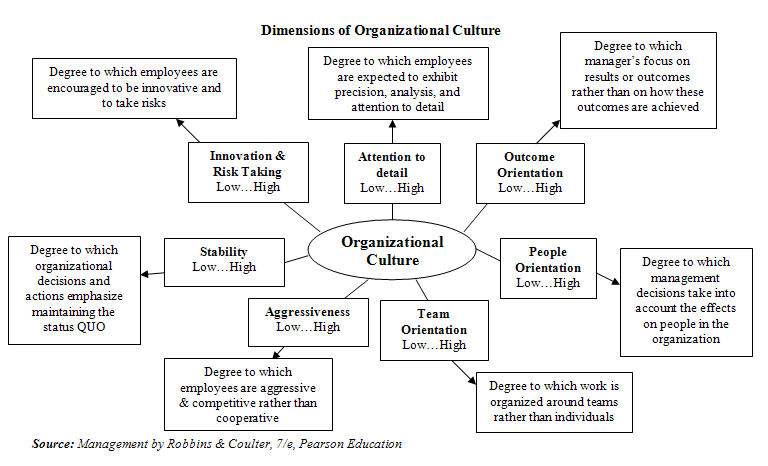
Organizational Culture Theory and Meaning
- The organization’s mission and vision.
Mission: To contribute to health, well-being and inspire hope by giving the best care to every patient through research, education, and integrated clinical practice.
Vision: The healthcare organization to provide the best and an unparalleled experience as the most trusted healthcare partner.
- Weaknesses that prevent the organization from achieving its mission and vision.
The cultural diversity of workers and patients may prevent the healthcare organization I am working with from getting the mission and vision fully running. Time and again, the cultural clash has surfaced, delaying service delivery.
- Potential threats if weakness are not addressed.
Surfacing from the unsolved weaknesses, threats such as delayed service provision and fear of being offended by patients due to cultural differences will occur. The clinic may be perceived as not as accommodative as painted in the mission and vision.
- How you can use the strengths identified in your personal SWOT analysis as an opportunity to help the organization improve in this area.
I am firm in decision-making, a great team player, and a motivator. Working with different people from each department will enable me to understand their ways and become a team player in helping each one to adopt a multi-diverse working environment. For those who are downcast due to an interaction with a patient that may not be so welcoming, I will motivate them to focus on the end game stated in the mission statement.
- Competencies you possess and can use to address the issue.
Innovation and being a visionary can help remind the people about the vision that the clinic has in the health care industry. Doing this will help bring people together to foster a diverse working environment that accommodates many people regardless of where they are from. Supervision is an essential competency by a manager, especially when the vision is new to the people and not deeply rooted.
- The leadership theory that is appropriate to address the organization’s weaknesses.
Situational theory appropriates the healthcare organization because it works best with different situations that are the norm in this field (Thompson & Glasø, 2018).
- The primary mechanisms that can be used within the organization to refine, maintain or change the organization’s culture.
Following Lewin’s change management model, unfreezing, changing, and freezing the activities will help refine the organizational culture through the different stages of organization growth.
- The secondary mechanisms that can be used to reinforce the primary embedding mechanisms.
Continues capacity building for both the leaders and other employees will help refine the changes that have been made and are continuing to be made. Leaders are tasked with the opportunity to model and constantly remind the employees of where they have come from and where they need to be in the present and future.
- The effect the organization’s culture has on the ability of a leader to drive change.
Organizational culture constitutes the way activities are done and why they are done. Every organization must cultivate a culture capable of helping people thrive in their personal development in the same line achieving what the organization wants in the end. Leaders follow the culture that the organization has set. If the culture is positive and gives people opportunities to become their best, they have an easy time dealing with people. If the culture is negative, the leader may find it difficult to lead people.
What is Fish! philosophy?
Fish! Philosophy was first modeled in a film called “Fish!” made by filmmaker John Christensen. He was in Seattle when he discovered a business, which was filled with commitment and enthusiasm (Pardieck et al., 2017). The business was the Pike Place Fish Market which is famous across the globe. People flock to watch the fishmongers work as they also buy the fish.
How does the Fish! philosophy promote a dynamic working environment?
Four practices are into play when practicing the “Fish!” philosophy. First, be there. To create a dynamic work environment for people, being emotionally present sends the message of respect, improving communication hence relationships.
How does the Fish! philosophy relate to change management theory?
Play comes second. It helps in tapping the most creative ideas in an enthusiastic and fun way. Thirdly, make their day. Creating an environment that gives room for dynamism contributes something positive to someone else’s life apart from yourself. Finally, choosing attitude is one sure way of developing shock absorbers. If everyone in the organization knows how to handle everything thrown at them with the balance it deserves, productivity and stability will be realized.
“Fish!” philosophy is critical in describing how adaptation is essential. Being there is not just a mechanical approach. It means that all facets are involved. In the same way, change theories perpetuate that change is not a one size fits all but change has to be tailored according to the need at hand. In the same way, the philosophy (Fish!) encourages adaptation to these changes.
What is one change management theory that would work in your organization?
Lewin’s model of change management theory would fit best. He describes three critical stages; unfreezing, making changes, and refreezing. It fits appropriately because the healthcare industry needs changes to be made first and, more so, being firm in what is passed as a decision.
How can leadership theories differ from one department to another as well as from one specific team to another?
Leadership theories are not one size fits all, rather tailored to fit the people being led. Each department has different people holding different roles. Since leadership theories differ from one to another due to these items, it is normal for different leaders to use different theories for their departments.
How might this directly affect the staff within the department or team?
Employees or team players are directly affected by how their leader views and treats them. If he or she is strict and always there to supervise, it may be because of the highly sensitive task that the department is tasked with.
How would you navigate through the various leadership styles within an organization and adjust to the differences in leadership?
Leadership comes in many styles depending on a multifactorial aspect. The best way to navigate is to empathize with the leader of that department to understand why he or she does what he does (Weiszbrod, 2020). However, in the process, the main item should to ensure that productivity is at its highest.
How do the competencies discussed in the text book readings apply to leaders in different areas of your organization?
Leadership competencies are key to good leadership, and when applied by all leaders their different roles notwithstanding, success is inevitable. Competencies are established to ensure that productivity is at its highest.
The democratic leadership approach would work best to bring cultural diversity to the organization.
How is the patient’s cultural perspective of quality care influenced by the changes in the health care law?
Health care laws tend to be everyone on board regardless of where they come from. When a patient views quality from a single cultural paradigm, it may not be as clear as to when they view it from a vantage point of different cultural backgrounds. However, with the law being enforced, the patient can change the view he or she has by understanding the “why.”
How do culture, language and tradition define quality?
Culture encompasses actions, cognition, knowledge, and perception of a certain group of people. Language and traditions give an aspect of control within a particular group of people. On the other hand, quality is the perception of a certain caliber of people of what they perceive to be of a good standard. Since people’s perception of quality is defined early by their cultures, their view before exposure and adaptation to other views is dependent purely on their background.
How does this influence the expectation of care?
How best people should treat us from reception to receiving medical care finds its foundations in the cultures we have come from have taught us. In the same light, the expectation of how best care should be given is predetermined by where we have come from.