1 Introduction
An organisation builds on its fundamental knowledge and its ability to interpret, harmonise and assess the objectives of the business to form a strategic plan in order to acquire and maintain a competitive advantage (Campbell & Faulkner, 2009). The outcome of this module is to formulate and execute a strategic plan for the chosen business Sirus Engineering, a building automation company based in Ireland. This paper seeks to analyse the organisation’s current strategic goals and assess the internal and external factors which influence these decisions. The following questions are laid down as guidance to achieve the aim of this study:
- Identify the factors that influence in the current business environment of your company and determine their effect on your selected business.
- Examine the present strategic role of the chosen company critically.
- Define and analyze two key strategic options and outline the preferred option.
- Critically evaluate the core concepts of successful change management and the initiatives that shape this effective strategic implementation.
2 Strategic management- Overview
2.1 Strategic management- Definition
Strategic management is defined as the “art of deciding, implementing, and evaluating inter-functional functions that enable the organisation to achieve its goals” (Khemesh, 2017). It is a dynamic process of decision-making that primarily focuses on the outcomes of a business in the long-run. Thus, it entails planning, coordinating, and controlling the organisational resources through which the business could acquire and maintain a competitive advantage besides achieving its main aims and objectives. Such a plan is often referred to as a strategy. A strategy is ‘’challenging and dangerous; it offers significant benefits if done well, and significant losses, if done badly’’(White, 2004, p. 23). Given that the development of such strategies is time, resource, and capital intensive, special attention and considerations should be given to it. Besides the aforementioned constraints, the business’ strategy is often based on a futuristic approach; thus, it is associated with many risks (Khemesh, 2017). A typical approach to the development of a strategy through strategic management includes five major processes namely, Internal Analysis, External Analysis, Strategy Formulation, Strategy Execution and Strategy Control (Navas López, Guerras Martín, and Macnair, 2018).
2.2 Strategic management theories
Strategic management is based on three main theories namely, the “Industrial Organisation” theory, the “Resource-based” theory, and the “Contingency” theory. The IO theory is primarily based on the organisation’s external environment. Therefore, such a theory entails the adaptation to the changes in the organisation’s industry in general. On the other hand, the resource-based theory mainly focuses on internal factors; thus, it incorporates the efficient use of an organisation’s resources including tangible assets such as equipment, employees, and finances, and intangible assets such as knowledge and information. The third theory is a combination of the former two theories. Hence, the contingency theory realizes the effects of both external and internal factors on the organisation’s success in strategic management (Navas López, Guerras Martín, and Macnair, 2018).
2.3 Strategic management- Benefits
The strategies developed through strategic management or strategic planning are beneficial to businesses in several ways. The main outcome of the implementation of successful business strategies is often granting a business a competitive advantage over its competitors; thus, leading to its growth and increased profitability. Such a competitive edge could be achieved through an increase in its market share, a decrease in the costs incurred, and the offering of unique products/services (Khemesh, 2017)
3 The chosen organization
The chosen organization for this report is Sirus Engineering which is specialized in building automation technologies and is based in Ireland. It currently employs over 100 employees. Its skillsets include mechanical, electrical, refrigeration, thermodynamic and automation. It serves several sectors such as the educational, commercial, retail, pharmaceutical and retail sectors. Thus, aiming to provide its customers with a high quality, compliant and comfortable workspaces that are energy efficient. The company is also accredited by the ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 (Sirus | Building Energy Solutions, 2021).
3.1 The chosen strategic management approach
This report will base its analysis upon the contingency theory which considers both the external and internal environment of the organisation. Thus, a SWOT analysis will be performed to the selected firm to identify the strengths, weaknesses, threats and opportunities associated with it. Furthermore, the theory is most appropriate for the generation of alternative strategies to enhance and augment the firm’s fit in its competitive environment (Navas López, Guerras Martín, and Macnair, 2018). Nonetheless, as common as this form of analysis is, Grundy (2003) states that it can be limited and even identified as being dangerous, for many factors such as subjectivity, inadequate interpretation and incompleteness of certain aspects.
3.2 Organisation’s operating environment
3.2.1 Internal Analysis
The internal analysis includes the analysis of all aspects that are inter-related to a firm and that are fully controlled by the management of that firm. Such an analysis is the basis for an appropriate strategic management as it deals with the management of all resources of the business (Stefan Claudiu, Andrei and Mara Gabriela, 1997).
Mission & Objectives
The main strategic aims of Sirus Engineering include the following (Sirus | Building Energy Solutions, 2021).
- Being a top employer.
- Being the best class in the sector of building environmental control.
- Being the best class in the sector of energy management.
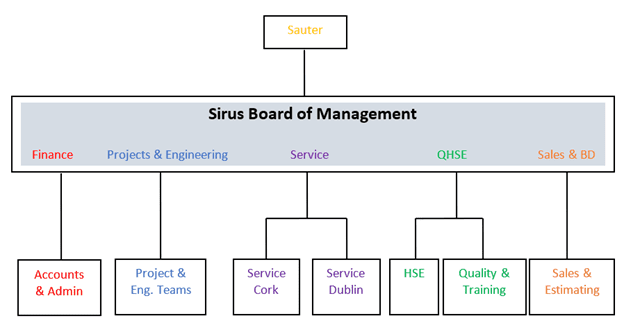
Business Structure
Figure 1:- Sirius’ business structure
Corporate culture
A corporate culture, also known as a value system, is the ethical beliefs of a firm towards its employees, customers and the society as a whole. Such beliefs provide guidance on the means through which a business could achieve its aims and objectives (Stefan Claudiu, Andrei and Mara Gabriela, 1997). Sirus’ policies emphasize the creation of long-lasting loyal relationships with all its stakeholder which is driven by the quality of services it provides. As it quotes “Precision and excellence in delivery and loyalty and longevity in approach are the common characteristics of Sirus…..in partnership with our customers, other service providers and suppliers.”
Business Idea
The business idea of Sirus Engineering is to implement Building Management Systems (BMS) to reduce energy and maintenance costs. It further provides consultancy services to energy management through the optimization of HVAC systems. Such services are provided to new and existing structures. With the increased momentum towards sustainability and energy efficiency, such services play a crucial role in meeting the global objectives towards sustainability and clean energy. The targeting of the existing buildings is a competitive edge since such a service allows clients to transform their structures without having to discard the existing equipment.
Human Resources
Sirus’ Human Resources are the most important towards achieving its main objectives. It employs two teams of energy expertise; the former specialises in HVAC systems and the latter specialises in consultancy and design of solutions for effective energy management.
Regarding the first team, the HVAC team is further divided into two subteams namely, the service engineers team that focuses on maintenance and quality control issues of the energy systems within a business and the service management team that is responsible for the energy optimization process. The second team, which is the energy team, is divided into designers and consultants who are capable of inventing and implementing novel innovations to augment energy savings within a structure.
Thus, Sirus’ human resources represent the core of the organization as they possess the “Know-how” which is crucial for the success and flourishment of the firm. Through such teams, Sirus is capable of developing new innovative technologies that aid in meeting the company’s objectives of being the best class in the energy management industry.
Technological Resources
- Sirus Servers- Sirus servers provide customers with an off-site monitoring service to the energy performance of their buildings through a web-connection. This remote service not only allows for smooth energy management but also, facilitates the monitoring and storage of data to be better able to control and optimize the outcomes.
- Sirus Softwares- Sirus had achieved great progress with the development of “RemoteHVAC” which is a data analysis tool that is cloud-based. Through the analysis of the data of existing structures as an input, the tool is capable of providing a range of solutions for the efficient utilisation of energy within structures.
Intellectual Resources
Sirus Engineering has developed a patent technology that could be implemented worldwide in different applications. Such technology is capable of recovering energy from the natural gas grid which is a breakthrough technology in the field of energy management.
3.2.2 External Analysis
External analysis is the analysis of all external factors that could directly or indirectly have an impact on the business. The external environment is further divided into two namely, the micro-environment and the macro-environment (Stefan Claudiu, Andrei and Mara Gabriela, 1997). The following paragraphs will give a thorough analysis of these factors.
3.2.2.1 Micro-environment
The micro-environment of a business is the environment that is directly related to the business. Such a direct relationship emerges from the interrelated and mutual benefits that are gained towards achieving the main objectives of an organisation. Thus, it includes suppliers, service providers and public entities (Stefan Claudiu, Andrei and Mara Gabriela, 1997). To analyse Sirus’ micro-environment, Porter’s Five Forces model will be utilised in this research. This method will identify forces that may lead to a competitive rivalry that Sirus as a business must deal with to maintain its competitive advantage. Galavan, Murray, & Markides (2008) suggested that Porter’s factors can be used to identify changes in the structure and dynamics of the related industry. However, Porter’s forces should not be accepted as givens, but used to enforce innovation, question, and disrupt competitive behaviour. The following is an analysis of porter’s five forces.
- Competitive Rivalry: Sirus as a business in the field of building automation have identified both local and international competitors. Many of these competitors competing in the market do not directly compete with the business’s offerings. Given that the pharmaceutical sector is one of the primary clients of Sirus Engineering, the expectations and quality required by such clients ensure a low level of local competition.
- The threat of Entry: Initiating a building automation company is not complex. This is related to market saturation of products which require system installers. In addition, other than building automation services, Sirus offer Heating Ventilation Air Conditioning (HVAC) products and services. This aspect of the business is not difficult to start-up and thus only requires experienced tradesmen that are widely available. Nonetheless, pharmaceutical clients have an expectation of quality, standards and certification which is difficult to achieve and gain access to.
- The threat of substitutes: With the advancements in technology and the effects of globalisation on markets, there are threats of alternatives and substitutes. These are companies that originally did not compete in the building automation market. However, artificial intelligence and the latest push for the Internet of Things (IoT) services linked to the IT world means that the business must strategically position themselves to mitigate these threats and identify ourselves as standing out from the crowd.
- Power of Buyers: There is no one set route to the market in the building automation industry. Cost, schedule, and quality of work will have different weightings depending on the particular industry targeted. For example, the cost will have less of an impact on the pharmaceutical industry that it will in the commercial buildings segment. Nonetheless, the drive for quality and satisfaction is taking precedence over cost alone, but the cost will always be key to success and must be balanced with other business strategies.
- Power of Suppliers: Over the last twenty years, Sirus was the sole supplier of Siemens products in Ireland. Therefore, this provided us with a competitive advantage over our rivals. In such a way, Sirus was the single market seller (market monopoly) on this product. However, in recent years Siemens has extended this offering to other automation companies and this has meant a change in the business strategy was needed. In 2018, Sirus was acquired by Sauter International, a Swiss-based automation business. Sauter acquired the majority shareholding and implemented a new strategic direction for the business.
3.2.2.2 Macro-environment
On the other hand, the macro-environment are external factors that affect an organisation indirectly in the long run. Such factors often enforce a business to adapt and change to be able to sustain its success (Stefan Claudiu, Andrei and Mara Gabriela, 1997). The macro-environment can be examined using many techniques; however, for this analysis, the PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental and Legal) technique was chosen. According to (Management Extra, 2005), the PESTEL analysis outlines a list of environmental factors which impacts the business. A summary of these factors which directly impact Sirus has been outlined in Appendix A.
Political
- Following the Brexit treaty, many businesses would be negatively affected due to the enforcement of new legislation. Similarly, Sirius engineering would encounter several challenges as some of its suppliers are based in the UK including Siemens which is a key supplier.
- The situation is further worsened with the COVID-19 pandemic and the new regulations adopted by many countries leading to uncertainties in the global trade.
- Certificates such as the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) and the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) are encouraging businesses to go green to augment their profiles.
Economic
- According to The Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (2017), the fuel prices are expected to change dramatically within the next decade; thus, creating an urge for the enhancement of the utilisation of energy within the country.
- Meanwhile, the projections of the economic growth of the country show rapid growth within all sectors increasing the demand for energy. Thus, there is a strong economic driver for the efficient use of energy since Ireland is an importer of energy (The Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland, 2017).
Social
- With the development of awareness campaigns with Dublin’s local authorities, there is an increase in public awareness towards a greener and more sustainable approaches. Hence, there is a considerable change in people’s behaviour and attitudes towards the utilisation of more energy-efficient technologies (Energy Awareness, 2016).
- Furthermore, the side-effects of poor indoor air quality have been established; thus, creating more demands for a healthy indoor environment by local citizens.
Technological
- It has been established that technological advancements in the sector of energy efficiency are surging due to the increased level of awareness, and the associated economical and environmental benefits. New technologies such as blockchain-based systems, Artificial Intelligence, ML, the internet of things (IoT) and digital twins are being heavily used in the energy sector (Jackson, 2020).
- The advancements in technology in the energy sector not only aims to use the available energy sources efficiently but also, to incorporate novel technologies of renewable energy in existing structures (Jackson, 2020).
- Furthermore, there is a shift towards Intelligent buildings that have automated control over the use of energy.
Environmental
- There is an increased momentum towards achieving sustainability all over the world. This is apparent from the development of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals for 2030. In these goals, goal number 11 “Sustainable cities & communities” focuses primarily on the effective utilisation of energy (THE 17 GOALS | Sustainable Development, 2015).
- This is further supported by goal number 12 “Responsible consumption & production” as an attempt to preserve the natural resources and avoid their depletion through the responsible use of such resources including energy (THE 17 GOALS | Sustainable Development, 2015).
- Recently. The Irish government is targeting to rely on 70% renewable energy sources, have a 30% reduction in its carbon emissions and achieve a 32.5% improvement in energy efficiency. Such schemes are carried out by the Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (SEAI). Such aims would be achieved through the National Energy Efficiency Action Plan (NEEAP) and in the National Renewable Energy Action Plan (NREAP) by 2020 (The Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland, 2017).
Legal
- The Irish government has been encouraging the efficient use of natural resources, including energy, since a long time. This is apparent in the establishment and enforcement of the Energy Efficiency Order (1999). Through such provision, the government has promoted the efficient utilisation of energy within all sectors of the economy.
- Moreover, the government has introduced the Energy Auditing Compliance Scheme in 2014 which is enforced by the Energy Efficiency Directive (EED) along with the SEAI. Thus, energy audits for buildings, industries, and the transport sector are laid out (SEAI, 2020).
4 Organization’s strategic position
4.1 Strategic position- Overview
To analyse the strategic position of Sirus Engineering, the SWOT analysis will be utilized in this paper. SWOT analysis involves the identification of strengths and weaknesses, and opportunities and threats that may be encountered by organisations. In such an analysis, a firm bases its findings on the internal and external environment to formulate strategic decisions. It has further been established that the firm’s strengths and weaknesses emerge from its internal environment while the opportunities and threats emerge from its external environment (Sammut-Bonnici and Galea, 2015). Based on that, the SWOT analysis of Sirus Engineering is presented hereunder.
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
| ● Solid Track Record in several industries including pharmaceutical, healthcare, commercial, etc.
● Varied Skill Sets and Competencies in Mechanical, Electrical, Energy, and Product applications. ● Novel Patents & technology ● Remote management and services to clients ● Strong Supplier relationships and bargaining power ● No debt and strong financial record ● Services are easily implemented onto existing structures with no need to fully discard the available equipment |
● Market focus is Ireland only
● Poor marketing techniques, not enough people know about us ● Lack of precise forecasting of future demands ● Lack of investigating available technologies in the sector ● Lack of incorporation of novel energy sources into products and services provided ● No set route to the market & the clients ● Our suppliers are dealing with our competitors |
| Opportunities | Threats |
| ● Environmental drivers will allow our products, solutions and services to be valued by building owners;
● Partnering with Utility Companies (ESB Smart Energy Services and Centrica) ● The intellectual resources could aid in diversification and the penetration of new markets ● Build relationships and alliances with Contractors who are having more and more Design & Build scope is improving our chances of winning more work with them (particularly in foreign markets ● Low level of local competition ● Assist several other industries in gaining certifications such as the LEED and the CSR ● Changes in fuel prices and the increase in economic growth could be utilised to promote the services of Sirus Engineering ● The global changes in behaviour and the increased level of awareness is an opportunity for expansion & growth abroad |
● Suppliers such as Siemens becoming competitors
● Availability of competent engineers & manager ● Other Automation Companies (traditionally process manufacturing automation integrators) coming into our space ● Hacking of servers and software used would result in loss of data and disruptions in the flow of work ● Obsolescence of the developed patent and the used technologies and software ● Larger multinationals such as Honeywell, JCI &Schneider aggressively trying to win market share ● Disruptions in the global trade due to Brexit & COVID-19 pandemic |
4.2 Strategic position- Analysis
From the aforementioned analysis, the following core findings are revealed.
- Due to the increasing environmental concerns and economic disruptions, the global shift towards more sustainable approaches is in favour of the services provided by Sirus engineering. This is further supported by the enforcement of new legislation, governmental assistance and changes in behaviours of clients.
- The energy sector is heavily dependent on the development of new technologies for better management and optimisation of energy usages. Thus, technologies are being developed at an unprecedented rate creating several threats of obsolescence and outdating,
- Although the competition level is not currently high, it is expected to increase rapidly due to the increasing demands for such services both on a local and global scale.
- The current political conditions are imposing several uncertainties to the global trade which is expected to negatively impact many businesses.
Thus, it could be argued that Sirus Engineering is at a good strategic position for the following reasons. Firstly, Sirus has grown from a business of 4 people to > 85 and continues to grow after 30 years in business; it has a good financial status with no debts. The original founders are still involved in the business and some employees have tenures of 27, 20 and 15 years. Laljani (2009) outlines that the competitive advantage and superior performance of an organisation are explained by the distinctiveness of its resources and capabilities. Through such resources, Sirius had successfully established itself and its brand image in the industries it had been dealing with. Besides, it has established strong long-lasting relationships with its suppliers. Furthermore, it has developed advanced technology and patents that constitute a solid competitive advantage in addition to the services it provides to existing structures.
However, due to the sole focus on Ireland as a targeted market, such a brand image is restricted to Ireland only. This is further worsened by the lack of adequate marketing that would aid in widening the range of clients and the lack of forecasting of future demands. Also, Sirus Engineering lacks a fundamental aspect which is the investigation of novel technologies in other markets. There seems to be a shift towards the incorporation of novel energy sources into existing buildings whereas Sirus’ primary focus is to efficiently use existing energy sources. Therefore, Sirus should consider fixing such weaknesses.
The current increase in momentum towards sustainability and the associated legislation being enforced all over the world creates several opportunities for Sirus Engineering for expansion and growth. There are other several industries with huge potential for Sirus Engineering due to their massive dependence and consumption of energy such as the manufacturing industry. Besides other industries within Ireland, Sirus Engineering has good opportunities to expand into other markets dealing with similar industries such as the pharmaceutical industry. It could take advantage of the low level of competition to establish itself as a leading company in this field. Also, it could take advantage of the different certifications available by being able to assist its clients in gaining such certifications to further expand and grow.
Regarding the threats, it is apparent that such a market is not overly competitive. However, competition levels are expected to increase dramatically as foreign organisations are aiming to enter the market. For Sirus to remain a market leader in the automation and HVAC segment, the business must strategically change and transition to adopt new goals and to adjust for the probable increase in competition levels and the external forces identified above to remain successful. Moreover, Sirus should change to advance its current technology due to the high risk of obsolescence and the development of novel technologies by competitors. Although Sirus Engineering had implemented several successful strategies to achieve its aims and objectives, there is a lack in the focus on intangible assets. Therefore, Sirus Engineering should focus on establishing a reputation through the development of its brand image. It should aim to further establish itself as a well-known leading brand in this sector through the formation of a solid corporate image.
5 Strategic Options
5.1 Strategic option 1- Diversification
With regards to strategic option number 1, Sirus should consider diversifying its products and services to suit a wider variety of clients, and to operate in different countries to be able to achieve its goals and objectives of being a leader in this sector. Thus, the proposed diversification is in the industries that Sirus deal with and in the countries in which it is operating. The following presents the advantages and disadvantages of this option.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| ● Diversification would ensure the growth and expansion of Sirus Engineering
● Diversification would ensure a constant inflow of contracts that might mitigate the possible negative impacts of new competitors. ● Diversification into several countries and industries would mitigate against the risks associated with focusing on certain markets and certain industries. ● The existing technology, software and patents would be utilized to their fullest potential increasing profits. ● Besides enhancing profitability, diversification would enhance the market share of Sirus Engineering ● Diversification could aid in achieving economies of scale and tax benefits
|
● Diversification into different industries would require a new skill set.
● Broad and extensive mismanaged diversification into several industries might fail due to the lack of sufficient resources and experience ● Diversification requires additional managerial efforts and strong coordination within the organisation ● Diversification is a capital intensive process that requires upfront funds. ● It requires a thorough and precise analysis of the proposed industries and markets. ● Establishing a solid brand image and reputation is laborious especially with the existence of competitors. |
5.2 Strategic option 2- Technological advantage
Considering strategic option number 2, Sirus should focus on technology as a primary source of its competitive advantage. Thus, it should focus on updating and upgrading its existing technology to cope with the advancements in this sector and establish itself as a technology leader. It should further seek to develop more patents to be able to withstand the increasing levels of competition. Moreover, Sirus should adopt the use of novel renewable energy into its systems and services, The following are the advantages and disadvantages of this option.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| ● Technology provides a form of sustainable competitive advantage due to the absence of competition over the novel technology
● Technology assists in achieving higher efficiency levels; thus, enhancing the outcomes and customer satisfaction ● Technology is capable of extensively elevating the profit margins of a business ● Technological advantages would aid in the establishment of a solid corporate image and goodwill ● Technological advantages would aid in the establishment of good reputation for innovation and creativity ● Such advantages could encourage governmental incentives to Sirus Engineering in an attempt to enhance energy usage within the country ● Technological advantages create strong entry barriers for competitors ● Could be easily protected using patents to prevent replication and ensure its validity for a long time ● The development of the automation services would lead to an enhancement of workflow at a lower cost leading to an increased demand level ● The focus on data analytics would give insights into future demands and risks enhancing its performance
|
● The technological advantage is at constant risk of obsolescence and outdating
● Patents are extremely expensive ● Technological developments are capital intensive and would require huge funds and investments into research ● Besides its development, the adoption of technological advantage requires several infrastructures ● There is a risk of cannibalizing existing products and services |
5.3 Preferred strategic option
Suitability, Acceptability and Feasibility test (SAF)
The SFA test consists of three processes namely, suitability, feasibility and acceptability. In suitability, the proposed strategic option is analysed to assess whether it fits within the analysis of the external and internal environment. Thus, suitability emerges from three primary factors which are the exploitation of organisation’s strengths, the extent to which an option overcome the imposed threats and weaknesses and the extent to which the option aligns with the objectives of the firm (Johnson & Scholes, 1997). Feasibility assesses the extent to which an option could be easily implemented with regards to the required funds, skills and resources, and the expected level of competitional responses (Johnson & Scholes, 1997). Finally, acceptability relates to assessing the stakeholders’ perceptions such as the effects on the capital structure, the relationships with external stakeholders and conducting a cost-benefit analysis (Johnson & Scholes, 1997).
| Option 1- Diversification | Option 2- Technological advantage | |
| Suitability | ● Would utilise the existing strengths as resources, technologies and patents would be used to their maximum potential
● Overcome weaknesses by mitigating the risks of focusing on one market ● Utilizes existing opportunities for expansion and growth
|
● Would utilise the existing strengths as resources, technologies and patents as a basis on which further developments would be built
● Overcome weaknesses by establishing a good reputation and a solid corporate image in innovation ● Utilizes existing opportunities for expansion and growth ● Overcome threats of increased levels of competition, advancements in technology and obsolescence |
| Acceptability | ● Acceptable by all stakeholders due to its ease of implementation | ● Not accepted by all stakeholders due to the complex processes associated with it given the small scale of the firm |
| Feasibility | ● Could be easily funded as funds are required for analysis of new markets and industries that would be penetrated using existing technologies
● Could easily be implemented with the required quality due to the experience acquired in this area ● If new markets are thoroughly investigated, competitive reactions could be coped with ● The required market position could easily be achieved in the short run |
● Is not easily funded as it requires massive investments in research and in patents
● Requires a high level of expertise, efforts and time to have an outcome |
Based on the conducted test, option 1- Diversification is the preferred option for the following reasons
- Easily implemented utilizing the existing know-know and expertise level
- Is not capital intensive and doesn’t require huge funds or investments
- Outcomes could be noticed in the short run soon after implementation
- Allows for the growth and expansion of Sirus engineering
6 Successful change program
6.1 Key principles
It has been established that strategic changes are crucial for the development of competitive advantages and the overall success of businesses. However, without an effective implementation scheme for the opted strategy, an organisation will not be able to benefit from such strategy (Brinkschröder, 2014). There are several key factors that should be considered for the successful implementation of a strategy. The following are a few of these factors.
- Leadership styles- Leadership styles are crucial for the successful implementation of a strategy as they are capable of influencing the behavior of employees by increasing motivation levels, loyalties and commitment to change. Thus, by adopting a right leadership style, Siruc Engineering could motivate its employees and encourage affective commitment to change and diversification within the organisation (Brinkschröder, 2014).
- Resource allocation- The appropriate allocation of resources such as the financial and human resources are crucial for the successful implementation of a strategy (Brinkschröder, 2014). To be able to diversify, Sirius Engineering should firmly analyze the allocation of resources between different industries and in different markets to avoid any possible derelictions.
- Strategic consensus- It is quite common to encounter several perceptions and contradicting opinions regarding a chosen strategy (Brinkschröder, 2014). Therefore, the top management of Sirus engineering should ensure a common understanding and strategic consensus among all stakeholders to achieve better outcomes
- Coordination- Coordination between different departments within the organisation is crucial to ensure a successful implementation of the chosen strategy (Pournasir, 2013). Thus, Sirius should have clear and transparent communication systems to ensure that the aims and objectives are aligned and that the efforts of different departments are exerted in the right direction.
- Monitoring and controlling- Monitoring and controlling the implementation of a strategy against predetermined benchmarks is beneficial as it allows for the early identification of flaws and deficiencies (Pournasir, 2013). Thus, corrective measures and actions could be easily implemented to be back on the right track and achieve the desired outcomes.
- Effective role formulations- Since the implementation of a strategy involves several interconnected departments, there should be a clear identification of the roles and responsibilities to avoid confusion, duplication, errors and wastage of time (Pournasir, 2013). Therefore, Sirus Engineering should clearly establish the roles and responsibilities of each individual within the organisation.
7 Conclusion
From the aforementioned analysis, it is clear that the implementation of a successful strategy involves five main processes namely, external analysis, internal analysis, strategy formulation, strategy implementation and strategy control. Multiple pieces of research have focused on the formulation of strategy according to the external and internal factors; however, it has been established that equal weights should be given to the implementation and control of a formulated strategy to ensure that the desired outcomes are achieved and to maintain a competitive advantage.