Introduction
Vodafone company was founded in 1983 as part of Racal, the British firm for radar and electronics, which was founded in 1950. Vodafone company became the first to build the Britain’s first cellular telephone network. The Britain’s first cellular telephone network was launched in 1985 (Dervishaj, 2016). Vodafone began to purchase other companies and establish various collaborations and partnerships across the globe. Vodafone company is planning to enter a new international market in the Asia continent, specifically in China by setting up a joint venture in partnership with an overseas organization (Dervishaj, 2016). Therefore, it would be important to evaluate the ways through which the national culture of China may impact on the company’s HR strategies and practices. The main aim of this paper is to evaluate the possible impacts of China’s national culture on Vodafone’s HR strategies and practices. The paper will also recommend how the company should conduct its HR strategies and practices in China through the use of ADKAR change model.
Analysis of UK Culture using GLOBE Model
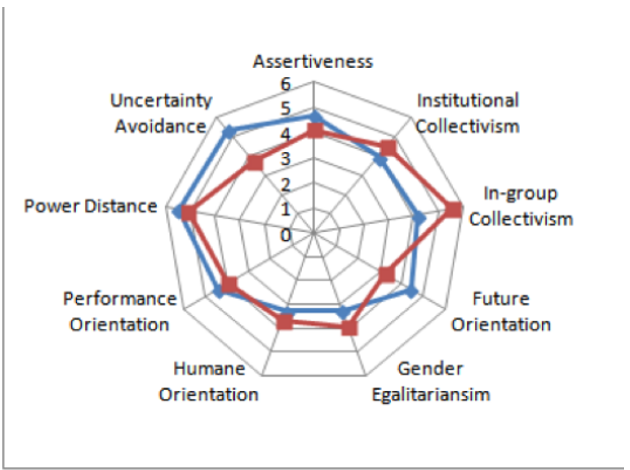
The paper used GLOBE’s model to analyze the UK’s national culture because the model provides the most valuable analyses of national culture, especially the intercultural communications. The researcher chose to use GLOBE’s to identify the characteristics and HR strategies and practices that Vodafone should implement while operating in China since the influence of culture on HRM cannot be dismissed (Iancu & Badea, 2020). Therefore, the paper used GLOBE’s model to analyze the 9 dimensions of UK’s culture and explain the impacts of the results on the new Vodafone’s HR strategies and practices to be implemented in China. The diagram provided below shows the 9 dimensions of GLOBE’s model of analyzing cultures.
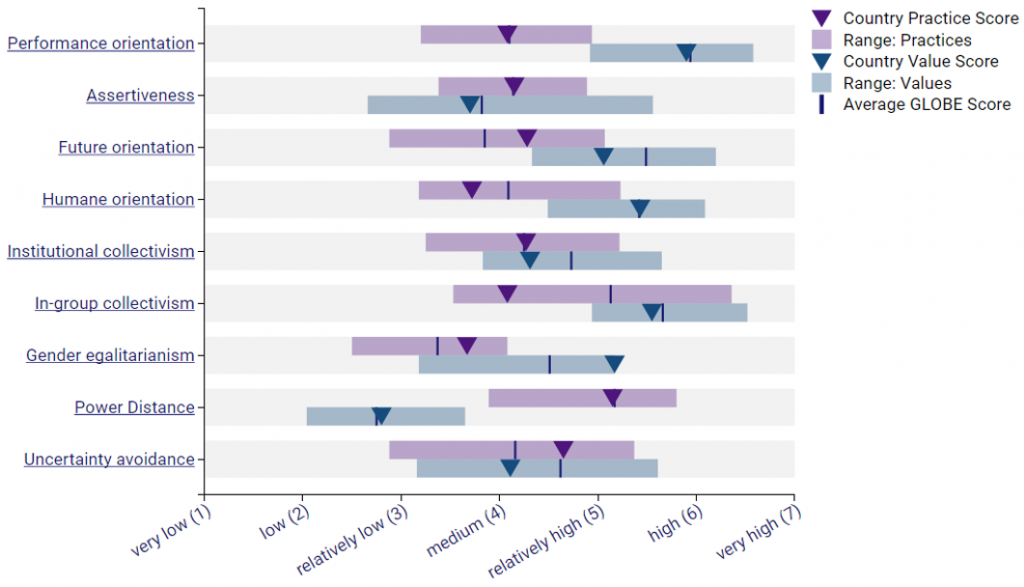
The diagram provided below shows graphical representation of Globe’s scores on the culture of United Kingdom.
| Dimensions | Score | Explanation |
| Power Distance | Low | Power-distance measures the degree at which the less powerful people is a given society accept the unequal power distributions. The people in UK believe that inequality in the society should be reduced (Iancu & Badea, 2020). |
| Institutional Collectivism | Low | Measures the extent to which institutions encourage individuals to integrate themselves into broader entities and live together in harmony and corporation. UK is an individualistic country; hence; people in this country prioritize their individual interest and the interests of the close family members (Iancu & Badea, 2020). |
| In-group Collectivism | Measures the extent at which a particular culture encourages people to be loyal to their respective families, organizations, and societies. People in UK invest less in the interests of a society or community or institution. The people of UK are never loyal to the society or organization’s interests. | |
| Gender Egalitarianism | High | Measures the extent at which a particular culture encourages gender equality. UK is highly masculine, which demonstrate that people value competition, success, and achievements. UK society focus less on various attributes such as being modest and considering the well-being of others. |
| Assertiveness | Measures the extent at which a particular culture encourages aggression. The people of UK are aggressive and they value their career goals and are comfortable expressing their distinct ambitions. | |
| Performance Orientation | Highly rewards Individuals’ achievements | Measures the degree at which a given culture rewards people for their achievements and performance. UK’s culture rewards people for their individual achievements, which encourages competition and innovation. |
| Uncertainty Avoidance | Low | UK is made of a society where people have low interest in uncertainty avoidance. These people are less interested in knowing what will happen in future since they are comfortable even in presence of uncertainty (Zhang, 2020). Therefore, people in UK are flexible and creative and are more likely to take risks while projecting potential benefits in their investments. |
| Future Orientation | Low | Measures the extent at which culture encourages people to defer their immediate actions for future benefits. UK’s scores on time-orientation is low, which indicates that people in this country have low chances of reconciling the present challenges while retaining the past links (Zhang, 2020). |
| Humane Orientation | Weak impulse control | Measures the degree at which people show kindness, care, and generosity to others. People in UK are strongly driven by their desires and show little amount of kindness, care, and generosity to others except their family members. |
The Current HR Strategies and Practices of Vodafone Company in United Kingdom
| HR Strategies and Practices | Impact of National Culture |
| Employees’ recruitment (Talent Acquisition) | · Vodafone company prioritize recruiting its workers through the use of the personal or relationship-oriented recruitment sources such as employees’ referrals and network if the recruiters come from the countries since UK is highly individualistic (Gupta, 2020). |
| Employees’ Selection process | · Employees’ selection process applied by Vodafone in UK focus on proactive employees who can autonomously perform the tasks since the country is highly individualistic. Vodafone also uses hard selection processes that focus on job related knowledge and technical skills since UK is highly masculine and people are highly performance-oriented (Gupta, 2020). Vodafone uses limited selection methods due to the low scores on uncertainty avoidance and employment decisions can be made from the limited methods used. |
| Workers’ training and Development | · Vodafone mostly uses individualised and goal-oriented training programs to train and develop its workers’ talents because the country in individualistic.
· The training programs are also designed in a way that the workers can easily access and consult the trainers due to the low power-difference index in the country · The training programs are also characterized by participative meeting approaches and the junior workers can also have a say in the decision-program on how these programs should be undertaken. |
| Employees’ performance Appraisal System | · Vodafone prefer task performance criteria of appraising the employees’ performance.
· Vodafone also prefer evaluating the individual performances such as individual’s level of performance output, innovation and creativity. · Vodafone also evaluates individuals’ engagement skills with their managers and superiors due to the low-power distance score in the United Kingdom.
|
| Workers’ Engagement and Compensation | · Vodafone engages its workers through participative meetings whereby the inputs of all the workers including the juniors are also involved in decision-making due to the low-power distance scores.
· Vodafone also rewards the individual results of its workers since the country is individualistic and workers’ focus on competition and creativity (Gupta, 2020). · Workers compensation and rewards in Vodafone are in form of money and promotion since United Kingdom is a highly masculine country. |
Analysis of Chinese Culture Using Globe Project
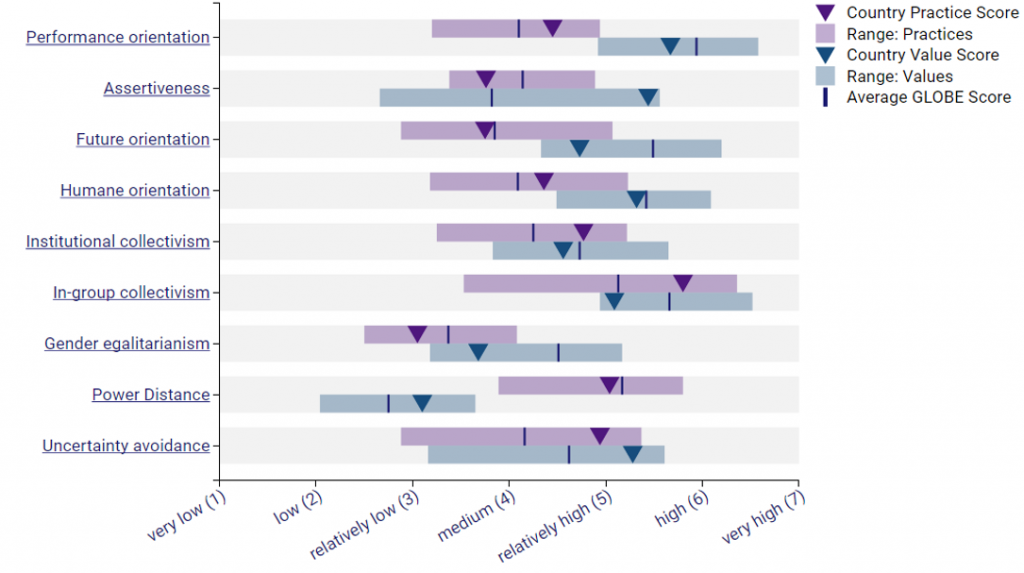
The diagram provided below shows the Globe’s scores on Chinese Culture
| Dimensions | Scores | Explanation |
| Power Distance | High | The culture of China is characterized by a high power-distance and there is significant gap between the lower and upper classes in terms of class and culture. The hierarchical communication is the most common approach used by the organizations in China (Iancu & Badea, 2020). |
| Institutional Collectivism | High | Measures the extent to which institutions encourage individuals to integrate themselves into broader entities and live together in harmony and corporation. The Chinese culture encourages individuals to live together in groups while observing peace, harmony, and care for each other. |
| In-group Collectivism | High | Measures the extent at which a particular culture encourages people to be loyal to their respective families, organizations, and societies. The culture of China is characterized by people working in groups. People in China also favor familial relationship while paying significant loyalty and obedience to the group work and seniors (Iancu & Badea, 2020) |
| Uncertainty Avoidance | High | China culture is characterized by people with medium scores on their levels of tolerance and ambiguity at the workplace. Employees in most organizations in China are afraid of taking risks and would more likely to seek for guidance before undertaking their chores instead of taking using their own knowledge and decisions (Iancu & Badea, 2020). |
| Future Orientation | High | Measures the extent at which culture encourages people to defer their immediate actions for future benefits. The culture of China comprises of people with longer term orientation and these would focus on long-term results instead of the short-term based results. Business activities in the country are influenced by the long-term projections to surmount the potential business obstacles instead of having the task performed within a short period of time (Iancu & Badea, 2020). Chinese also value time and are also always punctual for their daily duties and obligations. |
| Gender Egalitarianism | Low | Measures the extent at which a particular culture encourages gender equality. China does not gender stereotypes and biases. China does not subscribe to the gender-based work life even though the culture is paternalistic in nature. |
| Assertiveness | Low | Measures the extent at which a particular culture encourages aggression. The culture in China does not encourage the overt display of aggression and the typical gender differences. Even though there are instances of aggression in China, such displays are always controlled to an extent that the group behaviors and group-work perspectives are not impinged (Iancu & Badea, 2020) |
| Humane Orientation | High | Measures the degree at which people show kindness, care, and generosity to others. Chinese culture comprises of people who value each other and these people show generosity while serving the interests of the society. |
| Performance Orientation | High for group performance orientation | Measures the degree at which a given culture rewards people for their achievements and performance. Chinese culture rewards group-achievements instead of individual achievements. |
Similarities and Differences between UK Culture and Chinese Culture
Differences
The first difference between UK culture and Chinese culture is that China has high power-difference. The people in China are separated by a significant gap depending on the class that one belongs (upper or lower class). Chinese also value taking guidance from their seniors instead of taking action without seeking for guidance from the seniors and top managers. The juniors in China i.e. those who belong to the lower class always pay loyalty and obedience to the top managers (those from the upper class families) (Iancu & Badea, 2020). On the other hand, UK comprises of people with insignificant difference between the seniors and juniors (low power-difference index). In UK, juniors are always consulted through participative meetings when making decisions and decision of everyone is valued in the decision making process.
The second difference is that UK scores lower on in-group and institutional collectivism than China. UK’s culture comprises of individualistic people who prefer their interests and the interests of their close families to the interest of the society. People in UK mainly focus on achieving their individual goals and success through stiff competition and creativity. On the other hand, Chinese culture is characterized by low individualism (high in-group and institutional collectivism). Chinese value group-based goals and the well-being of the society. The third difference is that UK’s culture has higher scores on gender egalitarianism than Chinese culture. UK’s culture is highly masculine and people in UK focus less on various attributes such as being modest and considering the well-being of others (Zhang, 2020). However, Chinese culture is moderately masculine since the culture does not subscribe to the gender-based work life even though the culture is paternalistic in nature.
In addition, Chinese culture comprises of people with medium scores on uncertainty avoidance while UK culture has low uncertainty avoidance scores. People in UK are flexible and creative and are more likely to take risks based on the projected benefits in their investments. In China, people fear taking risks and would more likely to seek for guidance before undertaking their chores instead of taking using their own knowledge and decisions (Zhang, 2020). Chinese culture also has higher scores on long-term orientation than UK culture. The Chinese culture compels its constituents to focus on future orientation instead of the short-term based results while the UK culture comprises of people who are less interested in knowing what will happen in future since they are comfortable even in presence of uncertainty. Therefore, people in UK always and achieve the short-term goals. The Chinese culture comprises of the less aggressive persons whose level of aggression is controlled to an extent that the group behaviors and group-work perspectives are not impinged.
Similarities
There are no significant similarities between the UK and Chinese cultures based on the above illustrations using the Globe’s model. Even though Chinese culture shows certain level of aggression among its people like in UK, such level of aggression is to ensure that the group behaviors and group-work perspectives are not impinged (Zhang, 2020).
Recommendations on Employing either Local Workers from China or Expatriates
From the above analysis on cultural differences between UK and China, it can be observed that China and UK are two completely different in terms of culture. Therefore, it would be recommended that Vodafone should employ local Chinese to work in the new business venture. Employing the expatriate staffs will make it difficult for the company to compete with the other companies due to complexities in management and leadership (Al-Aali et al., 2020).
Recommendations
The recommendations provided in the table below shows that Vodafone should change almost all its HR strategies and practices, which are adopted in UK in order to succeed in its business ventures in China.
| HR Strategies and Practices | Impact of National Culture |
| Employees’ recruitment | · Vodafone should prioritise other recruitment sources such as newspapers, online recruitment, employment agencies, and other sources that do not value personal contacts because Chinese value the group interests.
· Vodafone should also recruit its workers by considering their teamwork abilities since people in China are always interested in group works and activities. |
| Selection process | · Vodafone’s employees’ selection process in China should prioritise workers who are ready and willing to work in a team
· The workers’ selection process should also use the soft criteria that analyses relational skills. · The company should use wide range of selection methods in order to make valid decisions since China is mainly characterized by high uncertainty avoidance scores. |
| Workers’ training and Development | · Training of Vodafone’s workers in China should use formalised communication and hierarchical communication strategies between the coaches and trainees due to the high power-distance index.
· The company should also use the group-oriented, unstructured training approaches, and informal training environment that promotes active participation and experimentation. |
| Employees’ performance Appraisal System | · Vodafone should also adopt the contextual performance measurement criteria that focus on evaluation of teamwork results.
· The designed performance appraisal system should also appraise employees’ loyalty and obedience to the superiors. |
| Employees’ Engagement and Compensation system | · Vodafone should design compensation packages that compensate the performance teamwork performance.
· The Salary remunerated should be fixed and varied depending on the teamwork results. · The designed compensation system should also focus on intangible rewards such as job security and recognition since Chinese culture is averagely feminine and masculine. · The compensation system used by Vodafone in China should also reward performance due to high degree of uncertainty avoidance. |
Change Model
This paper recommends the ADKAR model of change for when setting the changes for the new venture. Through application of the model, the company should sequentially change the HR strategies and practices by achieving the cumulative goals of the process to achieve the overall change goals (Al-Aali et al., 2020).
A-Awareness- Vodafone should recognize the need to change its HR strategies and practices
D-Desire- The company should participate in and support these changes
K-Knowledge- The company should analyze the new market in order to understand the process of change and the required changes in terms of skills and behaviors.
A-Ability- Vodafone should continuously invest in the change until it achieves the change goals
R-Reinforcement- The company should sustain the changes for long-term benefits
McKinsey 7-S Model
The paper also recommends that Vodafone should use McKinsey 7-S Model to implement the projected changes in HR strategies and practices. The application of the model would involve:
Strategy: The strategies for implementing the changes would involve having step-by-step procedures of undertaking the changes
Structure: Vodafone should establish its organizational structure that would implement the changes
Systems: The company should also develop and implement a system that will be used to complete the daily activities.
Shared Values: Vodafone should also develop the core values of managing the company in its new environment.
Style: The company should also develop the manner in which the changes would be adopted
Staff: The company should also employ the required workforce and employees in the new working environment. In this case, it would be recommended that Vodafone to employ workforce from Chinese Population.
Skills: The recruited employees should show high level of competencies and skills.
Conclusion
Application of Globe’s models has significantly demonstrated the impacts of national culture on HR strategies and practices. This paper focused on the intension of Vodafone to venture its new business goals in China which has completely different culture from UK. Through the analysis, the paper recommends that Vodafone should change its HR strategies and practices to succeed in it business goals in China. The new HR strategies and practices that Vodafone should implement while operating in China include; Recruiting workers based on their teamwork abilities, application of soft workers’ selection process, contextual performance measurement criteria that focus on evaluation of teamwork results, appraising workers’ loyalty and obedience, using formalized communication and hierarchical communication strategies, group-oriented, unstructured training approaches, and informal training environment, compensation of teamwork performance, intangible rewards such as job security and recognition, and fixing and varying salaries based on results of teamwork. The paper also recommends that Vodafone should use ADKAR and McKinsey 7-S models to implement the proposed changes.
Also look at some of our business services
– Business Essay Writing Service
– Business Dissertation Writing Services
– Business Report Writing
– Business Assignment Help
– Business Planning Writing Service
– Business Assignment Writing Service