Patients’ Adaptive Responses to Alterations Caused by Disease Processes
Scenario 1: 2-year-old female who presents with her mother
Pathophysiology
- Less playful
- Fussy and unsettled
- Fever on and off
Associated alterations
- Tympanic membranes reddened on the periphery
- The throat is erythematous with 4+ tonsils
- Diffuse exudates
- Anterior cervical nodes readily palpable
- Anterior cervical nodes tender to touch on the left side
- Hurtful throat and it is painful for her to swallow, hence the loss of interest in food
Patients’ adaptive responses to the alterations
- The 2-year old no longer wants to feed and appears less interested in her favourite activities like watching the cartoon.
- High temperatures that appeared normal after taking dosages of ibuprofen. Unstable temperatures that she had adjusted with the surrounding
- Hot and dry skin due to the high fever she has had for a few days
- Sleeping all the time to reduce the impact of the discomfort during the day
Diagnosis of the disorder
Treatment for the above disorder includes analysing the level of erythematous in the throat and tonsils (Burns & Grove, 2010). Prescribe the right medication plus one to control the temperature. Check up on the patient after one week to check the progress
Scenario 2: 27-year-old male who presents with redness and irritation of his hand
Pathophysiology
- Hot hands which feel a little bit uncomfortable
- Hands are red in appearance and flaky
- Irritated hands
- Allergic behaviour due to exposure to an allergen
Associated alterations
- Abnormal physical appearance of the hands
- Working with abrasive solvents and chemicals
- Patient does not wear the protective gloves used at work
Patients’ adaptive responses to the alterations caused by the disease processes.
- Applies steroid cream to contain the situation
- Washing his hands when he felt the discomfort
Diagnosis of the disorder
Treatment for this includes testing the presence of chemicals and abrasives in his hands. After identification of the chemical; give the relevant cream they can apply to reduce the pain (Benner et al., 2009). Advice patient to use gloves at all times to avoid future repetition. The nurse will follow the following mind map to find the solution in the patient’s condition:
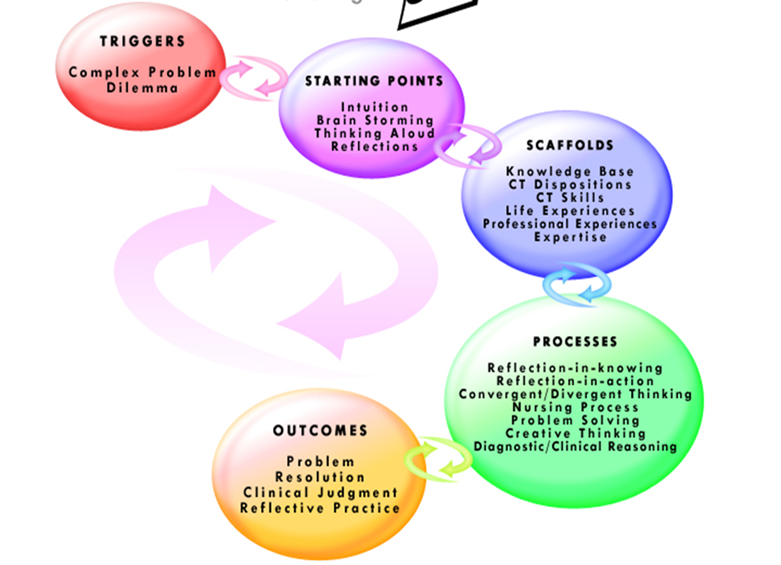
Mind Map
A mind map allows the health personnel develop treatment options when presented with a medical case in the hospital (Terry, 2011). They identify the trigger for the condition a patient has and identifies the long lasting solutions through advice to the patient on what they should do to avoid a repetition for such in the future.
Mind Map: the process a nurse goes through before making a medical decision
Figure 1: Mind map in solving nursing problems
Source: Healthcare Mind Maps (2014)
Scenario 3: 65-year-old woman
Pathophysiology
- Fatigue and loss of sleep at the old age of 65 years
- Loss of interest in food compared to before
Associated alterations
- Sleeping late and waking up early due to the mother who needs assistance
- Restlessness due to the racing heartbeat
Patients’ adaptive responses to the alterations caused by the disease processes.
- Loss of sleep due to the disrupted normal sleeping patterns
- Loss of appetite due to the busy schedule in caring for a sick person who needs her constant attention
- Fatigue from the activities in taking care of her mother who fully depends on her for everything
Diagnosis of the disorder
According to Porter-O’Grady & Malloch (2011), the patient experiences fatigue due to daily activities. She also has a mental breakdown due to the unexpected turn of events as the patient states that she did not think she would spend her retirement taking care of her mother; she should hire help to assist her in taking care of her mother. She should also accept the turn of events even though it is not within her expectations. Ultimately, she may need to slow down her activities that trigger the ‘heart racing’, which might lead to a heart attack.