Case Study: Apple Incorporated
Introduction: Apple’s Strategic Objectives
Apple Incorporated is an American multinational technology company with its head office in Cupertino, California. The company has existed for over forty years and is one of the largest company’s in its industry by revenues, profits, and the number of employees. It has enjoyed sustainable growth and success in recent years due to its high level of innovation and consumer confidence. The company states that its mission is to offer the best user experience to its customers through its innovative hardware, software, and services. Its vision statement is longer than those of other corporations but it points towards maintaining its approach to providing great products to its customers. Apple’s strategic objectives revolve around six key pillars. These pillars are accessibility, education, the environment, inclusion/diversity, privacy, and supplier responsibility (Apple Incorporated, 2020b). The firm strives to develop technologies that empower all people and enhance social programs such as education. The one planet plan strives to create sustainable use of resources including energy and recycling to reduce its environmental footprint.
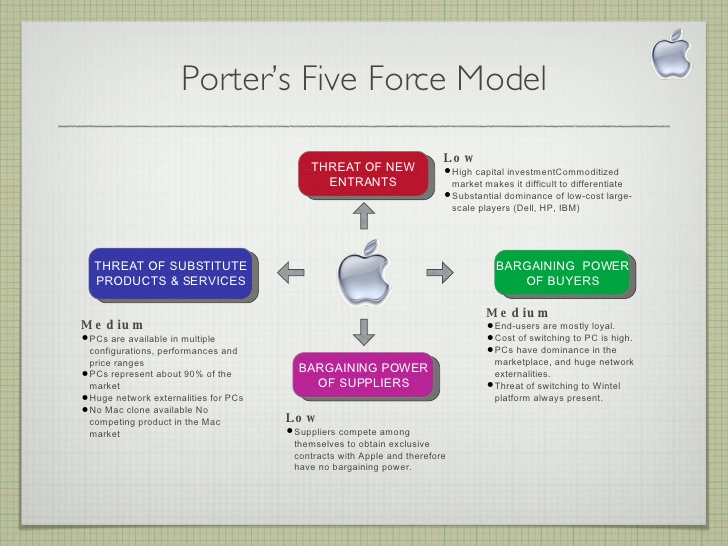
Market Analysis: Porters Five Forces
Threat of New Entrants: Low
Although competition among the leading technologies companies is fierce, the threat of new entrants remains significantly low. The scale at which Apple and other companies operate requires a massive capital expenditure on fixed assets as well as extensive research and development. The companies also have legal rights to some key components that are required for the mass production of computers and mobile phones. Instruments such as patents and rights of use effectively control access to these critical technologies thus reducing the threat of new entrants to immaterial levels.
Industry Rivalry: High
Several factors make Apple’s threat level from industry rivalry high. The company operates in two major technologies industries that are highly competitive. The computing industry has many players looking to provide similar products and services to exiting retail and corporate clients. The mobile phone industry also has many mobile phone manufacturers looking to sell the same products to existing customers. Switching costs are also relatively low in the mass markets thus increasing the level of industry rivalry. Some of the key competitors include Google Inc, HP, Samsung, and Amazon. These are companies that have sufficient financial resources to fund research and development as well as execute aggressive competitive activity to increase their market share.
Threat from Substitute Products: Low
When analyzing market competitiveness, substitute products refer to items that belong to a different class but can perform similar tasks. In Apple’s case, substitute products refer to items such as landlines, calculators, physical calendars, and other organizers that perform the tasks performed by the mobile phone and the computer. The advantages of using mobile phones and computers surpass those of using any substitute product since none of the substitute products available can consolidate different functionality with efficiencies such as the mobile phone and computer. These devices consolidate the functions of a calendar, a calculator, digital camera, entertainment system, and even professional services based on software availability. Therefore, the threat of substitute products is quite low.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers: Weak
Apple’s is a large multinational company that procures product and services on a large scale from its existing suppliers. The company also has a broad range of potential suppliers that it can engage for the supplier of raw material and the required components. This scale and competition among the suppliers increase Apple’s power over the suppliers. The company’s legal team also plays a central role in managing its relationships with existing and potential suppliers thus allowing it to seal any loopholes through legally binding contracts.
Bargaining Power of Customers: Moderate
Two main factors contribute to the bargaining power of the customer. the first is the availability of an alternative and the other is the switching cost involved when the customer opts for the alternative product. Apple’s threat from the bargaining power of its customer is moderate for two reasons. The first is that the switching cost is low and customers have a broad range of other products manufactured by other companies that serve the same purpose. However, the loss of a single customer has no material effect on the company’s market position or financial performance. However, the collective bargaining power of the customer is high since losing a higher number of customers has implications for the firm.
Recruitment and Selection
An organization’s human resource is one of its key assets since they provide the skills required to execute the tasks that are necessary to meet the set strategic objectives. In this light, an effective recruitment and selection process is key especially for companies that operate in highly competitive environments (Gobind, 2014). Apple has invested heavily in its selection process to ensure that it attracts and selects hardworking, committed, and innovative employees to join its ranks. The company also has a unique career advancement policy where each employee’s contribution and commitment to the company plays a critical role in determining their career path.
Training and Development
The technologies industry is diverse and constantly changing thus requiring Apple employees to continuously develop their skills. The company has a unique training schedule that allows its employees to learn from the past mistakes thus preventing them from repeating the same mistakes. The company drives innovation as a training and development approach while using its historical data and information to enhance the acquisition of new skills among its employees (Sikora & Ferris, 2014). The company also develops ad hoc teams to perform different tasks thus allowing the rapid sharing of expertise and experiences since the employees belong to multiple teams working on different teams simultaneously.
Diversity and Equal Employment Opportunities
The company states that it is an equal opportunity employer and that it encourages diversity across its workforce. This is an important strategic decision since it eliminates any deterrents that would prevent employees from seeking to join the firm. The accommodation and appreciation of employees from diverse backgrounds also allow the firm to enhance its employee retention rates thus preventing high employee turnover (Jackson, Schuler & Jiang, 2014). High employee turnover is a major problem in the technologies industry since it could stall research and development. Such stalls may result in delayed product launches thus reducing the company’s competitive edge in the market.
Compensation, Benefits, and Recognition
Although the provision of an ideal work environment has become a critical factor in employee satisfaction and retention. Compensation packages and benefits remain a critical factor for potential and existing employees. Uncompetitive compensation and benefits packages may affect a company’s ability to attract high-quality employees and result in high employee turnover as the existing employees accept better offers from other companies (Jackson, Schuler & Jiang, 2014). Apple recognizes this fact and offers its employees some of the most competitive compensation packages in the industry. The firm also creates some flexibility with the packages thus allowing he employees to select the benefits that best serve their lifestyles.
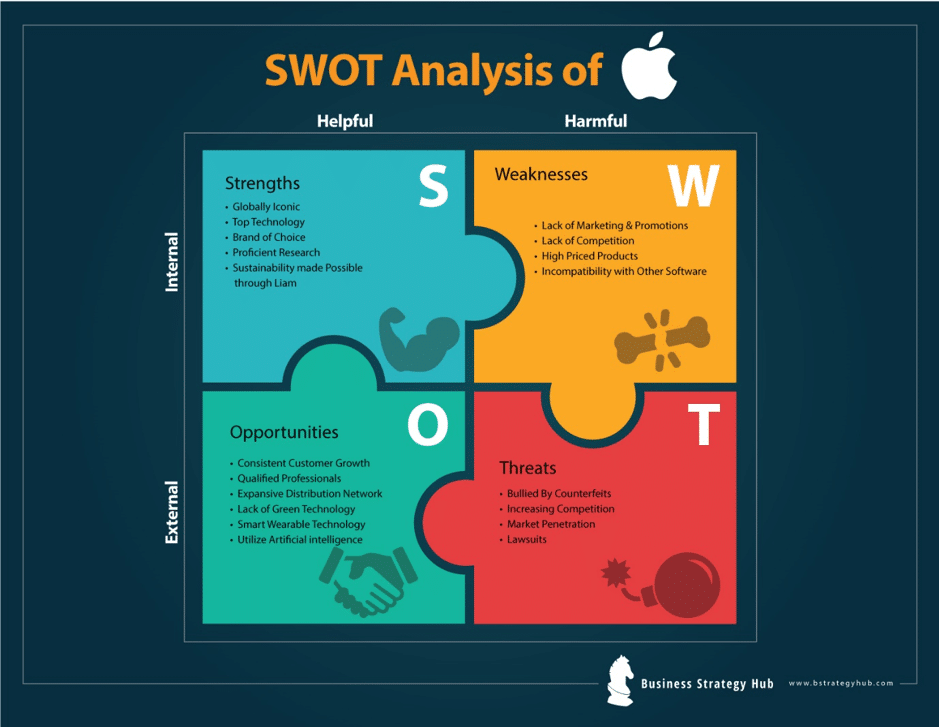
Strengths
Apple is a known brand its products receive positive receptions in different markets when they are launched and in subsequent periods. These two factors create two of the company’s key strengths. These key strengths are its market position and customer confidence. The company has built a strong brand in the technologies market and it has gained consumer confidence over the years (Aljafar, 2016). These are important factors for the company since they build customer loyalty thus driving revenue through the sale of products and service to these consumers. Innovation is another key strength for the company since it allows Apple to maintain its competitive advantage in the industry.
Weaknesses
Apple has several weaknesses that affect its financial performance and its market position in some geographical areas. One of these weaknesses is its products incompatibility with third-party software and accessories (Prakruthi & Ramu, 2018). While strict control of third-party software distributed through its Apple Store application enhances data security for the user, it also limits the development and distribution of software that would allow special functionality on the devices (Smithson, 2019). This gives other platforms such as android an advantage over its products since third party software is readily available from Google Play Store. Apple also has a weak distribution network outside its key markets thus creating delays with the availability of new products, repairs, and support for customers in these regions.
Opportunities
Apple’s key opportunities may result from addressing the weaknesses highlighted above. The company has some of the most innovative products in the world and many users could benefit from their use while the company makes revenues from the sale of products and services. However, its weak distribution network means that it does not address the needs of specific markets effectively (Prakruthi & Ramu, 2018). This includes the provision of after-sale services since most consumers in these markets buy the product from third party retailers who offer a limited scope of support services (Smithson, 2019). Enhancing the distribution network also means that the company executes market-specific strategic activities such as marketing. Improving the compatibility of its products with third-party products could also increase its market share since it makes the products attractive to more people and it does not deprive the existing customer of any usability or experience with the products.
Threats
The coronavirus pandemic presents one of the most unprecedented challenges to corporations across the world and Apple is no exception. The company has closed some of its stores operating in strategic markets in compliance with government directives as well as its response policy to the virus. The interference caused on many other support services such as transport and companies that manufacture components could also affect its ability to deliver if demand for its products does not fall. According to Bary (2020), Reduced or no household income means that its retail business could experience significant declines in the current financial year while the closing of businesses could affect its corporate business segments. Increased competitiveness in the mobile phone markets with players such as Samsung and Huawei maintaining their aggressive product development and market penetration in some of Apple’s key markets.
Financial Analysis
Trend Analysis
Table 1: Apple’s Trend Analysis 2017-2019
| Financial Measure | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 |
| Total Revenues | 260,174 | 265,595 | 229,234 |
| Gross Profit | 98,392 | 101,839 | 88,186 |
| Net Profit | 55,256 | 59,531 | 48,351 |
Table 2: Apple’s Trend Analysis 2017-2019
| Change | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 |
| Total Revenues | -2.04% | 15.86% | 6.30% |
| Gross Profit | -3.38% | 15.48% | 4.66% |
| Net Profit | -7.18% | 23.12% | 5.83% |
Apple managed to increase its revenues, gross profit, and net profit in 2017 and 2018. However, the company experienced a decline in all the three measures in 2019. The company attributed the decline to weak iPhone sales and a significant decline in sales made in China (Rushe, 2020).
Liquidity
Table 3: Apple’s Quick Ratio 2017-2019
| Quick Ratio | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 |
| Cash and Cash Equivalents | 48,844 | 25,913 | 20,289 |
| Current Liabilities | 105,718 | 115,929 | 100,814 |
| Ratio | 0.46 | 0.22 | 0.20 |
Table 4: Apple’s Current Ratio 2017-2019
| Current Ratio | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 |
| Current Assets | 162,819 | 131,339 | 128,645 |
| Current Liabilities | 105,718 | 115,929 | 100,814 |
| Ratio | 1.54 | 1.13 | 1.28 |
Apple maintains healthy liquidity since the current ratio remains above 1 and has improved from 1.28 in 2017 to 1.54 in 2019 (Apple Incorporated, 2020a). This means that it has sufficient current assets to meet its current liabilities. However, the company cannot meet the current liabilities using the cash and cash equivalents. However, the quick ratio has increased from 0.2 in 2017 to 0.46 in 2019.
Profitability
Table 5: Apple’s Gross Profit Ratio 2017-2019
| Gross Profit Ratio | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 |
| Gross Profit | 98,392 | 101,839 | 88,186 |
| Total Revenues | 260,174 | 265,595 | 229,234 |
| Ratio | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.38 |
Table 6: Apple’s Net Profit Ratio 2017-2019
| Net Profit Margin | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 |
| Net Profit | 55,256 | 59,531 | 48,351 |
| Total Revenues | 260,174 | 265,595 | 229,234 |
| Ratio | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.21 |
In terms of profitability, Apple has maintained the same grow profit ratio and has exhibited marginal changes in its net profit margin. This demonstrates strict adherence to the company’s cost structures through cost control and effective management of supplier contracts.
Solvency
Table 7: Apple’s Debt to Equity Ratio 2017-2019
| Debt to Equity Ratio | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 |
| Total Liabilities | 248,028 | 258,578 | 241,272 |
| Equity | 90,488 | 107,147 | 134,047 |
| Ratio | 2.74 | 2.41 | 1.80 |
The debt to equity ratio indicates that the company has a higher reliance on debt than equity to finance its operations. This is an effective cost management approach since debt financing is usually cheaper than equity financing for capital expenditure.
Recommendations
Apple is one of the leading technology companies in the world. Although the company has solidified its market position through innovation and manufacturing high-end products for its customers, it is currently facing stiff competition from other players in the industry. Based on the current challenges that the company is facing the following recommendations could help it mitigate the new challenges and maintain its position as a leader in mobile phone and computer technologies. The company first needs to improve compatibility in its devices to make them user friendly for a larger market. The company also need to expand its distribution network so that it reaches all its customers through its outlets or through authorized dealerships that provide services of similar quality. this will help the company mitigate the competition from other companies that have rolled out aggressive strategies to capture these markets. It will also support the company’s drive for more revenues and higher profits.
Students working on case studies or might need academic help, might find our custom Case Studies Writing Services helpful.
Here you can check some of our dissertation services:
– Dissertation Writing Services
– Write My Dissertation
– Buy Dissertation Online
– Dissertation Editing Services
– Custom Dissertation Writing Help Service
– Dissertation Proposal Services
– Dissertation Literature Review Writing
– Dissertation Consultation Services
– Dissertation Survey Help
Also look at some of our business services
– Business Essay Writing Service
– Business Dissertation Writing Services
– Business Report Writing
– Business Assignment Help
– Business Planning Writing Service
– Business Assignment Writing Service