Global Strategy Development of Lidl
Introduction
The aim of this paper to show the strategic global development of a United Kingdom MNC. Lidl of the UK is the company selected for study. The firm is involved in a retail business and was selected to perform the retail business of different consumer products as the most lucrative target market. In the first few sections, a short description of the business and its worldwide growth is provided. The following part presents the company’s potential worldwide target markets and the rationale for the selection of the target market. Potential difficulties linked to subsidiaries’ operating conditions in the selected markets are described in the two final sections and appropriate recommendations based on the discovered issues are suggested. At the end, there would be a concluding statement.
Company Overview
Lidl is the largest food retailer in the world. It started in Ludwigshafen, Germany, in 1973. its first shop (LIdl, 2021). It had just 3 people in the initial place and only 500 food items. Lidl intended to leave Germany after 1990 but opened its shops throughout Europe. After 1990, This business made the greatest stride in many years and established its shop in the United Kingdom. By the year 2000, its market had been firmly established in the UK. Lidl did not have to look back after that. The company was popular throughout Europe and the United Kingdom. The first shop was established by Lidl in the United States in 2017 with the slogan “High quality, low prices.”
With growth increasing by 12.5% and market share up to 6.1%, Lidl remained the top performing discounter. One of Lidl’s major problems is its competitive market (Blázquez, 2021). There are other businesses worldwide that also operate as food retailers. Aldi, Walmart, Careefour are some of Lidl’s economic market food shops comprtitors. Lidl has recently extended its operations into the United States. But in this industry, owing to inadequate strategic planning, it already faces many difficulties. Lidl operates 53 stores in the US but has not reached its objective since the capacity for execution has not improved. Lidl can only develop if it reflects on its business strategy and methods for dealing with its competition. Lidl will encounter difficulties with political and environmental problems in developing his company in Pakistan. It may overcome such difficulties by adopting appropriate strategic management choices.
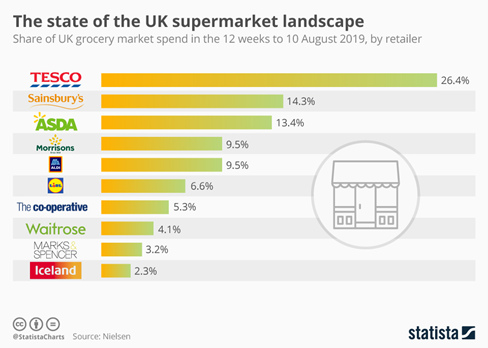
Figure: Lidl Top Competitors in UK
Reasons for International Expansion
Currently, in the UK, there are local participants in the retail sector. Compared with other industries, international actors are much less prevalent in the retail business. Based on this, businesses should choose different advantages for worldwide development in new and profitable areas:
- The first benefit of international expansion may be that new markets are exposed to different business variables. In order to grow its company, Lidl has the potential to establish a new consumer base overseas(Xiao, 2017). Accessing new markets would assist businesses in their particular sector to increase their worldwide market share. In addition, businesses can rapidly access open borders in undisputed marketplaces.
- Another major benefit of global expansion is that local talent is available in the target market. The business may not discover in its own nation skilled and specialized employees who may easily be accessible in the target markets(Yonezawa, 2020). These employees may offer the company with extra advantages and assist in achieving a competitive edge in the market.
- The second benefit of company expansion beyond national frontiers is that business is growing and growing. The business may expand its worldwide impact to new consumers by entering the foreign market(Horner, 2016). This will improve the company’s brand name and appeal on a worldwide platform. Goodwill is an essential immaterial asset that business may readily gain through worldwide growth.
- Competition in the same sector may remain in front of us, another cause for worldwide growth. Research has shown that retail players involved in the manufacture and distribution of home appliances in the international market did not grow tremendously(Mukherjee, 2018). Under these conditions, via its worldwide growth, Lidl would be able to achieve a top place in the market.
- The provision of dependable and convenient service to foreign customers may be another significant cause for international expansion. The establishment of a company in a foreign nation will enable operating expenses to be reduced. This is because the target market will provide inexpensive labor, infrastructure and resources.
Possible strategic choices available to the parent company
A business may examine two key elements in the target markets throughout the expansion process before selecting its target growth market. These two requirements, as suggested by Bartlett and Ghoshal in their developed theories, may include global integration and local response. According to this matrix, companies with strong global integration seek to save costs through economies of scale (Nuruzzaman, 2020). In all operating nations, these companies provide a uniform product. On the other hand, local companies adapt their goods and services in accordance with local tastes and consumer preferences. In view of the worldwide development of Lidl, four types of strategies may be pursued, namely multi-international, global, transnational and international.
- Multidomestic: This type of approach works effectively when the business chooses minimal integration and reactivity. They respond to local consumers’ wants and demands and adapt their goods appropriately(Wheelen, 2018) . The demand for these businesses to standardize their goods is low since their subsidiaries operate independently and have full authority. The Nestle business, with a distinct marketing and sales strategy in each country, is an excellent example of multi-domestic growth. The business has loosely linked subsidiary structures that operate globally and, by adopting this approach, it has achieved great success on the international stage.
- Global: This approach is applicable to businesses which need strong global integration and minimal local market response. In all operating nations, these businesses provide a uniform product. All of the businesses’ subsidiaries are merged in order to accomplish a shared purpose(Wheelen, 2018). The activities and functions of each subsidiary are all very centralized and linked. The parent company is the central entity in which the subsidiaries’ activities are controlled. Pfizer, a pharmaceutical firm, is a common example of this kind of approach.
- Transnational: Businesses aim to be highly integrated and responsive in this kind of approach. A transnational business is a fusion of a global and multi-domestic enterprise (Wheelen, 2018). These businesses generate flexible value chains and adaptable marketing and sales techniques locally. The Unilever Company is a typical example.
- International: This approach works when businesses choose to export a market capture strategy. The businesses manufacture goods and export them to target consumers in their native nations. In general, subsidiaries serve as local channels where the goods are sold to their end-users.
In any of the aforementioned possibilities, Mexico, Pakistan, the United States, Norway, the Netherlands, and Chile may be the potential target markets for the business. Due to their favorable business characteristics, all those nations have encountered international retail firms from other corporations. These nations are very profitable and profitable for retail companies, particularly in the consumer goods and other comparable products sector (Khawaja, 2021). The strategic decision of market entry will vary depending on unique variables from nation to country. The most lucrative target market of all these may be Pakistan, owing to the existence of favorable business variables, according to current market research.
The company will choice multidomestic strategies for expanding into Pakistani grocery market where it will manufacture products local preferences. As a result firm can compete more effectively in Pakistani local market and increase local market share.
Reasons for choosing the target market
Pakistan is the market that has been chosen to expand Lidl. Pakistan’s retail industry was one of the fastest-expanding sectors, contributing nearly 20% to Pakistan’s national GDP. It is the country’s third biggest industry and the second largest employer and employs 15% of the population. Pakistan has about 2 million merchants, 0.8 million of which are FMCG modern channels of trade and general commerce, including kiryana shops, general stores, medical stores, supermarkets, hypermarkets, etc. The market has enormous potential, with the fifth largest population in the world at 220 million, since consumption is always growing. In the past ten years, sales in Pakistan’s retail industry have almost doubled. This continuous development makes Pakistan an attractive opportunity for foreign investors and brands, with the purchase of Engro Foods by Dutch powerhouse Royal Friesland Campina in 2016 providing stakeholders with more trust (Khawaja, 2021).
The country’s youth bulge is one of the main drivers of retail development in Pakistan. With an estimated 35% below 15 years of age, Pakistan has one of the youngest populations worldwide. The economy is well positioned for development with its recent inflow of technology and internet adoption. Pakistan is, however, with Internet users at 27.5% of the population and overall broadband subscriptions at 46.4%-one of the lowest levels of penetration in South Asia. However, the current base has large, untapped potential, and the increased penetration of smartphones has guaranteed that the economy continues to move along a favorable development path. The figures indicated that the production of mobile phones in the first two months of 2021 was 1.2 million, compared with 2.1 million and 119,639 devices manufactured in both 2020 and 2019 (Khawaja, 2021).
PESTLE Analysis
Pakistan’s political status is unstable (BBC, 2019). Pakistan is a nation in which there are a lot of terrorist organizations. So, for the Lidl company, where terrorist organizations are operating, it will be extremely dangerous. Pakistan’s foreign commercial policy is flexible. This may thus be a chance for Lidl to operate in Pakistan.
In (Economics, 2020), the World Bank claims that Pakistan’s GDP was at EUR 320 billion in 2019. Pakistan aims to become one of the top 25 economies in the world by 2025 and one of the top 10 countries with large revenues by 2047. Although it needs to go a long way towards achieving its goals, it should be mentioned that throughout the years, Pakistan has achieved considerable economic development. Too many nations are in debt (Saudi Arabia, USA). Thus, Pakistan’s economic situation is not going to support Lidl. However, Pakistan is a chance country. The total rate of the tariff imposed is 10.09%. The Pakistani government encourages international firms to operate in Pakistan by lowering the tariff rate. Therefore, Lidl has a chance to begin her company there.
Pakistan is the world’s fifth largest nation by population. The population total amounted to about 219 million as of March 2020. The main religion is Islam, while Christianity and Hinduism follow a small proportion of the people. English, Urdu, Punjabi, Sindhi, Pashto, and Balochi are the main languages (BBC, 2019). Anything that conflicts with Pakistan’s Islamic culture won’t stand on the market. Before adopting any strategy, the Lidl strategic manager must examine it. The people of Pakistan should not accept alcoholic goods and beverages such as beer. Everything produced by pigs is likewise rejected by Pakistani Muslims. Therefore, Lidl should only sell non-alcoholic goods.
Pakistan is extremely rapid technologically. In the IT industry, it is well developed. Nearly 70% of Pakistani citizens use smartphones (StatCounter, 2020). This is a chance for Lidl to keep an automated supply chain in Pakistan. By building a distinct Pakistan website, Lidl may conduct its online operations.
In Pakistan, there are a few desert regions. These places are business unfriendly. Furthermore, Pakistan has a lack of clean drinking water (Huma, 2018). This will impact the company Lidl. In Pakistan, there aren’t any major natural catastrophes. This is thus a chance for Lidl to operate in Pakistan without any dangerous circumstances. Managers should take this aspect into consideration when making decisions.
Customer protection and labor laws in Pakistan are extremely stringent (Huma, 2018). However, it’s somewhat less stringent than Great Britain. Therefore, Lidl will not encounter any legal difficulties. Pakistan’s government is a corporate-friendly administration. The customs duties and tariff levels in Pakistan have been constantly lowered to encourage international investment.
Strategic Methods of entry and possible consequences
In light of the particular economic circumstances, businesses may use two approaches to expand the Pakistani market. Direct export is the first method and partnership/joint venture are the second.
- Direct exporting: By these means, Lidl may exportation of the goods through manufacturer or agents of the nation straight to the Pakistani customers. This is helpful if the business needs minimal integration worldwide and low buyer reaction (Radebaugh, 2019). In this way, the companies would serve as a distribution channel for the parent business and would sell the products to the end consumers via retail channels. This approach calls the exporters the manufacturers exporters, and direct exports are termed the products delivered in the consignments. This approach would provide the parent firm numerous benefits because the risk would be much lower. In addition, for the use of this technique the business would not have to undergo law procedures. For the effective use of this method, the business must contact an agent.
- Joint Venture/Partnering: A Partnership is the procedure in which a corporation may partner with a local retail company that has comparable operations in Pakistan. Partnerships, for example, a sophisticated strategic or co-marketing partnership, may be carried out in various ways. In this scenario, the business may create an advanced strategic alliance where local and international companies share manufacturing operations (Ahmed, 2019). This approach may be helpful for Lidl’s growth since British and Pakistani culture are substantially different. The business can understand Pakistani consumers’ likes and preferences and produce tailor-made goods on a multi-domestic basis. The business may concentrate more on local responsiveness and bring forth the independence of its subsidiaries in accordance with this plan.
The Lidl will choose direct exporting, because Exporting is a strategic low risk, which companies feel appealing for a number of reasons. First, in a local market mature goods may discover fresh possibilities for development abroad. Second, in place of creating new goods, some companies consider exporting current products less risky and more lucrative.
Potential Organizational and Managerial Problems faced by Subsidiaries
The following may be summarized of the various difficulties facing the subsidiaries.
Talent acquisition: For companies that operate in the worldwide arena, this may be a difficult job. Talented employees would be hired by subsidiaries with autonomy in operations for the rapidly expanding business sector. It may be extremely difficult to start up a company while at the same time recruiting skills. This increases stress and strain on the subsidiary recruiting team (Schmidt, 2019). Before the process can be completed, the hiring process may not be the same as in the country and the hiring crew should learn properly.
Employee management: The efficient management of employees via different training methods is another problem facing the subsidiary. This is critical to productivity improvement and risk reduction. Because the workers are Pakistani, the company’s management should have a positive feeling towards them (Djørup, 2019). The business is challenged by a uniform corporate culture in its workplace which favors both British and Pakistani workers.
Choosing the right partners: The parent company faces an extremely important challenge while carrying out business abroad. Sometimes, businesses may select the incorrect business partner and deal with business management problems (Hoffmann, 2019). The partner may take advantage of the subsidiary since the subsidiary is totally new to the market and is not familiar with the basics of the business. It is therefore very important to choose the right partner to carry on business abroad.
The Transaction Cost Idea is an essential theory which may be advanced with respect to company internationalisation. This idea speaks about transactions in companies or outside companies. This hypothesis suggests that the transactors must be rational and risk neutral (Parida, 2016). The characteristics, management structures, expenses and skills of all major transactions performed in subsidiaries as well as in parent companies should be linked. Sometimes a few characteristics of transactions may increase expenses, such as accuracy, insecurity and transaction frequency. For market success, these factors should be removed.
The idea of internationalisation, which is oriented towards strategic goals of the business, is another significant theory relevant in this context. According to this hypothesis, companies undergoing this process of internationalisation prefer to invest directly in intangible assets linked to information. After the purchase of foreign companies, other businesses with lack of information and expertise get zero or anomalous returns. First, a business must get internally involved in its local market, namely gaining brand popularity in the local market before being internationalized (Robson, 2019). After internalisation, the process of internationalisation allows a business to enjoy cost reduction. This idea is often seen to be hazardous and extensive in the internationalisation process. This method involves time management and resource engagement. The idea of internationalisation applies to big businesses, such as Lidl, that aim to access markets other than theirs.
Recommendations for overcoming these problems
Lidl has to find answers to the above-mentioned problems and challenges and to successfully manage its international affairs through its subsidiaries. The business must locate the appropriate personnel for its subsidiary in Pakistan. The firm must also address training and managerial issues in the overseas subsidiary and select a good partner for the company. In this regard, some suggested solutions may be seen below:
Pakistani businesses are following a strategy of employing university workers and different vocational institutions. This method is called “new recruiting of graduates.” The business, as a subsidiary of Pakistan, may use this technology. The new pupils are willing to join a business and may recruit them through special screening (Kossev, 2019). The screening procedure may involve stages such as a written test and a one-to-one examination. This procedure may be helped by Pakistan’s partner because he knows well about the recruiting efforts in Pakistan. Before using the individual, the recruiting team must be able to understand the candidate’s potential.
The training and management of workers should be carried out progressively throughout stages in order to address the doubts and questions of each individual. Certain staff may be ambitious or fast learners. The duration of their instruction may be dull. Businesses should provide these workers with on-the-job training (Bowen, 2019). Pakistani enterprises have another distinctive rotating culture where workers are often moved from one department to another. This method is used by the subsidiary, which allows the workers to obtain a homey working environment.
For the operation of a subsidiary abroad, it is extremely essential to choose the appropriate partner. The main factors are the partner’s ability to offer the parent company complementary resources and capacity. These resources may be technological expertise and other comparable factors. The business should prepare a certain number of talents and then choose its partner (Dinca, 2019). The business may analyse its skills and compare them to those of the partner, according to the strategic goals of the organization. Local market knows how, distribution channels, post-sales support networks, brand visibility and regulatory expertise may be other significant considerations for selecting a partner.
Conclusion
Lidl is a renowned UK retailer. It took the UK’s 6% market share. It may be inferred from this debate that Lidl, in other words, can grow its market in Pakistan in order to get lucrative returns. Since the firm is active in the retail sales of home equipment, Pakistan may be an enterprise-wide profitable market. That is because consumers are eager to spend money on the purchase of highly available consumer goods. The business will use multi-domestic expansion in Pakistan, where it produces goods depending on local tastes. It will go direct exporting in the market through exporters or agents of Pakistani market. Lidl strategic managers may thus decide positively to develop their operations in Pakistan. The international market problems encountered by subsidiaries may be addressed by means of the suggested remedies.