REPORT ON CAUSES OF STAFF TURNOVER IN HONG KONG BRIGHT HOSPITAL
Abstract
The healthcare sector is facing a shortage of medical staff due to the turnover rates experienced around Hong Kong and the world. Many of the healthcare professionals work in two or more hospitals to help reduce the turnover gap. However, its effects are still being felt by major healthcare providers such as Hong Kong Bright Hospital. Elite Management Consultants, an experienced consultancy firm, conducted a study on the Hospital’s medical staff to understand the causes of staff turnover and recommend ways to reduce the numbers and solve the situation. The study was carried out in two months and received a good reception from the Hospital’s medical staff. The study employed all the processes of literature review, research methodology, analysis and interpretation, and the presentation of the results. Qualitative research methods such as questionnaires, interviews, and focus groups were used to collect data from sampled medical staff. After data analysis, the study identified long working hours, poor growth and development criteria, lack of job autonomy, and ineffective recognition and feedback systems are the causes of high turnover rates. Following the results and analysis supported by literature review on previews studies, conclusions and recommendations are made. The study recommends that the Hospital should invest in the employees to create a valued relationship with them. It should reward and accordingly compensate the employees’ contributions, perfect their selection process, give considerately, thorough, and timely feedback to employee concerns, complaints, and recommendations, and ensure a good life balance between work and personal lives of the staff. Further, the study report provides comments for future research and study areas.
1. Introduction
1.1 Historical Background
The healthcare system in Hong Kong has seen a rise in private hospitals in the last decade. The number of people employed in the healthcare sector has seen an increase. This can be attributed to the fact that more people are studying medical courses now than before. In addition, it can also be related to the increase in diseases related to lifestyle and environmental pollution. The situation can also result from a growing population and other effects of tragic diseases such as cancer and the COVID-19 pandemic. Nonetheless, more hospitals are opening up to provide medical services. The best healthcare providers are mostly busy providing their services to patients across Hong Kong. The Hospitals have reported high rates of employee turnover cases. New job markets created by the healthcare sector growth have provided hospitals with a difficult time managing and retaining human resources. Recently, many healthcare professionals work in two or more hospitals and medical centers by taking up different shifts to fill the staff gaps left by the shortage (Hung & Lam 2020, p. 3834).
Hong Kong Bright Hospital is among the leading private Hospitals in the City. The healthcare center provides one-stop medical services that include physical examinations, computer scans, 24-hour emergency services, surgery, and various specialist medical services. Given its strategic position and wide range of medical services, the Hospital is always busy with patients. Thus, the Hospital requires experienced employees to be able to meet the patients’ needs when required. To this end, the Hospital must retain its currents employees to maintain a balance between staff and patients’ service provision. According to a Private hospitals Organization report, the Hospital has seen many employee turnovers, making it challenging to maintain a good and experienced medical workforce. The Hospital’s management requires a professional company to help mitigate the turnover risks it is facing. This study by Elite Management Consultant will understand the causes of staff turnover and offer possible ways to reduce them in Hong Kong Bright Hospital. In addition, the consultancy will develop ways to avoid similar management crises in the future. The report identifies and understands the working hours and shifts, growth and development criteria, employee selection models, decision-making and autonomy, feedback, and recognition system.
1.2 Research Aims
The research objectifies the main causes of employee turnover, which will help the company form its base for formulating and conducting the study.
1.3 Research Question and Objectives
1.3.1 Research Question
The study by Elite Management Consultant will purpose to understand the causes of staff turnover and offer possible ways to reduce them in Hong Kong Bright Hospital. In addition, the consultancy will develop ways to avoid similar management crises in the future
1.3.2 Research Objectives
The research objectifies to identify the main causes of employee turnover. The objectives are formed on the following basis.
- Working Hours and Shifts
The study will learn and identify all medical staff’s various working hours and shift changes. This objective will allow the study to identify the hours each member’s department staff work and how the shifts are turnover. Further, it will provide a flat area for comparison with other departments to create a lean system.
- Growth and Development Criteria
This objective will look to access the criteria used in providing growth and development for the medical staff. The standards used will provide information on whether the staff is aligned with them or feel dissatisfied with the criteria.
- Employee Selection Models
To access the models used by the hospital management in staff selection will help identify the effectiveness and considerations taken into place during the process. This will help in understanding and creating a standardized and neutral selection process.
- Decision making and autonomy
To identify the staff management style in the hospital. This objective will help Elite Consultancy Management to learn the level of autonomy the medical staff is given and the level and involvement in decision making.
- Feedback and recognition System
The objective will study the various ways used by the hospital in recognizing employees’ good work and skills. It will further examine the various instruments of offering feedback to employee concerns, complaints, and recommendations. This will help understand and create a working and effective recognition and feedback sys
1.4 Report Structure and Route Map
The study begins with the review of literature that involves a survey of scholarly sources related to the research objectives. Secondly, it follows the research methods used in data collection where data from the staff is collected and recorded for analysis. The analysis part will include data cleaning and categorization to create meaningful and easy analysis. The third part will interpret findings and provide answers to the research questions and objectives. Then the final part is the drawing of conclusions and offering recommendations to the research objectives. It will answer the study questions and objectives while supporting the main purpose of the research. The study’s findings are addressed and aligned with the literature review, and the ethical issues experienced during the study are highlighted. Elite Management Consultant will make recommendations to Hong Kong Bright Hospital. Further, the section provides comments for future research and study areas.
2. Literature Review
2.1 Working Hours and Shifts
Staff turnover is the percentage of employees that leave a business and need to be replaced over a certain period (Grace et al. 2019, p.38). Individuals join and leave companies due to many reasons, and it’s a typical scenario. The reasons for leaving are numerous, and some unavoidable. But when employees leave due to unhappiness at the workplace, the company’s management needs to reconsider many aspects of the relationship and working environment. According to Willard-Grace et al. (2019, p.38), burnout from long working hours and numerous shifts has led to turnover among medical staff. The finding from the study concluded that high rates of burnout and turnover are compelling problems for clinicians and primary caregivers. Although the authors acknowledge that there are other multifactorial reasons for medical employee turnover, burnout from long shifts is one of the most common causes. The burnouts deny the medical staff good rest time, social engagement, and other physical activities. Some aspects of life that some staff values. Further, in phases of economic pressure, asking employees to take up extra responsibilities without extra allowances and remunerations is another cause of staff turnover. Most may agree to take up extra hours, but they will feel frustrated and overworked when the job schedule interferes with their personal lives. Overworking employees contributes to high turnover rates since it creates fatigue and frustrations that affect the everyday lives of the staff (Grace et al. 2019, p.38).
According to Harun (2020, p.79), the working hours and long shifts in the healthcare sector have been identified as one of the reasons for employee turnover. Given the nature of their work, most medical staff cannot leave patients unattended without a replacement with another staff. They end up working long hours until another medical staff comes to release them from their shift. Sometimes, the shifts change is dependent on another personnel from a different hospital or medical center. Thus their delay makes the staff on shift stand by even after their shift ends. Lack of proper planning of adequate hours and shift change contributes to a vast number of medical staff turnover. The author explains that poor shift and working hours planning affect the employees physically, socially, and mentally, hindering their maximum effectiveness for future work hours and shift.
2.2 Growth and Development Criteria
Al Mamun and Hasan (2017, p.69) state that poor growth and development among employees is a recipe for staff turnover. The authors narrate that every member of an organization finds the opportunity to learn new skills and participate in developing the organization and their individual development as essential. When medical staff feels trapped or stagnant in position and daily activities, they are likely to look outside for other companies that might present better opportunities. Development of skills and involvement in developmental ideas provide employees with the avenue to grow and network with other professionals in their areas. Therefore, employees need to witness their growth and development for them to be easily retained by an organization. A company without a clear vision of development and growth faces a massive number of employee turnover.
Medical staff, like any other organization employees, value the opportunities for growth presented by their organizations. They look forward to a better future with the organizations they work for. The future includes career opportunities, status, and better income. According to Al Mamun and Hasan (2017, p.70), employees’ personal growth and development are mainly based on improving their working status and increasing remunerations and allowances. Therefore, medical centers need to offer progressive opportunities for their employees to grow and develop in all aspects. In addition, in competitive industries such as the healthcare sector, where private hospitals are on the rise, emerging hospitals offer better pay and growth opportunities as incentives to lure medical personnel to their camp. Without such opportunities, an organization will find it hard to retain its employees. Further, it is appealing for the management to frequently reassure its employees on its developmental goals that often involve their individual developments.
2.3 Employee Selection Models
Mahoney et al. (2020 pp.39-48) explain that poor selection process of employees may render the organization low retention rate. It is challenging to find a perfect employee for a job. However, forcing a task or job to match an employee who is not fit for an organization is more challenging. The undertaking of the position’s requirement will prove difficult for the employee, especially when they do not understand it well. It will keep the company lagging, and the employee may always feel under pressure to take up the tasks to satisfy the management. The desperation on the management part to fill the position will collide with the pressure for an employee to do their job, which will lead to employer dissatisfaction and employee devaluing and unhappiness. The result will be the employee looking forward to other fitting organizations that align with their job expertise. The authors emphasize that incompatible staffs are unlikely to be content with their new unfitting positions.
The employee selection and placement process require a step-by-step process that ensures the resumes are screened and background checks are done on previous worked and references contacted. It also includes an essential process of in-person employee interviewing to express the areas they are good at working effectively (Mahoney et al. 2020 p. 42). Bypassing or underplaying the process creates a vacuum in the selection process, leading to management placing employees in less effective departments. This is clear, especially in hospitals where a wrong selection may lead to even further damage. With time, the involved employees will seek reprieve from other medical centers where their skills will be highly utilized. Mass employee turnover may be caused by wrong selection criteria or desperation to fill in positions due to work or market demands (Mahoney et al. 2020 p. 44).
2.4 Decision making and autonomy
According to Boakye et al. (2021, p.138), supervisory support, employee engagement, and interpersonal support deliver employee retention. In addition, the authors explain supportive management helps the employees to feel comfortable and happy in providing their services to clients and achieving their set objectives. They feel free to undertake their tasks and approach their supervisors if they might face any obstacles. However, an environment where there are no support and engagement systems derails the effectiveness and confidence of the employees. The workforce may always feel intimidated when their supervisors are around their workplace. Following this observation, employees will always bottom their inquest and disengage with management, leading them with no supervisory and interpersonal support. With time, such employees will start sorting for better supportive working environments. Poor or lack of supervisory, interpersonal, and employee support is a significant cause of employee turnover in all industries (Boakye et al. 2021, p.139).
Additionally, Boakye et al. (2021, p.141) explain that micromanaging hospital staff leads to distress in the workplace. The inability to show trust and capability among employees creates a lack of confidence and freedom. Most healthcare employees enjoy job autonomy, where they are allowed to undertake their tasks peacefully and with complete confidence in themselves from the management. Staff that is micromanaged are likely to grow frustrations and work ineffectiveness. It kills their enthusiasm and morale to carefully do their work to perfection since they are constantly worrying about the comments of their supervisors. Giving autonomy of decision-making to employees grows their confidence and effectiveness and promotes innovation and creativity in the organization. There are mutually beneficial ways of expressing dissatisfaction and correction to employees that can be used such as experience and skill sharing sessions. When employees feel frustrated from micromanaging supervisors, they are likely to leave and contribute to high rates of turnovers.
2.5 Feedback and recognition System
Work engagements such as proper, timely, and constructive feedbacks allow the employees to feel valued and engaged in the development of the organizations (Zhang et al. 2018, p.988). Every employee feels valued when they received responses about their concerns, contributions, and recommendations on various topics at the workplace. It works better when the feedbacks are on time and constructive. It shows that the management is attentive to their contributions and needs. In cases where an employee may be struggling at work, timely and honest feedback from the supervisor may help them refocus and take on the workloads. However, high staff turnover is attributed to a lack of feedback, which pushes the employees away. In addition, ignoring employees’ concerns by not providing helpful feedback leaves them discouraged and struggling, eventually leading them to give up and leave the organization.
According to Zhang et al. (2018, p. 988) most employees experience job satisfaction when they are fairly recognized when they do a great job. Every little appreciation from the management goes a long way and accumulates to job satisfaction and retention. When employees feel that the organizations merely recognize their efforts, they feel discouraged and lack the confidence to do future jobs effectively. Appreciations boost the morale and enthusiasm of the employees to work even harder to attain the organization’s goals and objectives. Lack of recognition makes employees who work effectively and efficiently feel devalued and think they are not seen as contributing to the organization. Further, lack of appreciation and recognition kills the creativity and innovative aspects of a workforce, making them seek avenues where their talents and efforts will be well appreciated.
3. Research Methodology
3.1 Research Assumptions & Philosophies
The research uses several levels of data analysis to assist in analysing the data since the study is seen as a series of cogently related stages. Reliability and Validity were employed as basis of the qualitative approaches in the data collection and analysis. Reliability is the point of consistency to which a tool measures the aspect it is supposed to measure (Lakshmi and Mohideen 2013, p.2752). Questionnaires, Interviews, and Focus groups exposed consistencies in responses from specific departments. Reliability was achieved by minimizing data collector bias through the administration of questionnaires and focus groups. Further, the environment where interviews were carried out was comfortable and private to ensure the subjects were confident and physically comfortable. The windows offered unrestricted airflow, and the chairs were comfortable, and a bottle of refreshment was also offered.
The validity of a tool is the point to which a tool measures what it is projected to measure (Hayashi et al. 2019, p.99). To ensure content validity of the study, the questionnaires included questions on the knowledge of the subjects on the study questions and ways to make them reduce. The questions on both questionnaires and interviews were based on information acquired from the literature review. The validity was ensured through consistency in questionnaires administration and queries probed in the interviews. The questions and topics of discussions were framed in modest language for stress-free consideration and answering. All employees advanced to partake in the study completed the three-part data collection exercise. The study required to be strategic to limit the investment strains on subjects to increase participation. This was a result of the time and nature of the work of the medical staff.
Pretest was used as minimize the flaws of the data collection method. Pretest refers to prior administration of the questionnaires to understand its flaws (Willis 2016, p.360). The study prearranged a meeting with seven medical staff and administered the questionnaires and interview questions at Hong Kong Bright Hospital to pretest the questions. All the subjects answered the questions, and none of the questions were amended.
3.1.1 Ethical Considerations
The research process requires more than expertise and professionalism; it calls for integrity and honesty. The two are incorporated to protect the rights of the subjects of the study. The ethical aspect of the study recognized the rights to informed consent, confidentiality, anonymity, and self-determination (Cacciattolo 2015, p. 56).
The permission to conduct the research was granted by the Board and management of Hong Kong Bright Hospital in writing to Elite Management Consultants. The consent of the subjects was obtained before the start of the data collection process. The participants were well-versed of their right to participate, decline or pull out at whichever time from the process. The drive of the research was explained to the participants, and assurance of no potential risks was made.
Confidentiality and anonymity were maintained in the whole research process. The process ensured anonymity by concealing the names of the subjects throughout the study process, and the consents were detached from the questionnaires and interview logs. Confidentiality was maintained by not revealing the names of the subjects, even when reporting the study’s findings. Self-determination was upheld by informing the employees about the report’s purpose and allowing them to choose whether to participate or not voluntarily. It was also observed by avoiding any manipulation of research design or data collection process. The answers were truthfully recorded during interviews. During the interpretation process, the data were aligned with the original subject answers to eliminate data manipulation errors.
3.2 Research Strategies
3.2.1 Research Setting
The study was carried out at Hong Kong Bright Hospital, located in the City of Hong Kong. The Hospital has 250 medical and Hospital staff. Given the Hospital’s busy schedule, they cater for over one thousand patients a day from all over Hong Kong.
3.2.2 Study Population and Sample
A population is a component that meets the sample standards for addition in a study (Simon et al. 2017p. 456). The study population included five employees from each Hospital department of Hong Kong Bright Hospital. A convenient sample of seventy subjects from all 14 departments was selected from the Hospital. A sample is components selected with the goal of identifying something from a population from which they were selected (Simon et al. 2017p. 456). The convenient sample used in the study appeared at the right place and the best at the time of the study. Each personnel identified by the study that met the sampling conditions were recorded up to the sample size of 70 was acquired.
The sampling conditions included staff members who worked long hours in the past three months, those who worked regular shifts, those that worked inconsistent departments for over six months, those that worked in pressure areas such as Emergency rooms and operation areas, and those that work in the human resource areas.
3.3.3 Data Collection Procedure
Questionnaires were individually distributed by the researchers to the employees. The questionnaires were done over 12 working hours and were collected at the end of the day. The researchers did the interviews in two different conference rooms for a duration of 15 minutes for each interview. The nature of work influenced the allocation of time in the Hospitals. The study took the most minimal time available to allow the staff to get back to serving the patients. The focus groups were conducted during tea and lunch breaks to utilize the social gatherings at times. The discussions took 45 minutes per session for two sessions. The data was collected for two weeks.
3.3 Research Design
The study methods chapter highlights the validity of the research setting and methods used in data collection. It explains the samples used and the reasons for the choice, the materials, and the types of tests done. It also includes the tests procedures and the time allocated for interviews and questionnaire filling. A qualitative approach was employed to examine the cause and effect interactions among variables systematically. In the study, further information was collected through questionnaires distributed by the researcher to the subjects of the study. A descriptive survey was selected to get an accurate account of individuals’ opinions, knowledge, and situation. The design was chosen to align with the study’s objectives, namely to identify the causes of staff turnover and the remedies at Hong Kong Bright Hospital.
3.4 Research Project Implementation
Questionnaires, interviews, and focus groups were used as data collection instruments. Questions used in questionnaires and interviews are designed to elicit information from the subjects (Clark & Vealé 2018, p.482C). The questions from the interviews were administered orally, and the answers were recorded for further use in the follow-up process of data analysis. The questions used in questionnaires were written and printed and handed out to subjects over a specific period. Though questionnaires are advantageous and fast, they have a weakness of validity and accuracy where subjects may not reflect their genuine opinions about a study topic (Clark & Vealé 2018, p.482C). Some information may be lost due to the brief nature of the questions.
The questionnaires used consisted of two sections. One closed-ended question and the other section had a few open-ended questions where the staff members would explain or express their feeling using a few sentences. Open-ended questions were included to allow the subjects to express their feeling in their own words in writing without limitation by the research (Krosnick 2018, p. 439). Close-ended questions were used due to their ease of administration and analysis. In addition, subjects find them easy to fill over a certain period. All the questionnaires were in English since the Hospital uses English to communicate to its employees, and all employees have accepted it. Instructions on answering the questionnaires were attached to assist the subjects on whether to tick, circle, or explain a question.
The interviews were carried out on closed doors in the conference rooms of the Hospital. They were done for each subject upon completion of the questionnaires. The face-to-face interviews followed the questionnaires since the subjects already had a clue of the study objectives, thus making it easy and efficient to answer the questions in the interviews (Palmieri 2020, p.109). The interview questions were divided into two sections. Section A aimed at getting general information about the Hospital’s working environment and its management. This information could assist the study in interpreting and categorizing the results. Section B looked at getting information about specific departments and their supervision. This information would help categorize and understand the views about each department and its contribution to the achievement of the study objectives.
The focus groups were conducted as the last part to allow the subjects to discuss the questions and share opinions about the research objectives (Gammie 2017, p. 373). The focus groups contained seven members, each from different departments. The discussions included hints on various topics to be discussed. The main aim of the focus groups was to identify and explore how the subjects think about the multiple issues related to employee turnover and express their opinions on why it is high in Hong Kong Bright Hospital. The final results from the focus groups would be submitted at the end of the discussions and stored for analysis.
4.0 Results (Findings and Analysis)
The study’s main objective was to investigate the causes of staff turnover at Hong Kong Bright Hospital. This chapter provides the findings and analysis of the results of the accumulated figures. Data analysis is the process used to reduce large data collected to interpret and insightful data that can be discussed and understood (Richards & Hemphill 2018, p.225). The data is brought to a good structure, order, and meaning for the Hong Kong Bright Hospital. The analysis process used was qualitative data analysis methods. The study manually read the answers and responses from the data collected and created a database for categorization and placement into readable figures. Narrative analysis was used to analyze the subjects’ opinions and responses from the data collection methods (Richards & Hemphill 2018, p.225). The questionnaires, interviews, and focus groups provided qualitative data analyzed and presented in tables and charts.
4.1 Results
The table below shows a compiled results from the questionnaires Section A.
| No | Question | Yes % | No% |
| 1 | Are you satisfied with the maximum working Hours? | 35 | 65 |
| 2 | Are the Shift Changes Favorable? | 36 | 64 |
| 3 | Are there Growth and Development possibilities? | 32 | 68 |
| 4 | Are you satisfied with the job selection method? | 45 | 55 |
| 5 | Are you happy with your work area/ Department? | 60 | 40 |
| 6 | Are you happy with your involvement in decision-making processes? | 42 | 58 |
| 7 | Do you enjoy job Autonomy? | 31 | 69 |
| 8 | Are you happy with job recognition systems? | 28 | 72 |
| 9 | How would you rate the feedback system of the Hospital? | Good= 33% | Bad= 67% |
The table above represents the percentage of responses given by employees on how they feel above different study objective questions.
The charts below show the results from Section B of the questionnaires.
Q.1 what would you say about the overall human resource management of the Hospital?
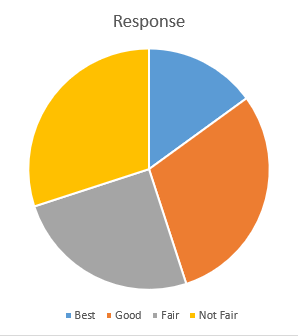
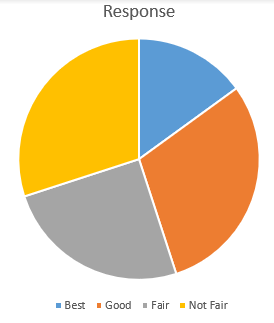
Figure 1 Human Resource Relationship Responses
The chart above shows the distribution of responses on how they feel about Human resource management at the Hospital. The responses were categorized into four parts: best, good, fair, and not fair.
Q.2 would you Consider leaving work anytime soon? And why? Would you please provide an explanation?
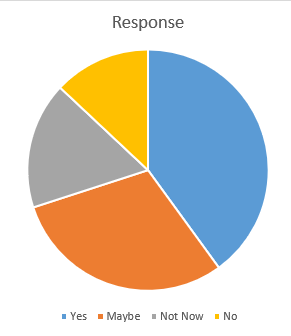
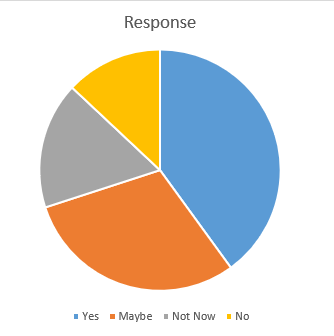
Figure 2 Leaving Working Responses
The chart above shows the distribution of responses to whether employees would consider leaving their work at any time. The responses were categorized into four parts: Yes, Maybe, Not now, and No.
The explanation to the above question was categorized into four main parts, as shown in the table below.
| Explanation | % |
| No room for growth or development | 69 |
| Long Working Hours | 62 |
| Poor relationship and support from management | 70 |
| Inadequate Remunerations and allowances | 72 |
Table 2 Reasons for leaving work
The table above indicates an overall percentage of the explanations given to the answers in the interviews. The main answers were categorized into four parts that provided a brief but inclusive bracket of the subject’s answers.
The table below shows the results from the interviews
| Question | Response | Overall % |
| Green Red | ||
| Do you enjoy doing your job? | * | 60 |
| Are the working Hours and Shifts favorable? | * | 62 |
| Is your department supportive of your personal development? | * | 65 |
| How many times have you been recognized for good work? | * | 20 |
| How is your work relationship with your immediate supervisor? | * | 45 |
| Are you happy with the promotion system? | * | 32 |
| Describe your work environment with a single word | * | 67 |
| Do you look forward to coming to work? | * | 53 |
The green label in the table indicates a positive response, while the red label indicates a negative response. The stars show the intensity of respondent’s response either positively or negatively. The overall % part indicates the percentage at which the subjects expressed their overall positive results over negative results and vice versa.
The chart below shows the main responses from the focus groups discussion.
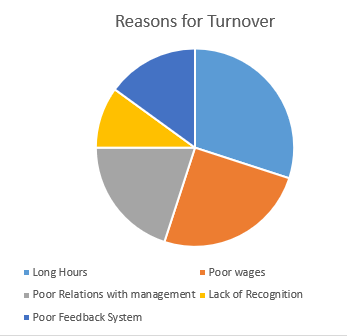
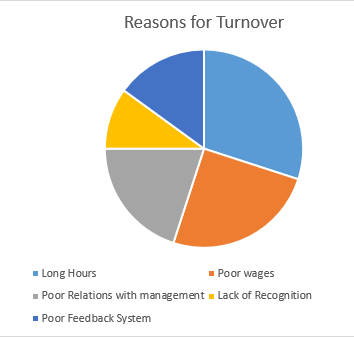
Figure 3 Focus Groups Discussion’s Reasons
The chart above represents the main outcomes and results from the focus groups. The results were categorized into five reasons: long hours, poor relations with management, poor feedback system, poor wages, and lack of recognition.
4.2 Discussion
4.2.1 Interpretation of Findings
The objective of the study was to understand the causes of staff turnover. Following the data collection, data analysis, and results processes this section interprets the facts and figures (Richards & Hemphill 2018, p.228). Guided by Literature review and research objectives, the findings are categorized into five major causes, as explained in the following paragraphs.
The table below shows the overall answers given in Section B of the questionnaires.
The chart shows that 40% of the participants expressed that they can leave the workplace, 30% expressed some doubt about leaving, and 17% said they showed that they would not go now, while 13% revealed that they would never leave.
4.2.2 Working Hours and Shifts
Results of the questions from Section A regarding this objective are indicated below.
| No | Question | Yes % | No % |
| 1 | Are you satisfied with the maximum working Hours? | 35 | 65 |
| 2 | Are the Shift Changes Favorable? | 36 | 64 |
Table 4 Working Hours Responses
The response from question one shows that 35% of the respondents are satisfied with the maximum working hours, while 65% showed dissatisfaction. 35% of the sample population represents 25 employees, while 65% represents 45 employees. This indicates that 45 out of the 70 participants are not satisfied with the maximum working hours. The Second question demonstrates that 36% find the shift changes favorable while 645 find the changes unfavorable. This figure translates to 25 participants find the shift changes favorable while 45 participants found the changes unfavorable.
From Section B of the questionnaires, the following table provides an explanation of why the participants would consider leaving work.
| Explanation | % |
| Long Working Hours | 62 |
| Inadequate Remuneration and allowances | 72 |
Table 5 Working Hours Answers for Section B
The results show that 62% of the participants gave long working hours as the main reason they would consider leaving work at Hong Kong Bright Hospital. This figure translates into 43 people from the sample. Meaning 42 employees out of 70 would leave work because of the long working hours. The second explanation indicates that 72% of the subjects indicated inadequate wages and allowances as the reason they would consider leaving their work at the Hospital. This translates to 50 people out of 70.
The table below shows the response from the interview on a question of the research objective.
| Question | Response | Overall % |
| Green Red | ||
| Are the working Hours and Shifts favorable? | * | 62 |
Table 6 Favorability of working hours and Shifts
The results indicate that 62% of the participants gave a negative opinion on whether they find the working hours and shifts favorable. That translates to 42 out of 70 participants expressing negative opinions about unfavorable working hours and shifts.
The chart below shows results from the Focus groups discussions.
Figure 5 Long Hours Percentage from Focus groups
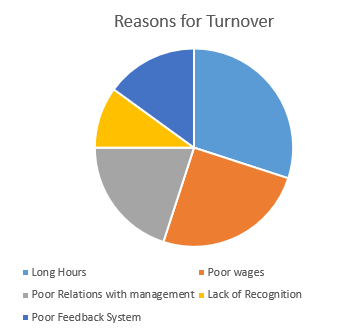
The results show that 30%, the most, was attributed to long working hours. This indicates that out of five reasons given, long working hours received the largest share, showing that it was discussed as the main reason why employees leave their work at Hong Kong Bright Hospital. Additionally, 25% of the reasons from the focus groups indicated poor wages as the second reason for high employee turnover.
4.2.3 Growth and Development
The table below shows the results from questions in Section A of the questionnaire.
| No | Question | Yes % | No% |
| 3 | Are there Growth and Development possibilities? | 32 | 68 |
Table 7 Results from Section A on Growth and Development
The results indicate that 32% think there are growth and development possibilities while 68% do not. This shows that 22 participants believe that there are growth opportunities in the Hospital, while 48 out of 70 participants think there are no growth and development opportunities.
The table below shows the results from a follow-up explanation on why employees would consider leaving work.
| Explanation | % |
| No room for growth or development | 69 |
Table 8 Explanation for leaving work
The results indicate that 69% of the participants gave a lack of room for growth and development as a reason they would consider leaving work at Hong Kong Bright Hospital. This translates to 48 out of 70 participants explaining that there is no room for growth and development in the Hospital.
The table below shows results from the interview on the research objective
| Question | Response | Overall % |
| Green Red | ||
| Is your department supportive of your personal development? | * | 65 |
Table 9 Interview Results for Growth and Development
The results show that 65% of the participants negatively responded to whether their departments support their personal development. This translates to 46 out of 70 participants expressing a negative opinion about the lack of departmental support on personal development.
4.2.4 Employee Selection Models
The table below shows the results from questions in Section A of the questionnaire.
| No | Question | Yes % | No% |
| 4 | Are you satisfied with the job selection method? | 45 | 55 |
| 5 | Are you happy with your work area/ Department? | 60 | 40 |
Table 10 Results from Section A on Employee Selection
The results indicate that 45% of the participants are satisfied by the selection model of the Hospital, while 55% are not. Another 60% of the participants show that they are happy with their department work area while 40% are not. These results translate that 32 out of 70 participants are satisfied with the job selection model while 38 employees are not. On the fifth question, 42 participants expressed happiness in their working area, while 28 out of 70 are not happy with their work area.
The chart below shows the opinions of the participants on what they think about the human resource department.
Figure 6 Relationship with Human Resource
The results show that 15% of the participants feel that the human resource department is the best, 30% feels it is good, 25% of them think the department is fair, another 25% thinks the department is fair, and 30% of the participants showed that the department is not fair.
The table below shows the results from the interview about the research objective.
| Question | Response | Overall % |
| Green Red | ||
| Describe your work environment with a single word | * | 67 |
| Do you look forward to coming to work? | * | 53 |
| Are you happy with the promotion system? | * | 68 |
Table 11 Results from Interviews on Employee Selection
The responses from the interview show that 67% of the participants described their overall working environment negatively, while another 53% narrated that they look forward to coming to work. This result indicates that 47 participants from the sample of 70 described their working environment negatively while 37 of them said they are looking forwards to coming to work. The third column shows that 68% of the responses from the interviews were negative when asked whether they are happy with the promotion system. This translates to 48 out of the 70 participants who are not pleased with the promotion system.
4.2.5 Decision Making and Autonomy
The table below shows results from Section A of the questionnaire related to this research objective.
| No | Question | Yes % | No% |
| 6 | Are you happy with your involvement in decision-making processes? | 42 | 58 |
| 7 | Do you enjoy job Autonomy? | 31 | 69 |
Table 12 Results from Section A on Decision making and Autonomy
The results indicate that 42% of the subjects are content with their participation in the decision-making procedure in the Hospital, while 58% are not. This shows that 29 out of 70 participants are content with their decision-making procedures while 41 employees from the study are not. The results from the seventh question show that 31% of the participants enjoy job autonomy while 69% do not enjoy it. The figures translate into 22 participants that enjoy job autonomy and 48 employees who do not.
The table below shows the results from Section B of the questionnaire
| Explanation | % |
| Poor relationship and support from management | 70 |
Table 13 Explanation from Section B
70% of the participants explained that they would leave their job because of poor relationships and support from the hospital’s management. That translates to 49 out of 70 participants who feel that would leave work due to poor relationship, and lack of support from the administration.
| Question | Response | Overall % |
| Green Red | ||
| How is your work relationship with your immediate supervisor? | * | 45 |
Table 14 Results from Interview on Supervisory support
The table indicates that 45% of the interviewees expressed negative comments about their relationship with their immediate supervisors. This shows that the relationship between the participants and their immediate supervisors was negatively expressed by 32 out of 70 sampled subjects.
4.2.6 Feedback and Recognition System
The table below shows results from the questionnaire in Section A related to this research objective.
| No | Question | Yes % | No% |
| 8 | Are you happy with job recognition systems? | 28 | 72 |
| 9 | How would you rate the feedback system of the Hospital? | Good= 33% | Bad= 67% |
Table 15 Results from Section A on Feedback and recognition
The table shows that 28% of the participants are happy with the job recognition apparatus in the Hospital, while 72% are unhappy with the system. The following row shows that 33% rate the feedback system of Hong Kong Bright Hospital as good while 67% rate it as bad. The figures in the table indicate that 20 participants out of 70 are happy with the recognition they get, while the remaining 50 are unhappy with the system. The second result shows that 23 out of 70 participants find the feedback system good while the remaining 47 rates at as bad.
The following table shows the percentage of responses from the interviews
| Question | Response | Overall % |
| Green Red | ||
| How many times have you been recognized for good work? | * | 80 |
Table 16 Results from Interviews on Job Recognition
The results show that 80% of the participants gave negative answers when asked about how many times they had been recognized at work. This figure translates to 56 out of 70 participants who narrated negative comments on how many times they were recognized for good jobs at the Hospital.
The below chart shows the results from the focus groups discussion.
Figure 7 Results from Focus groups on Reason for Turnover
The discussions on employee turnover in the focus groups indicate that 10% of the five reasons given are attributed to lack of recognition will poor feedback system is attributed to 15% of the reasons for employee turnovers by the participants.
4.3 Limitations
Limitations of the research are the design characteristics that influenced the interpretation of data in the study (Theofanidis & Fountouki 2018, p.155). The study faced difficulty in distributing, submission and collecting the questionnaires. Some of the participants in the study were from the Emergency room department, where they were always on call. Even though the Hospital had made plans for all to avail themselves on the days of the questionnaires and interviews, the nature of work, such as saving lives and timely medical attention, influenced the study to allow them to work. During such times, the questionnaires and interviews were stopped and continued at their availability.
Some members of specific departments such as finance and human resource may have provided all positive information that would affect the study. This is because they prepare and implement most of the research objective areas such as wage and salary allocation, work hours, and shift planning and selection processes. Another limitation was the selection of samples, some influential departments such as Critical Care Units and general Surgery were not available, and they sent representatives from the internship programs. Interns may provide inaccurate information since they are there for a certain period, unlike the others who are permanent. Lastly, the study faced challenges using a larger population sample size that would have provided a more accurate data collection and analysis. The challenge was due to the work environment of offering timely lifesaving services to patients. In such an environment that treats and saves people’s lives, prior planning has minimal effect.
5. Conclusion and Recommendations
5.1 Conclusion
The results from the study are consistent with all three data collection methods, showing the causes of employee turnover at the Hospital. The first cause of employee turnover is the unfavorable working hours and shifts. The employees expressed dissatisfaction with the maximum hours they put to work without fair compensation. The study identified that 45 out of 70 employees expressed opinions that the working hours and shift changes are unfavorable. Thus it affects their social and physical life. This can be attributed to the fact that most medical staff do their work standing or moving. Similarly, the shift changes were unfavorable to 45 employees. Given the challenging economic times and increasing medical attention needed by people in Hong Kong, most Hospital employees feel under-compensated, with 50 out of 70 expressing the same.
The second cause was identified as a lack of room for growth and development. The research determined that only 32% of the employees feel that the Hospital nurtures an environment for growth and development. In the interviews, 48 participants expressed the fear of lack of support for any development in the Hospital. When there is no clear strategy that allows mutual growth and development of the organization and its employees, it casts doubt on the members’ future. This factor prompts them to seek outside development-oriented Hospitals in the city. Mainly, employees are motivated to work when they are insight into future growth in the organizations.
The selection and placement processes of the Hospital are seen as unsatisfactory by 32 members of the sample population. Another 28 staff members expressed unhappiness towards their work areas and departments. This shows that the selection process was ineffective and did not fit with some of the medical staff. This is further demonstrated by the 30% of employees who find the Human Resource department unfair while undertaking its duties in the Hospital. Additionally, the promotion process is described negatively by 48 members, who narrated that they are unhappy with the process. With the other departments in the Hospital, the Human resource department may cause a high employee turnover when they are unfair in the selection, placement, and promotion processes, since some employees may leave the Hospital when they feel they are not fully considered for such operations.
Poor or lack of inclusion of employees in making decisions that directly affect them is a factor that causes staff turnover. Forty-one employees from the study explained that they are unhappy with their lack of involvement in decision-making. In Hospitals, not including employees in matters that affect them is dangerous in their retention. Making shift changes, allocating future off days are essential and straightforward things employees like being involved in when the decisions are being made. Secondly, job autonomy was negatively explained by 48 participants. This means that they find it challenging to do their jobs when they are not accorded freedom and trust from their supervisors. Employees struggle with a lack of confidence and trust when they know they enjoy less freedom, self-sufficiency, and trust from the management. It makes them feel that their skills and expertise are questionable and not trusted.
The final identified cause is poor feedback and recognition system in the Hospital. Fifty participating employees are unhappy with the feedback and recognition systems. They rated the feedback ability of the management as bad, with 47 in number. The results indicate that the employees feel that the administration does not fully recognize their efforts and hard work. Their concerns, complaints, and recommendations are not timely responded to, making them feel devalued and unappreciated. Lack of recognition, feedback, and support may give room for employees to look outside the Hospital for other workplaces where they will be fully appreciated and recognized.
5.2 Recommendations
Elite Management Consultants recommends that Hong Kong Bright Hospital revise its working hours and shift changes to minimize burnout among medical staff. The compensation, allowances, and benefits should be current, fair, and aligned with job inputs. Its effective how salary increment or benefits allocation increases employee retention rates. The Hospital should show timely gratitude and recognition to celebrate the success of its members. The management should prioritize employee happiness since it is a vital indicator of job satisfaction and productivity. Employees look forward to coming to work environments that are engaging and make them happy. The Hospital should invest in its employees and offer opportunities for growth and development. This will make them commit their future and invest the time in activities that will benefit the Hospital. The management should provide an inclusive atmosphere where consultations are done on issues affecting the employees and encourage knowledge and skill sharing. These factors promote cohesion and unity among employees, making them feel involved in the Hospital’s daily activities. The hiring and selection of employees should be based on merit and expertise. The processes should be fair and open. Thus, promoting hard work and skill development. The study recommends future research on ways to create a better working environment for medical employees.
Appendices
Questionnaire
Section A
| No | Question | Yes | No |
| 1 | Are you satisfied with the maximum working Hours? | ||
| 2 | Are the Shift Changes Favorable? | ||
| 3 | Are there Growth and Development possibilities? | ||
| 4 | Are you satisfied with the job selection method? | ||
| 5 | Are you happy with your work area/ Department? | ||
| 6 | Are you happy with your involvement in decision-making processes? | ||
| 7 | Do you enjoy job Autonomy? | ||
| 8 | Are you happy with job recognition systems? | ||
| 9 | How would you rate the feedback system of the Hospital? |
NB Please use a tick or a cross to mark into the appropriate area.
Section B
Q.1 what would you say about the overall human resource management of the Hospital?
Best
Good
Fair
Not Fair
Q.2 would you Consider leaving work anytime soon? And why? Would you please provide an explanation?
Yes
Maybe
Not Now
No
Would you please provide an explanation?
Interview questions
| Question |
| Do you enjoy doing your job? |
| Are the working Hours and Shifts favorable? |
| Is your department supportive of your personal development? |
| How many times have you been recognized for good work? |
| How is your work relationship with your immediate supervisor? |
| Are you happy with the promotion system? |
| Describe your work environment with a single word |
| Do you look forward to coming to work? |
Focus Group Topics was on main reasons the members think contribute